
What is the common origin of the superficial layer of forearm?
May 11, 2020 · The superficial posterior forearm muscles originate from the distal portion of the humerus , most of them sharing a common origin via the common extensor tendon that arises from the lateral epicondyle of humerus.
What are the superficial posterior forearm muscles?
What is the common origin of the superficial layer of the posterior forearm muscles? The superficial layer of the posterior forearm contains seven muscles. Four of these muscles – extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor digitorum, extensor carpi ulnaris and extensor digiti minimi share a common tendinous origin at the lateral epicondyle.
What is the origin of the anterior forearm muscles?
What is the common origin of all 7 muscles in the superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm? The lateral supraepicondylar of the distal humerus and the lateral epicondyle of the distal humerus.
What nerve innervates the superficial anterior forearm?
Which muscles in the superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm share a common tendinous origin? extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, extensor carpi radialis brevis and extensor carpi ulnaris Where is the common tendinous origin of the 4 muscles in the superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm?
What are the superficial muscles of the posterior forearm?
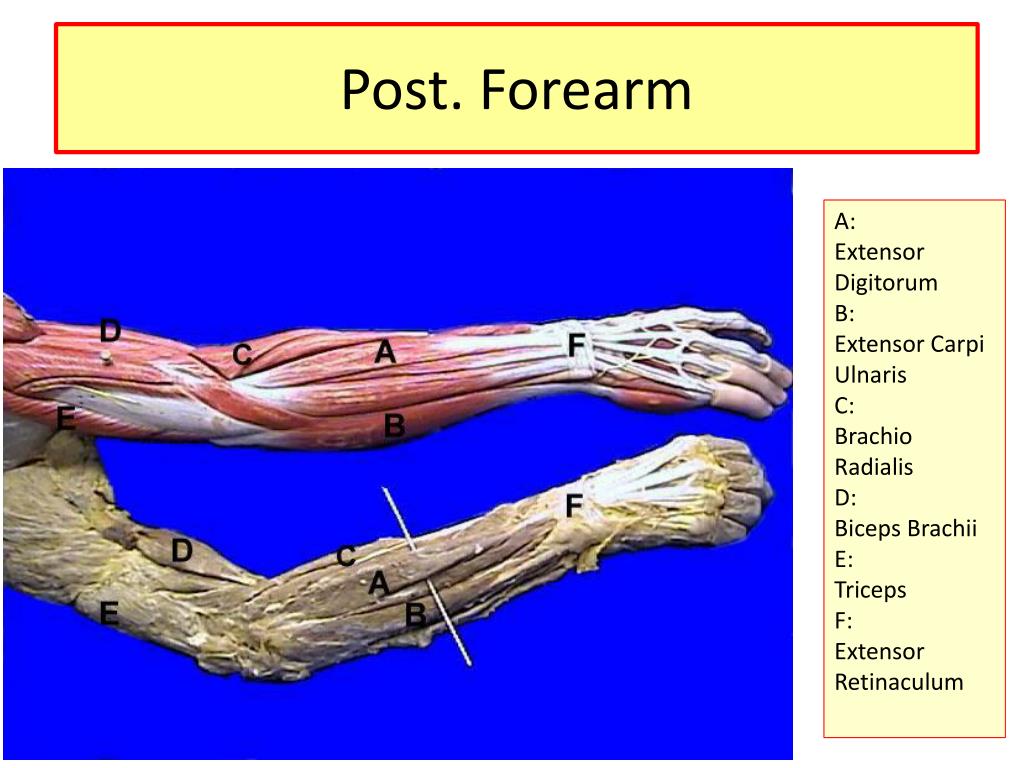
The muscles of the posterior forearm seen in this superficial view are the:Extensor carpi radialis longus.Extensor carpi radialis brevis.Extensor digitorum.Extensor digiti minimi.Extensor carpi ulnaris.Anconeus.Dec 19, 2020
What is the common origin of the superficial flexors of the forearm?
The superficial compartment of the flexor surface of the forearm contains the pronator teres, the flexor carpi radialis longus, the palmaris longus, the flexor carpi ulnaris, and the flexor digitorum superficialis. All of these muscles originate primarily from the medial epicondyle of the humerus.Jul 26, 2021
What is the common origin of the superficial and intermediate layer of the anterior forearm muscles?
common flexor tendonAll 4 muscles have a common origin at the medial epicondyle of the humerus, known as the common flexor tendon. Figure 2. Superficial muscles of the anterior forearm.Feb 22, 2022
What structure is a common attachment site for the muscles located in the posterior forearm?
The abductor pollicis longus is a long muscle that originates from the posterior aspect of the proximal half of the radius and ulna, and the adjacent interosseous membrane. The muscle then runs distally and ends in a tendon, which inserts onto the base of metacarpal bone 1 and the trapezium bone.
What is the most likely origin of wrist flexors?
Flexor carpi radialis muscleOriginMedial epicondyle of humerusInsertionBases of metacarpal bones 2-3ActionWrist joint: Wrist flexion, wrist abductionInnervationMedian nerve (C6, C7)Blood supplyAnterior/posterior recurrent ulnar artery, radial artery
What is the superficial muscle covering the anterior neck?
platysmaThe platysma is visible, with skin removed. The muscles of the face, platysma visible at bottom right. The platysma muscle is a superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially.
What are the superficial muscles?
Superficial muscles are close to the surface of the skin. Muscles which lie closer to bone or internal organs are called deep muscles.May 4, 2021
Which of the superficial anterior forearm muscles is absent in about 10% of individuals and only weakly assists in wrist flexion?
The palmaris longus is a very small muscle and weak flexor of the wrist. It is not present in 10-20% of the population.
What is the origin and insertion of flexor carpi ulnaris?
Flexor carpi ulnaris is a fusiform muscle located in the anterior compartment of the forearm....Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle.OriginMedial epicondyle of humerus, olecranon and posterior border of ulnaInsertionPisiform bone, hamate bone, base of metacarpal bone 53 more rows
What is the origin of the extensor digitorum communis muscle?
Extensor digitorum muscleOriginLateral epicondyle of humerus (common extensor tendon)InsertionExtensor expansions of digits 2-5ActionMetacarpophalangeal / Interphalangeal joints 2-5: Finger extensionInnervationPosterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8)1 more row•May 11, 2020
What is the origin of most muscles that move the femur?
Most muscles that insert on the femur (the thigh bone) and move it, originate on the pelvic girdle. The psoas major and iliacus make up the iliopsoas group. Some of the largest and most powerful muscles in the body are the gluteal muscles or gluteal group.
Which muscle refers to the superficial layer of the extensor compartment that extends digits 2-5?
Extensor digitorum muscleExtensor digitorum muscle The extensor digitorum is a long fusiform muscle originating on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus via the common extensor tendon. From here, the muscle fibers run distally, extending into four separate tendons that insert onto the extensor expansions of digits 2-5, respectively.
Why do forearms hurt?
Share on Pinterest Forearm pain may be caused by injury, nerve entrapment, or arthritis. Nerve entrapment can be caused by a range of different syndromes affecting the forearm. The most common of which is carpal tunnel syndrome. Arthritis: Arthritis can occur in the wrist or elbow, causing a dull ache in the forearm.
What are the forearm extensors?
The superficial extensors of the forearm are the brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, anconeus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi. The extrinsic hand muscles originate in the forearm and insert on structures within the hand.
What is the function of the forearm?
It extends from the elbow joint to the hand, and it is made up of the ulna and radius bones. These two long bones form a rotational joint, allowing the forearm to turn so that the palm of the hand faces up or down. The forearm is covered by skin, which provides a sensory function.
What muscles comprise of the posterior compartment?
The posterior compartment of the arm is also known as the "extensor compartment", as its main action is extension. The muscles of this compartment are the triceps brachii and anconeus muscle and these are innervated by the radial nerve. Their blood supply is from the profunda brachii.
What is the opposite side of forearm called?
Ulna. The ulna runs parallel to the radius. It's on the side of the forearm that's closest to the pinky finger.
What is the top of your forearm called?
Brachioradialis: This muscle, located at the top of the forearm near the elbow, helps rotate the forearm both outwardly and inwardly.
Is an arm an organ?
The internal organs which we cannot see, are the heart, the lungs, the stomach, the liver with the gall-bladder, the pancreas, the spleen, the kidneys and the small and large intestines (bowels). The arms and legs are called the limbs.
Which muscle is the last superficial muscle of the posterior forearm supplied by the radial nerve before it is
The little sibling of the extensor carpi radialis longus, the extensor carpi radialis brevis is distinguishable because of its seemingly larger muscle belly, shorter tendon, and deep appearance to the extensor car pi radialis longus. It is the last superficial muscle of the posterior forearm supplied by the radial nerve before it passes through the supinator.
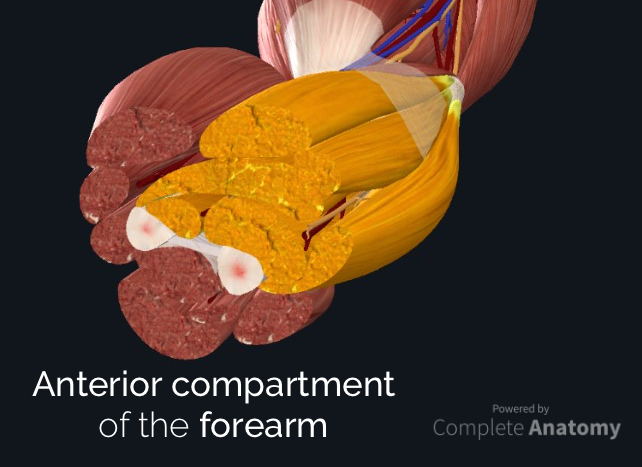
What is the forearm?
The forearm is the portion of the arm distal to the elbow and proximal to the wrist. There are 20 muscles separated into two compartments . Here, we will discuss the posterior compartment of the forearm in the setting of their attachment points, function, innervation and vascular supply. In addition, we’ll also be providing clinical examples ...
Where is the pain in the forearm?
Pain is felt down the lateral side of the distal forearm, radiating to the thumb and region of the dorsal interossei. It is usually diagnosed clinically with Finkelstein’s test, but MRI can confirm the presence of inflammation and local oedema around the tendons of extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus.
What is the function of the anconeus?
Anconeus. Named for its triangular shape, the anconeus is a small muscle that provides accessory support to other posterior forearm muscles. Function: extension; in pronation, abducts ulna. Origin: lateral epicondyle. Insertion: the dorsolateral surface of the olecranon process and dorsal ulna.
Which muscle is responsible for supinate the forearm?
The supinator muscle has superficial and deep heads that help to supinate the forearm. Passing between these two heads is the deep branch of the radial nerve. As the superficial head forms the ‘roof’ of this tunnel, it is termed the Arcade of Frohse.
What is intersection syndrome?
Intersection syndrome is a painful inflammatory condition that occurs at the intersection of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis muscle bellies as they cross over extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis on the dorsolateral forearm.
What is the extensor carpi radialis longus?
The extensor carpi radialis longus has a relatively short muscle belly and longer tendon. It is this long tendon, and its superficial appearance, that identifies it from the extensor carpi radialis brevis. Function: wrist extension and abduction. Origin: lateral supracondylar ridge and lateral epicondyle.
Where are the superficial anterior forearm muscles located?
The superficial anterior forearm muscles are a group of five muscles located in the anterior (flexor) compartment of the forearm. These muscles include the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus and flexor digitorum superficialis.
Where is the Flexor Carpi Radialis located?
The flexor carpi radialis is a fusiform muscle of the forearm situated medially to the pronator teres muscle. It originates from the medial epicondyle of humer us and descends inferomedially to the midpoint of the forearm, where it extends into a long tendon.
Which nerve innervates the flexor carpi radialis?
Like the majority of the muscles in this compartment, it is innervated by the median nerve (C6, C7) and vascularized by the branches of the recurrent ulnar and radial arteries. The contraction of flexor carpi radialis produces movements of the hand at the wrist joint.
Which nerve innervates the palmaris longus?
Palmaris longus is innervated by the median nerve (C7, C8) and vascularized by the anterior ulnar recurrent artery. The palmaris longus primarily acts with other superficial anterior forearm muscles and contributes to the balanced flexion of the hand on the wrist joint.
Where does the humeral head come from?
The humeral head arises from the medial epicondyle of humerus, while the ulnar head arises from the olecranon and proximal two-thirds of the posterior surface of the ulna. The heads converge into a thick tendon which goes on to insert onto the pisiform and hamate bones and the base of metacarpal bone 5.
Where does the Flexor Carpi Ulnaris get its blood supply?
The blood supply for this muscle comes from the posterior ulnar recurrent artery. Flexor carpi ulnaris contributes to the flexion of the hand at the wrist joint.
Where does the palmaris longus originate?
The palmaris longus is the most superficial muscle of the superficial anterior forearm muscles. It originates from the medial epicondyle of humerus and descends to the midpoint of the forearm, where it becomes tendinous. The tendon continues towards the wrist and passes superficial to the flexor retinaculum and goes on to insert onto ...
What is the forearm?
The forearm is the portion of the arm distal to the elbow and proximal to the wrist. There are 20 muscles separated into two compartments . Here, we will discuss the anterior compartment of the forearm in the setting of their attachment points, function, innervation and vascular supply, while providing clinical examples to reinforce this ...
Where is the flexor carpi radialis?
When the palmaris longus is present, the flexor carpi radialis lies immediately lateral to the palmaris longus. As we move more laterally in the forearm, the radial artery can be palpated lateral to the tendon of flexor carpi radialis.
Which muscle is the most medial?
The flexor carpi ulnaris is the most medial muscle in the superficial layer of the forearm. It is a relatively broad, strap-like muscle that plays a powerful role in movements at the wrist.
What is the pronator quadratus?
The pronator quadratus is a flat square-shaped muscle in the distal forearm that assists and stabilises the forearm pronation produced by pronator teres. Function: pronation and stabilisation of the forearm. Origin: antero-medial surface of the distal ulna. Insertion: antero-lateral surface of the radius.
Where is the pronator teres?
Pronator teres. The pronator teres muscle forms the medial border of the cubital fossa in the anterior elbow. It is a functionally important muscle that contains two heads. The median nerve passes into the forearm between the two heads of the pronator teres and is separated from the ulnar artery by the ulnar head of pronator teres.
What is the function of the flexor pollicis longus?
Function: flexion of the thumb. Origin: anterior surface of the radius and interosseous membrane. Insertion: base of the distal phalanx of the thumb.
What is the flexor digitorum profundus?
The flexor digitorum profundus is a powerful finger and wrist flexor that is one of several crucial elements in both grip strength and performing a pincer grip. It has four tendons that pass through the inferior region of the carpal tunnel before diverging to digits II-V, where it passes through the tunnel created by the splitting of the tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis.
Overview
Superficial Layer of The Posterior Compartment
- Thesuperficial layer of the posterior compartment contains seven muscles that have a common origin of the supracondylar ridge and laterally epicondyle of the humerus (the common extensor tendon): 1. Brachioradialis 2. Extensor carpi radialis longus 3. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 4. Extensor digitorum 5. Extensor digiti minimi 6. Extensor carpi u...
Deep Layer of The Posterior Compartment
- The deep layer of the posterior compartment contains five muscles, all of which are innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve: 1. Supinator 2. Abductor pollicus longus 3. Extensor pollicus longus 4. Extensor pollicus brevis 5. Extensor indicis
Exam Tips
- Theradial nerve supplies all muscles of the extensor compartment
- The order of tendons running down the lateral aspect of the forearm can provide a simple basis for learning the muscles, or help you out in a spot of trouble in anatomy exams:
- If you get stuck on an exam and forget the name of a muscle, break down the name into logical components: