.PNG)
Composition of Cell membrane
- Most of the cell membrane is composed of 40-50 % protein and 50-60 % lipids.
- Membrane lipids are of three types: a) Phospholipids b) Glycolipids c) Steroids
- In the different membrane, the proportion of the lipid varies:
What are the 5 components of the cell membrane?
Cell Membrane Structure
- Phospholipids. Phospholipids are referred to as glycerophospholipids, these phospholipids are part of the cell membrane of living beings as well as a group of lipid compounds; i.e. ...
- Protein. This protein itself is derived from the Greek word “Protos” which means “most importantly”. ...
- Glycolipids and glycoproteins. ...
- Oligosaccharides. ...
- Cholesterol. ...
What is the cell membrane mainly composed of?
The cell membrane consists of three classes of amphipathic lipids: phospholipids, glycolipids, and sterols. The amount of each depends upon the type of cell, but in the majority of cases phospholipids are the most abundant, often contributing for over 50% of all lipids in plasma membranes.
What is the major CompoNet of the cell membrane?
Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane. The exact mix or ratio of proteins and lipids can vary depending on the function of a specific cell. Phospholipids are important components of cell membranes.
What are cell membranes are primarily composed of?
cell membrane (also known as cell membrane) lies at the border of the cells primarily made up of proteins and lipids, especially phospholipids within the membrane, proteins carry out many functions semipermiable. phospholipids have a phosphorous-containing polar end and a non-polar end composed of the fatty acid chain.

What is the composition and function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What is the composition of cell membrane class 8?
Cell membrane is made up of lipids and proteins. It is present in both plant and animal. This membrane is living, thin, and delicate. The cell membrane is a semi-permeable membrane, that allows the transmission of a very few molecules across it.
What is the composition of cell membrane class 9?
The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids. The bi-layered phospholipids are the lipids to which a phosphate group is attached and have a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails.
What is the composition of cell wall and cell membrane class 9?
Cell wallCell membraneIt is made up of pectin, chitin, lignin, glycoproteins, glycolipids, sugar, and cellulose.It is a lipid bilayer. And is composed of lipoproteins and carbohydrates.The cell wall is 0.1 μm to several μm in thickness.The cell membrane is 7.5–10 nm in thickness.7 more rows
What is the work of cell membrane class 8?
The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane. It provides protection for the cell and its cellular components from the external environment. It is selectively permeable and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
What are the functions of cell membrane class 8?
Functions of cell membrane:They keep toxic substances out of the cell.They contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules to pass between organelles and between the cell and the outside environment, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products.More items...
What is cell wall for Class 8?
The cell wall is the outer covering of a cell, present adjacent to the cell membrane, which is also called the plasma membrane. As mentioned earlier, the cell wall is present in all plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea.
What are the three functions of cell membrane class 8?
Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the ...
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
Which organelle is encased in plasma membranes?
Animal cells, plant cells, prokaryotic cells, and fungal cells have plasma membranes. Internal organelles are also encased by membranes.
What Are Cell Membranes?
Let's begin this lesson with a question: what do all cells have in common? Truth be told, there are several characteristics cells all share, things like basic metabolism or having genetic material. But for the purposes of this lesson, we'll focus on the fact that all cells contain a cell membrane.
What is the first component of the cell membrane?
The first major component of the cell membrane is the phospholipid. Phospholipids are amphipathic fats that form the majority of the membrane. In the cell membrane below, the red pieces with the two yellow tails are phospholipids. Phospholipids are the red pieces with two yellow tails.
What is the waxy material found in the cell membrane?
Cholesterol is a waxy material found embedded within the membrane. Sterols are waxy fats that are important in cell membrane structure in plants, fungi and bacteria. Learning Outcomes. Your understanding of the major structural components of the cell membrane could enable you to accomplish these objectives:
What is the function of carbohydrates in the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates are large molecules made from simple sugars. Their function is to link cells together or act as binding sites. Finally, the cell membrane has a slightly rigid nature that is created due to sterols and cholesterol. Cholesterol is a waxy material found embedded within the membrane.
Why are phospholipids arranged in a double layer?
This arrangement works because the head of the phospholipid is hydrophilic and immerses itself inside the watery environment inside and outside the cell.
What are the proteins in the cell membrane?
Proteins. Proteins form another integral part of the cell membrane. Proteins are large molecules formed from long chains of amino acids. You'll notice that there are many different types of proteins.
Which cell has waxy fats that play a role in the cell membrane?
Cholesterol. Finally, we come to the sterols and cholesterol. Plant, fungi cells and bacteria have different types of sterols, waxy fats that play a role in the cell membrane. These molecules serve a structural role in the membrane, reinforcing it and also participating in lipid signaling pathways.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane, also called plasma membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell’s constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, ...
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions: first, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and , second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. Intrinsic proteins penetrate and bind tightly to the lipid bilayer, ...
What is the innermost layer of a cell?
The innermost layer is a plasma membrane similar to the ones that surround most cells. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. Some of the proteins are embedded entirely within the lipid layer, others extend to one or the other surface, and still others…
What repels water soluble molecules?
Lipid-soluble molecules and some small molecules can permeate the membrane, but the lipid bilayer effectively repels the many large, water-soluble molecules and electrically charged ions that the cell must import or export in order to live.
What is the membrane of a neuron?
The neuron is bound by a plasma membrane, a structure so thin that its fine detail can be revealed only by high-resolution electron microscopy. About half of the membrane is the lipid bilayer, two sheets of mainly phospholipids with a space between. One…
What are the two types of lipids in membranes?
Membrane lipids are principally of two types, phospholipids and sterols (generally cholesterol ). Both types share the defining characteristic of lipids—they dissolve readily in organic solvents—but in addition they both have a region that is attracted to and soluble in water.
How thick is the lipid bilayer?
Intrinsic proteins penetrate and bind tightly to the lipid bilayer, which is made up largely of phospholipids and cholesterol and which typically is between 4 and 10 nanometers (nm; 1 nm = 10 −9 metre) in thickness.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane (Plasma membrane) The outer thin membrane or the layer of the living cell is known as the cell membrane. It is also known as the plasma membrane in animal cells. In the plant cells, it is known as plasmalemma. The term cell membrane was given by Nageli and Cramer (1885) for the membrane covering of the protoplast.
How many types of cell membranes are there?
There are two types of cell membrane. They are:
What are the three types of lipids in the cell membrane?
Most of the cell membrane is composed of 40-50 % protein and 50-60 % lipids. Membrane lipids are of three types: a) Phospholipids b) Glycolipids c) Steroids. In the different membrane, the proportion of the lipid varies:
Which model suggests that the cell membrane is a solid and stable structure?
It was proposed by James Danielli and Hugh Davsan in the year 1935. This model suggests the cell membrane as the solid and the stable structure. Four molecular layers are present in it i.e. two phospholipids and two protein layers. It consists of the phospholipid.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Cell membrane helps to maintain homeostasis. It provides protection to all the internal organelles of the cell.
What is the interaction between lipids and proteins?
Between the lipids and the proteins, there is interaction which results in the fluidity of the membrane.
Which structure is present in the amoeba?
In the amoeba, pseudopodia are present for locomotion which is the modified structure of the cell membrane.
What is the cell membrane?
Definition. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. a 3D diagram of the cell membrane.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Function of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and leave the cell. It is a selectively permeable barrier, meaning it allows some substances to cross, but not others. Like a drawbridge intended to protect a castle and keep out enemies, the cell membrane only allows certain ...
What is the technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane?
The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Structure of the cell membrane and its associated components.
What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic phospholipids?
When in water or an aqueous solution (including inside the body) the hydrophobic heads of phospholipids will orient themselves to be on the inside, as far away from the water as possible. In contrast, the hydrophilic heads will be on the outside, making contact with the water. The result is that a double layer of phospholipids is formed, with the hydrophobic heads clustering together in the center, and the hydrophilic tails forming the outside of the structure. The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Bilayer. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are lipid molecules made up of a phosphate group head and two fatty acid tails. Importantly, the properties of phospholipid molecules allow them to spontaneously form a double-layered membrane. The phosphate group head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic, ...
How does the cell control the rate of diffusion of substances?
Another way the cell membrane can bring molecules into the cytoplasm is through endocytosis. The reverse process, where the cell delivers contents outside the membrane barrier, is called exocytosis. Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) ...
What is the process of endocytosis?
Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) and pinocytosis (“cell drinking”). During these processes, the cell membrane forms a depression, surrounding the particle that it is engulfing. It then “pinches off” to form a small sphere of membrane called a vesicle that contains the molecule and transports it to wherever it will be used in ...
What is the average thickness of a cell membrane?
They are quasifluid, elastic, pliable and film-like thin partitions over and inside cytoplasm. Average thickness is 75 A (50—100 A). Bio membranes are selectively permeable for solutes but semipermeable for water. They are dynamic in nature. Any injured part of the membrane is repaired within no time.
What are the lipids in the membrane?
The important lipids of the membrane are phosphoglycerides or phospholipids (some 100 types). Carbohydrates present in the membrane are branched or un-branched oligosaccharides, e.g., hexose, fucose, hexoamine, sialic acid, etc. Proteins can be fibrous or globular, structural, carrier, receptor or enzymatic.
Why are bio membranes not visible under light microscopes?
Bio membranes are not visible under the light microscope because their plasma thickness is below the resolving power of the microscope. Under electron microscope bio membranes appear to be trilaminar or tripartite. There is an electron dense or dark layer on either side of middle electron transparent layer (Fig. 8.20). Freeze etching technique has shown that a membrane possesses particles of different sizes.
How do fat soluble substances move across the plasma membrane?
Neutral solutes and fat soluble substances can move across the plasma membrane through simple diffusion along their concentration gradient or from the side of higher concentration to the side of their lower concentration. Based on the free movement of lipid soluble substances across the cell membrane, Overton (1900) proposed that cell membranes are made of lipids.
Where are lipids found in the fluid-mosaic model?
Fluid-mosaic model postulates that the lipid molecules are present in a viscous bilayer as in lamellar model. Protein molecules occur at places both inside and on the outer side of lipid bilayer (Fig. 8.22) — protein icebergs in a sea of lipids.
How are the polar heads of phospholipids held together?
The hydrophilic polar heads of the phospholipid molecules are directed towards the proteins. The two are held together by electrostatic forces. The hydrophobic nonpolar tails of the two lipid layers are directed towards the centre where they are held together by hydrophobic bonds and vander Waals forces.
Where do membranes occur in eukaryotic cells?
Membranes also occur inside the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells as covering of several cell organelles like nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, peroxisomes, etc. They line endoplasmic reticulum, cover thylakoids in plastids or form cristae inside mitochondria. Vacuoles are separated from cytoplasm by a membrane called tonoplast.
Which proteins are present in the inner membrane?
Inner membrane: phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol. Integral proteins (transmembrane proteins and lipid-anchored proteins which are confined to only one side of the membrane) Present between lipid molecules in a highly organised form, as well as bulk water in pores and channels.
Why is the whole membrane thicker than the whole membrane?
The whole membrane, of course, ends up appearing thicker than this (hence the 7-10 nm estimates) because it is packed full of proteins and polysaccharides, such that the entire membrane probably resembles a "cobblestone pavement" ( Takamori et al, 2006 ) with the lipid bilayer acting as a thin mortar between large thick clusters of transmembrane proteins. Again borrowing (stealing) shamelessly from Phillips (2018), the diagram below demonstrates the relative sizes of these transmembrane structures.
How are surface proteins and transmembrane proteins divided?
Historically, the division of surface proteins and transmembrane proteins was by whether or not they were soluble in polar solvents. Peripheral proteins would dissolve and drift away, they would say, and integral transmembrane proteins would remain stuck in the membrane until you use a non-polar solvent or detergent to disrupt the lipid bilayer.
What are the physical properties of a bilayer?
Physical properties of the cell membrane: Impermeable to water-soluble molecules (but not to water) Soft and flexible. Spontaneously prone to forming self-repairing pores.
What attracts phospholipids to the membrane?
Attracted to the membrane by the intrinsic negative charge of the phospholipid heads
Why is membrane potential difference not entirely due to the membrane acting as a separator between two electrolyte solutions?
The generation of the membrane potential difference is not entirely due to the membrane acting as a separator between two electrolyte solutions, but also due to the collection of charged ions at the membrane surface ( Tamagawa et al, 2014 ).
Which bilayer is hydrophilic?
The lipid bilayer consists of phospholipids, which are amphipathic molecules (i.e. where one end of the molecule is hydrophilic and the other end is hydrophobic)
What was the plasma membrane's core made of?
They made the analogy of proteins to bread, and lipids to the filling. In the 1950s, advances in microscopy, notably transmission electron microscopy (TEM), allowed researchers to see that the plasma membrane’s core consisted of a double, rather than a single, layer.
What percentage of the plasma membrane is protein?
The protein, lipid, and carbohydrate proportions in the plasma membrane vary with cell type, but for a typical human cell, protein accounts for about 50 percent of the composition by mass, lipids (of all types) account for about 40 percent, and carbohydrates comprise the remaining 10 percent. However, protein and lipid concentration varies ...
What is the protein in the mitochondria?
The mitochondrial inner membrane contains 76 percent protein and only 24 percent lipid. The plasma membrane of human red blood cells is 30 percent lipid. Carbohydrates are present only on the plasma membrane’s exterior surface and are attached to proteins, forming glycoproteins, or attached to lipids, forming glycolipids.
What are phospholipids made of?
A phospholipid is a molecule consisting of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate-linked head group. Cholesterol, another lipid comprised of four fused carbon rings, is situated alongside the phospholipids in the membrane’s core. The protein, lipid, and carbohydrate proportions in the plasma membrane vary with cell type, ...
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
Among the most sophisticated plasma membrane functions is the ability for complex, integral proteins, receptors to transmit signals. These proteins act both as extracellular input receivers and as intracellular processing activators.
What is the landscape of the membrane?
The landscape of the membrane is studded with proteins, some of which span the membrane. Some of these proteins serve to transport materials into or out of the cell. Carbohydrates are attached to some of the proteins and lipids on the outward-facing surface of the membrane.
When was the plasma membrane discovered?
Scientists identified the plasma membrane in the 1890s, and its chemical components in 1915. The principal components they identified were lipids and proteins. In 1935, Hugh Davson and James Danielli proposed the plasma membrane’s structure. This was the first model that others in the scientific community widely accepted.
What are the membranes of animal cells?
The most important membranes in animal cells are the plasma membrane, the inner and outer nuclear membranes, the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi apparatus, and the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. Lysosomes, peroxisomes, and various vesicles are also separated from the cytoplasm by membranes.
How thick is a membrane?
All biological membranes are constructed according to a standard pattern. They consist of a continuous bilayer of amphipathic lipids approximately 5 nm thick, into which proteins are embedded.
What are the carbohydrates in the plasma membrane?
In addition, some membranes also carry carbohydrates (mono- and oligosaccharides) on their exterior, which are bound to lipids and proteins. The proportions of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates differ markedly depending on the type of cell and membrane. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer containing embedded and peripheral proteins.
What is the polar hydrophilic head group?
Membrane lipids are strongly amphipathic molecules with a polar hydrophilic “head group” and a polar hydrophobic “tail.” In membranes, they are primarily held together by the hydrophobic effect and weak Van der Waals forces and are therefore mobile relative to each other. This gives membranes a more or less fluid quality.
What are lipids that separate the contents of the compartment they surround from its environment?
Membranes are lipid structures that separate the contents of the compartment they surround from its environment.
Why is the plasma membrane important?
The plasma membrane is essential for maintaining differences in the concentration of many substances between the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Regulated transport of substances.
Which membrane contains short chains of carbohydrates attached to proteins and lipids?
The plasma membrane glycocalyx consists of short chains of carbohydrates attached to proteins and lipids which extend in the aqueous media and both protects the cell from digestion and restricts the uptake of hydrophobic molecules.
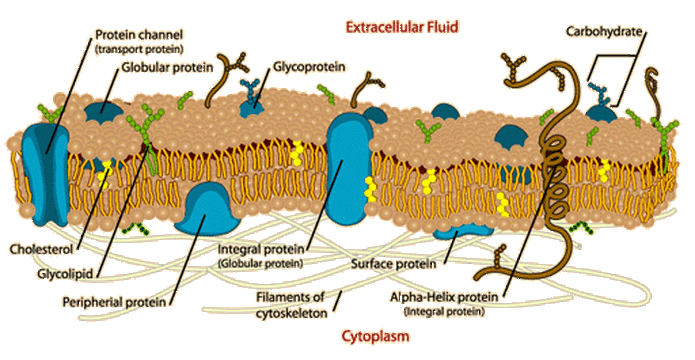
Cell Membrane
Composition of Cell Membrane
- Most of the cell membrane is composed of 40-50 % protein and 50-60 % lipids.
- Membrane lipids are of three types: a) Phospholipids b) Glycolipids c) Steroids
- In the different membrane, the proportion of the lipid varies:
Structure of The Cell Membrane
- The structure of the cell membrane is explained by the different models. They are as follows : 1. Danielli-Davson Trilaminar sandwich model 2. Fluid mosaic model of the Singer and Nicolson 3. Unit membrane of Robertson
Functions of The Cell Membrane
- Cell recognition and communication 1. In the cell membrane, glycolipids and glycoproteins are present. It helps in recognizing the cell. 2. It is essential during the defense against microbes and tissue formation. 3. The binding of the ligands to the specific receptors induces signal transduction. Blood grouping 1. Based on the antigens present in the cell membrane, blood grou…
References and Sources
- Shakya M, Mehata KR, Gautam MK, Pokhrel KR and Khanal K (2020 ) “ Principles of Biology”, Asmita Books Publisher and Distributors Ltd, Bhotahity, Nepal
- 1% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/20685751_Lipid_regulation_of_membrane_structu…
- 1% – https://www.mechanobio.info/what-is-the-plasma-membrane/what-types-of-proteins-ar…
- Shakya M, Mehata KR, Gautam MK, Pokhrel KR and Khanal K (2020 ) “ Principles of Biology”, Asmita Books Publisher and Distributors Ltd, Bhotahity, Nepal
- 1% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/20685751_Lipid_regulation_of_membrane_structu…
- 1% – https://www.mechanobio.info/what-is-the-plasma-membrane/what-types-of-proteins-are-found-in-the-plasma-membrane/
- 1% – https://www.khanacademy.org/science/high-school-biology/hs-cells/hs-the-cell-membrane/a/hs-the-cell-membrane-review