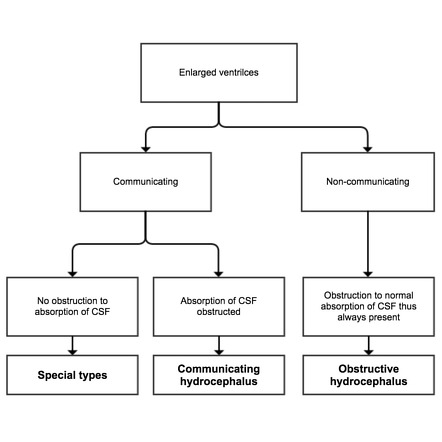
What is communicating hydrocephalus?
Communicating hydrocephalus occurs when the flow of CSF is blocked after it exits the ventricles. This form is called communicating because the CSF can still flow between the ventricles, the passages between which remain open.
What is R55?
Syncope and collapse (R55)
What is the ICD 10 code for congenital hydrocephalus?
ICD-10 code Q03. 9 for Congenital hydrocephalus, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
What is the ICD-10-CM code for obstructive hydrocephalus?
G91. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM G91. 1 became effective on October 1, 2022.
Is R55 a valid ICD-10 code?
R55 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM R55 became effective on October 1, 2022.
What are the 4 classifications of syncope?
Syncope can be classified into four categories: reflex mediated, cardiac, orthostatic, and cerebrovascular. A cardiac cause of syncope is associated with significantly higher rates of morbidity and mortality than other causes.
What are the three types of hydrocephalus?
Types of hydrocephalus include:Congenital hydrocephalus , which is present at birth. ... Acquired hydrocephalus, which develops at the time of birth or later. ... Normal-pressure hydrocephalus, which usually develops in people who are age 55 or older.More items...
What is the diagnosis code F80 89?
ICD-10 code F80. 89 for Other developmental disorders of speech and language is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
What is the diagnosis code F80 1?
1: Expressive language disorder.
What is the difference between obstructive and communicating hydrocephalus?
The word “communicating” refers to the fact that CSF can still flow between the ventricles, which remain open. Non-communicating hydrocephalus - also called obstructive hydrocephalus - occurs when the flow of CSF is blocked along one or more of the narrow passages connecting the ventricles.
Is normal pressure hydrocephalus communicating or Noncommunicating?
NPH is a form of communicating hydrocephalus and is distinguished from obstructive or noncommunicating hydrocephalus, in which there is a structural blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulation within the ventricular system (eg, stenosis of aqueduct of Sylvius).
What are 4 types of hydrocephalus?
The four main types of hydrocephalus are communicating hydrocephalus, non-communicating hydrocephalus, normal pressure hydrocephalus and hydrocephalus ex-vacuo. Communicating hydrocephalus occurs when the flow of CSF is blocked after it leaves your ventricles.
What does a diagnosis of near syncope mean?
Presyncope or near-syncope is often ill-defined and may have different meanings to different providers but denotes near fainting or a prodrome of syncope. The most uniform definition is "feeling like one was going to pass out but without actual loss of consciousness." Near syncope can last for seconds to minutes.
What is a syncopal patient?
Someone is considered to have syncope if they become unconscious and go limp, then soon recover. For most people, syncope occurs once in a great while, if ever, and is not a sign of serious illness. However in others, syncope can be the first and only warning sign prior to an episode of sudden cardiac death.
What diagnosis is syncope?
Syncope (pronounced “sin ko pea”) is the medical term for fainting or passing out. It is caused by a temporary drop in the amount of blood that flows to the brain. Syncope can happen if you have a sudden drop in blood pressure, a drop in heart rate, or changes in the amount of blood in areas of your body.
What is the ICD 10 code for fall with loss of consciousness?
0X9A for Concussion with loss of consciousness of unspecified duration, initial encounter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is the difference between communicating hydrocephalus and noncommunicating hydrocephalus?
Communicating hydrocephalus occurs when there is dilatation of the ventricles due to obstruction of CSF flow outside the ventricular system (i.e., distal to the foramen of Magendie), so the CSF communicates with the subarachnoid space. Noncommunicating hydrocephalus occurs when there is dilatation of the ventricles due to an obstruction of CSF flow within the ventricular system at or above the foramen of Magendie.
What is noncommunicating hydrocephalus?
Noncommunicating hydrocephalus refers to conditions causing intraventricular obstruction and alteration of the flow of dye into the lumbar CSF. Congenital malformations (especially aqueductal stenosis and Dandy-Walker syndrome with cystic dilation of the fourth ventricle) and mass lesions (e.g., tumors, arteriovenous malformations) can cause noncommunicating hydrocephalus.
Why does hydrocephalus occur?
Additional causes of communicating hydrocephalus include the interruption of CSF movement through the subarachnoid space caused by either subarachnoid hemorrhage or a major CNS infection, such as leptomeningitis, and the subsequent inflammatory response. Overproduction of CSF in patients with papilloma of the choroid plexus may also be a factor. In all of these situations, there is an enlargement of all parts of the ventricular system. Although rare, hydrocephalus may also be seen in patients with impaired venous flow from the brain.
Why does hydrocephalus occur in the lumbar arachnoid?
This type of hydrocephalus is caused by an inability to normally reabsorb CSF by the arachnoid granulations, which can occur from meningeal scarring as a result of bacterial meningitis or intraventricular hemorrhage.
What causes obstructive hydrocephalus?
Obstructive (non-communicating) hydrocephalus results from compression of the ventricular system or its associated foramina (e.g. Monroe, sylvian aqueduct) (Fig. 6–15). As outlined above, common causes included neoplasms, intraventricular or subarachnoid blood, and meningitis. Other etiologies which should be considered include congenital aqueductal stenosis, myelomeningocele, and in endemic areas, cysticercosis. 142
What etiologies should be considered for obstructive hydrocephalus?
Other etiologies which should be considered include congenital aqueductal stenosis, myelomeningocele, and in endemic areas, cysticercosis. 142. In addition to treatment of the primary problem, many patients with obstructive hydrocephalus will require a shunting procedure.
How do you know if you have hydrocephalus?
In the neonate and young infant, there are typically few symptoms. The child often feeds well and is attentive and happy, and the only clue may be an accelerated rate of head growth .
What is the cause of communicating hydrocephalus?
Communicating hydrocephalus (non-obstructive hydrocephalus) is caused by inadequate reabsorption of CSF. The excessive accumulation of CSF results in an abnormal enlargement of the spaces in the brain called ventricles. This causes potentially harmful pressure on the tissues of the brain.
How do you know if you have hydrocephalus?
In infancy, the most obvious indication of hydrocephalus is often the rapid increase in head circumference or an unusually large head size. In older children and adults, symptoms may include one or more of the following: headache, vomiting, nausea, downward deviation of the eyes (called “sunsetting”), problems with balance, poor coordination, gait disturbance, urinary incontinence, slowing or loss of development, lethargy, drowsiness, irritability, or other changes in personality or cognition, including memory loss.
How is hydrocephalus treated?
Hydrocephalus is most often treated with the surgical placement of a shunt system, which is a pressure valve and flexible plastic tube. This system diverts the flow of excessive CSF from the ventricles to another area of the body, typically the abdominal cavity, where it can be absorbed as part of the circulatory process.
What is the water in the brain called?
Hydrocephalus was once known as “water” on the brain. The “water” is actually cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a clear fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. The CSF protects the brain and spinal cord from injury by providing a liquid cushion, and is continually being produced, circulated and absorbed.
What is the problem with hydrocephalus?
Communicating hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the ventricles of the brain) is a common, but often undiagnosed, problem in individuals with MPS I, MPS II, MPS VI and MPS VII and may be associated with some cortical atrophy (loss of brain cells). Children with greater neurological involvement have a greater risk of developing hydrocephalus. Early detection and treatment of hydrocephalus is believed to improve quality of life. However, neurosurgeons are often unfamiliar with the unique aspects of diagnosing communicating hydrocephalus in MPS and related diseases, creating a frustrating situation for parents.
Does hydrocephalus improve quality of life?
Early detection and treatment of hydrocephalus is believed to improve quality of life. However, neurosurgeons are often unfamiliar with the unique aspects of diagnosing communicating hydrocephalus in MPS and related diseases, creating a frustrating situation for parents.
What is non-communicating hydrocephalus?
Non-communicating hydrocephalus, also known as obstructive hydrocephalus, occurs when the flow of CSF is blocked along one of or more of the narrow passages connecting the ventricles.
What is the procedure for hydrocephalus?
Some individuals with non-communicating (obstructive) hydrocephalus can have a surgical procedure called an endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV). This surgery creates an opening to allow CSF to flow in and around the brain as it would do under normal circumstances.
What causes hydrocephalus in the brain?
This type of hydrocephalus may result from a thickening of the arachnoid around the base of the brain , which blocks the flow of CSF from the spinal to the cortical subarachnoid spaces. CSF normally flows unrestricted through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space.
Can you have an ETV with hydrocephalus?
Typically, individuals with communicating hydrocephalus are not candidates for an Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV), though it is not completely ruled out as an option as each case, and individual is unique.
Communicating hydrocephalus occurs when the cerebrospinal fluid is inefficiently absorbed back into the blood stream
This results in significant back-pressure and enlargement of all the four ventricles. Causes of this include:
About Hydrocephalus
If you are registered on Doximity, and board-certified in one or more of the ranked medical specialties, you are eligible to vote for next year’s U.S. News & World Report Best Hospitals. Providence Southern California hospitals and affiliates are honored to have received more than…
How to treat hydrocephalus?
Treatment usually involves surgery to insert a shunt. Medicine and rehabilitation therapy can also help. Hydrocephalus that results from head trauma, brain tumors, intracranial hemorrhage, or meningitis. The abnormal buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
What is the term for the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranium?
Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be a congenital or acquired disorder; hydrocephalus ex-vacuo refers to ventricular dilation that occurs as a result of brain substance loss from cerebral infarction and other conditions.
What is cerebrospinal fluid?
Clinical Information. (hye-dro-sef-uh-lus) the abnormal buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain. A disorder characterized by an abnormal increase of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be a congenital or acquired disorder;
When will the ICD-10 G91 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can hydrocephalus be fatal?
hydrocephalus can permanently damage the brain, causing problems with physical and mental development. If untreated, it is usually fatal. With treatment, many people lead normal lives with few limitations. Treatment usually involves surgery to insert a shunt.
What is the term for the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranium?
Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be a congenital or acquired disorder; hydrocephalus ex-vacuo refers to ventricular dilation that occurs as a result of brain substance loss from cerebral infarction and other conditions.
When will the ICD-10 G91.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G91.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can hydrocephalus cause memory problems?
thinking and memory problems. hydrocephalus can permanently damage the brain, causing problems with physical and mental development. If untreated, it is usually fatal. With treatment, many people lead normal lives with few limitations.