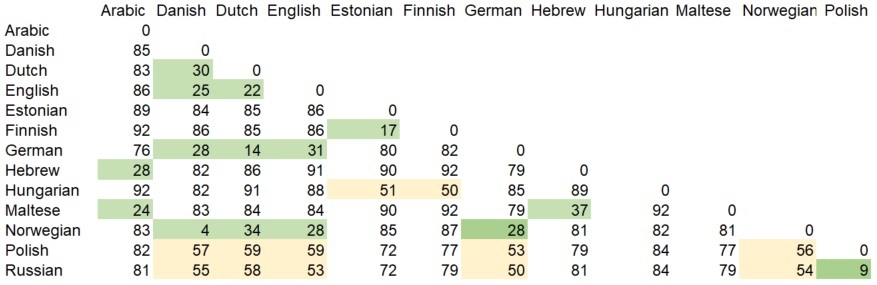
The Comparative Method and Linguistic Reconstruction
- Assemble cognates. A popular form for these is Swadesh lists. They are tables of “core vocabulary” in languages. ...
- Reconstruct the proto-sound. Eventually you have to use these alignments. Directionality. ...
- Determine the status of similar (partially overlapping) correspondence sets. Sometimes, two different hypotheses both reconstruct the same phoneme. ...
What are the most common misconceptions about linguistics?
- Linguistics is not about learning as many languages as humanly possible; it’s the study of how language works. The question “Oh, you’re a linguist? ...
- Oscar Tay's answer to What is the biggest misconception in your field of expertise?
- The
What is the best university to study linguistics?
- The University of Kent at Paris, Paris France
- The University of Kent at Brussels, Brussels Belgium
- Medway campus, Chatham United Kingdom
- Tonbridge Campus, Tonbridge United Kingdom
What can I do with major in linguistics?
Linguistics, the systematic study of human language, provides a strong foundation for working in speech pathology, education, journalism, law, artificial intelligence and computer-mediated language learning, among other fields. “Language is such an integral part of almost everything we do, so there’s bound to be a way to apply your ...
What are the main characteristics of linguistics?
- Phonetics - the study of speech sounds in their physical aspects
- Phonology - the study of speech sounds in their cognitive aspects
- Morphology - the study of the formation of words
- Syntax - the study of the formation of sentences
- Semantics - the study of meaning
- Pragmatics - the study of language use
What is an example of the comparative method?
Two languages are genetically related if they descended from the same ancestor language. For example, Italian and French both come from Latin and therefore belong to the same family, the Romance languages.
What is meant by the comparative method?
Comparative methods seek evidence for adaptive evolution by investigating how the characteristics of organisms, such as their size, shape, life histories, and behaviors, evolve together across species. They are one of evolutionary biology's most enduring approaches for testing hypotheses of adaptation.
What is comparative study in linguistics?
comparative linguistics, formerly Comparative Grammar, or Comparative Philology, study of the relationships or correspondences between two or more languages and the techniques used to discover whether the languages have a common ancestor.
What are the types of comparative method?
There are several methods of doing comparative analysis and Tilly (1984) distinguishes four types of comparative analysis namely: individualizing, universalizing, variation-finding and encompassing (p. 82).
What are the advantages of comparative method?
The comparative methodThe comparative methodAdvantages Discovers cause and effect relationships Poses no ethical issues Can be studied in the past It avoids artificialityDisadvantages No control over variables 'Thought experiemnt'2 more rows•Dec 2, 2020
Who is called the father of comparative method?
Abstract. More than any other historical figure, Marc-Antoine Jullien of Paris has been considered the 'Father' of Comparative Education, and his Esquisse d'un ouvrage sur l'éducation compare, appearing in 1816–17, has been viewed as that field's originating source.
Why is comparative linguistics important?
Identifying clusters of features in the shape of lexical and morphological evidence derived from the traditional methods of historical/comparative linguistics can produce plausible generalizations and help us get a relative fix on when and from where words first entered the language.
What is comparative phonetics?
3) Comparative phonetics – studies the correlation between the phonetic systems of two or more languages, especially kindred ones. It finds out the correspondences between the speech sounds of kindred languages.
What are two types of linguistics?
What are the two types of linguistics? Comparative and descriptive.
What are the 3 types of comparative?
CAS offers three comparative modes: intra-regional, cross-regional, and trans-regional. A number of scholars have used CAS's comparative rubrics, even without knowing about the wider CAS agenda and program.
What are the problems of comparative method?
These are: (a) The problem resulting from complexity of social data. (b) The problem of using empirical methods in the study of human political relations and interactions. (c) The problem of verification and prediction making in politics. (d) The issue of explanation and prediction in politics.
What is the purpose of comparative study?
The major aim of comparative research is to identify similarities and differences between social entities. Comparative research seeks to compare and contrast nations, cultures, societies, and institutions.
What is meant by comparative method in sociology?
The Phrase “comparative method” refers to the method of comparing different. societies or groups within the same society to show whether and why they are. similar or different in certain respects.
What is the comparative method in politics?
The method involves analyzing the relationship between variables that are different or similar to one another. Comparative politics commonly uses this comparative method on two or more countries and evaluating a specific variable across these countries, such as a political structure, institution, behavior, or policy.
What is the comparative method in anthropology?
Page 1. THE COMPARATIVE METHOD OF ANTHROPOLOGY. I. The basic operation in the comparative method is an arrangement of social or cultural conditions observed among existing peoples into a series that is then taken to represent a process of evolution.
What's the comparative method in sociology?
The comparative method – involves comparing two or more similar societies or groups which are similar in some respects but varied in others, and looking for correlations.
What is the Neogrammarian principle?
The Neogrammarian principle. The foundation of the comparative method, and of comparative linguistics in general, is the Neogrammarians ' fundamental assumption that "sound laws have no exceptions".
What is the Neogrammarian hypothesis?
The Neogrammarian hypothesis led to the application of the comparative method to reconstruct Proto-Indo-European since Indo-European was then by far the most well-studied language family. Linguists working with other families soon followed suit, and the comparative method quickly became the established method for uncovering linguistic relationships.
What was Jacob Grimm's method of comparative study?
Jacob Grimm, better known for his Fairy Tales, used the comparative method in Deutsche Grammatik (published 1819–1837 in four volumes), which attempted to show the development of the Germanic languages from a common origin, which was the first systematic study of diachronic language change.
What is the purpose of comparative method?
The aim of the comparative method is to highlight and interpret systematic phonological and semantic correspondences between two or more attested languages. If those correspondences cannot be rationally explained as the result of language contact ( borrowings, areal influence, etc.), and if they are sufficiently numerous and systematic that they cannot be dismissed as chance similarities, then it must be assumed that they descend from a single proto-language.
How does comparative method work?
In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor and then extrapolating backwards to infer the properties of that ancestor. The comparative method may be contrasted with the method of internal reconstruction in which the internal development of a single language is inferred by the analysis of features within that language. Ordinarily, both methods are used together to reconstruct prehistoric phases of languages; to fill in gaps in the historical record of a language; to discover the development of phonological, morphological and other linguistic systems and to confirm or to refute hypothesised relationships between languages.
What is a linguistic map?
Linguistic map representing a tree model of the Romance languages based on the comparative method. The family tree has been rendered here as an Euler diagram without overlapping subareas. The wave model allows overlapping regions.
When was the wave model developed?
The wave model was developed in the 1870s as an alternative to the tree model to represent the historical patterns of language diversification. Both the tree-based and the wave-based representations are compatible with the comparative method.
What is comparative grammar?
Comparative grammar was the most important branch of linguistics in the 19th century in Europe. Also called comparative philology, the study was originally stimulated by the discovery by Sir William Jones in 1786 that Sanskrit was related to Latin, Greek, and German.
What is comparative method in historical linguistics?
The comparative method in historical linguistics is concerned with the reconstruction of an earlier language or earlier state of a language on the basis of a comparison of related words and expressions in different languages or dialects derived from it. The comparative method…
What was the most important achievement of linguistic scholarship in the 19th century?
It is generally agreed that the most outstanding achievement of linguistic scholarship in the 19th century was the development of the comparative method, which comprised a set of principles whereby languages could be systematically compared with respect to their sound systems, grammatical structure,…
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Is English related to Italian?
As an example of the method, English is seen to be related to Italian if a number of words that have the same meaning and that have not been borrowed are compared: piede and “foot,” padre and “father,” pesce and “fish.”.
What is the wave model?
The Wave Model has been proposed as an alternative to the tree model for representing language change. In this Venn diagram, each circle represents a “wave” or isogloss, i.e. the maximum geographical extension of a linguistic change as it propagated through the speaker population. These circles, which represent successive historical events of propagation, typically intersect. Each language in the family differs as to which isoglosses it belongs to, i.e. which innovations it reflects. The tree model presumes that all the circles should be nested, and never crosscut; but studies in dialectology and historical linguistics have shown this assumption to be usually wrong, suggesting that the wave-based approach may be more realistic than the tree model. A genealogical family in which isoglosses intersect is called a dialect continuum or a linkage.
What is comparative method?
The comparative method is used to construct a Tree model (German Stammbaum) of language evolution, in which daughter languages are seen as branching from the proto-language, gradually growing more distant from it through accumulated phonological, morpho-syntactic, and lexical changes.
What is analogy in a sentence?
Analogy is the sporadic change of a feature to be like another feature in the same or a different language. It may affect a single word or be generalized to an entire class of features, such as a verb paradigm. For example, the Russian word for nine, by regular sound changes from Proto-Slavic, should have been /nʲevʲatʲ/, but is in fact /dʲevʲatʲ/. It is believed that the initial nʲ- changed to dʲ- under influence of the word for "ten" in Russian, /dʲesʲatʲ/.
What is borrowing on a larger scale?
Borrowing on a larger scale occurs in areal diffusion, when features are adopted by contiguous languages over a geographical area. The borrowing may be phonological, morphological or lexical. A false proto-language over the area may be reconstructed for them or may be taken to be a third language serving as a source of diffused features.
What is the foundation of comparative linguistics?
The foundation of the comparative method, and of comparative linguistics in general, is the Neogrammarians ' fundamental assumption that "sound laws have no exceptions." When it was initially proposed, critics of the Neogrammarians proposed an alternate position, summarized by the maxim "each word has its own history". Several types of change do in fact alter words in non-regular ways. Unless identified, they may hide or distort laws and cause false perceptions of relationship.
How to prove that two or more historically attested languages are descended from a single proto-language?
The comparative method aims to prove that two or more historically attested languages are descended from a single proto-language by comparing lists of cognate terms. From them, regular sound correspondences between the languages are established, and a sequence of regular sound changes can then be postulated, which allows the proto-language to be reconstructed. Relation is deemed certain only if at least a partial reconstruction of the common ancestor is feasible, and if regular sound correspondences can be established with chance similarities ruled out.
What is descendance in language?
Descent is defined as transmission across the generations: children learn a language from the parents' generation and after being influenced by their peers transmit it to the next generation , and so on. For example, a continuous chain of speakers across the centuries links Vulgar Latin to all of its modern descendants.

Overview
In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor and then extrapolating backwards to infer the properties of that ancestor. The comparative method may be contrasted with the method of internal reconstruct…
Definition
The aim of the comparative method is to highlight and interpret systematic phonological and semantic correspondences between two or more attested languages. If those correspondences cannot be rationally explained as the result of language contact (borrowings, areal influence, etc.) or linguistic universals, and if they are sufficiently numerous and systematic that they cannot be dismissed as chance similarities, then it must be assumed that they descend from a single pare…
Origin and development
In Antiquity, Romans were aware of the similarities between Greek and Latin, but did not study them systematically. They sometimes explained them mythologically, as the result of Rome being a Greek colony speaking a debased dialect.
Even though grammarians of Antiquity had access to other languages around …
Application
There is no fixed set of steps to be followed in the application of the comparative method, but some steps are suggested by Lyle Campbell and Terry Crowley, who are both authors of introductory texts in historical linguistics. This abbreviated summary is based on their concepts of how to proceed.
This step involves making lists of words that are likely cognates among the languages being co…
Complications
The limitations of the comparative method were recognized by the very linguists who developed it, but it is still seen as a valuable tool. In the case of Indo-European, the method seemed at least a partial validation of the centuries-old search for an Ursprache, the original language. The others were presumed to be ordered in a family tree, which was the tree model of the neogrammarians.
See also
• Comparative linguistics
• Historical linguistics
• Lexicostatistics
• Proto-language
• Swadesh list
External links
• Hubbard, Kathleen. "Everything you ever wanted to know about Proto-Indo-European (and the comparative method), but were afraid to ask!". University of Texas Department of Classics. Archived from the original on 5 October 2009. Retrieved 22 December 2009.
• Gordon, Matthew. "Week 3:Comparative method and linguistic reconstruction" (PDF). Department of Linguistics, University of California, Santa Barbara. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2008. …