How are DNA fragments separated from other DNA fragments?
May 03, 2020 · What is the composition of a DNA fragment? DNA is made up of molecules called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group and a nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Click to see full answer.
How do you determine the size of DNA fragments?
This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. What is the composition of a DNA fragment? In other words, what is a DNA fragment made of? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the ...
What is enzymatic DNA fragmentation used for?
What is the composition of a DNA fragment? DNA fragment DNA is a double helical structure containing sets of nucleotides that contain genetic information (Deoxyribonucleic acid). …
What is the structure of DNA?
Feb 03, 2011 · Sixfold concentrates of these buffers are often composed of 0.25% bromophenol blue (BPB) which ...

How do you make a DNA fragment?
0:285:02DNA Technology - Producing DNA Fragments - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd there are two ways of doing this you can convert RNA to DNA or. You can use different enzymes toMoreAnd there are two ways of doing this you can convert RNA to DNA or. You can use different enzymes to cut DNA at specific base sequences.
Which of the following is the composition of DNA?
The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands.
What is genomic DNA fragments?
genomic DNA library. A genomic DNA library is a collection of DNA fragments that make up the full-length genome of an organism. A genomic library is created by isolating DNA from cells and then amplifying it using DNA cloning technology.
How do you identify a DNA fragment?
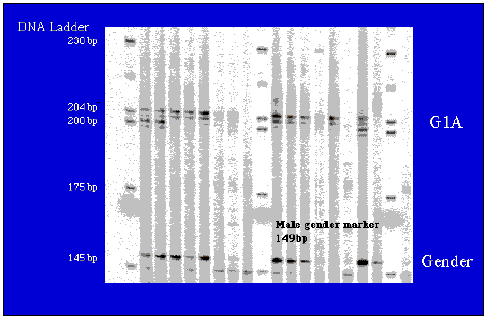
The separation and identification of DNA fragments based on their size is possible using a ubiquitous tool called gel electrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis is used to isolate, identify, and characterize properties of DNA fragments (Figure 10.4).
What are the 3 composition of DNA?
DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. These building blocks are made of three parts: a phosphate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases.Aug 24, 2020
What is the composition of DNA and RNA?
Both DNA and RNA are made from nucleotides, each containing a five-carbon sugar backbone, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. DNA provides the code for the cell's activities, while RNA converts that code into proteins to carry out cellular functions.
How is a genomic DNA library made?
In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase.
What causes DNA fragmentation?
DNA is negatively charged, therefore, when an electric current is applied to the gel, DNA will migrate towards the positively charged electrode. Shorter strands of DNA move more quickly through the gel than longer strands resulting in the fragments being arranged in order of size.Jul 21, 2021
What is bacterial genomic DNA?
Most bacteria have a genome that consists of a single DNA molecule (i.e., one chromosome) that is several million base pairs in size and is "circular" (doesn't have ends like chromosomes of eukaryotic organisms).
What do DNA fragments tell us?
All DNA molecules have the same amount of charge per mass. Because of this, gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments separates them based on size only. Using electrophoresis, we can see how many different DNA fragments are present in a sample and how large they are relative to one another.
How do you cut DNA into fragments?
Restriction enzymes, found naturally in bacteria, can be used to cut DNA fragments at specific sequences, while another enzyme, DNA ligase, can attach or rejoin DNA fragments with complementary ends.
How are DNA fragments separated?
To separate DNA using agarose gel electrophoresis, the DNA is loaded into pre-cast wells in the gel and a current applied. The phosphate backbone of the DNA (and RNA) molecule is negatively charged, therefore when placed in an electric field, DNA fragments will migrate to the positively charged anode.Apr 20, 2012
What is DNA fragment?
DNA fragment. DNA is a double helical structure containing sets of nucleotides that contain genetic information (Deoxyribonucleic acid). It contains information instruction an organic need to develop, live and reproduce.
What is DNA made of?
View this answer. DNA is made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, sugar group, and a nitrogen base. Phosphate group contains a phosphorus... See full answer below.
What is DNA made of?
Answer and Explanation: 1. Become a Study.com member to unlock this answer! Create your account. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is made up of molecules, called nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of three main parts: a phosphate group, sugar... See full answer below.
What are the components of nucleotides?
Nucleotides have a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base. Learn how these simple components allow nucleotides to join together to make polymers like DNA and RNA, as well as energy carrying molecules like ATP.
Why is DNA important?
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a vital molecule because it stores and encodes all of the information necessary for life. It is essentially the genetic blueprint of life and carries in its sequences all of the instructions an organism needs to function, develop, and reproduce.
How to make a recombinant plasmid?
Steps in making a recombinant DNA plasmid. First, a scientist uses molds to make an agarose gel with wells at one end for placing DNA samples. The gel is placed in an electrophoresis chamber and DNA samples are added to the wells. The electrophoresis apparatus produces a small electrical field, driving negatively charged DNA strands away from ...
Why is DNA analysis difficult?
DNA fragments are difficult to separate under normal CE conditions due to their virtually constant charge-to-mass ratio. Therefore, analyses are performed using a replaceable sieving matrix, consisting of a water-soluble polymer dissolved in a suitable buffer. Such solutions are referred to as entangled polymer buffers and the DNA sieved based on its ability to fit within pores created within the polymer matrix. The fact that these polymer matrices are not rigid makes them different from rigid agarose or polyacrylamide gels traditionally used in DNA analysis. The advantage of using an entangled polymer buffer is that fresh polymer solution can be pumped into the capillary at the conclusion of each analysis, cleaning the capillary and limiting problems with carryover. Experiments carried out using a variety of entangled polymer buffers have shown that with careful optimization of molecular weight and concentration, high-resolution DNA separations can be produced.
What is Southern Blot? What are some examples?
Southern blotting has numerous research and clinical applications. For example, the technique is used in the clinical molecular diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy. The disorder is caused by abnormal expansion of a region of CTG trinucleotide repeats in the DMPK gene. Unaffected individuals have 5–35 copies of the CTG repeat, while affected individuals can have several thousand copies. A normal or slightly enlarged number of repeats is detected with PCR. The number of repeats in an allele with a large expansion is determined by the size of bands on a Southern blot ( Figure 1 ).
What is used to prevent nonspecific binding?
Before hybridization, blots are first treated with a blocking solution to prevent nonspecific binding of the probe; solutions may include dry milk, unrelated sheared DNA such as salmon sperm DNA, or sodium dodecyl sulfate. The single-stranded DNA probe, in solution, is brought in contact with the membrane under conditions that allow binding to the complementary DNA on the membrane. Following hybridization, the membrane is washed at a stringency that will release nonspecific probe binding. The specificity of the reaction is critical, as the probe must bind only to the unique target and not to nonspecific sites. The probe design, hybridization conditions, and washing stringency contribute to the specificity.
What temperature is the DNA fragment incubated at?
The DNA fragment, which includes the aptazyme and gfp genes, is mixed with the cell-free transcription–translation system and incubated at 37 °C for 1–3 h. During the incubation, the fluorescence of the expressed GFP protein is monitored in real time.
What is the effect of uncoated silica capillaries?
This effect is known as the electroosmotic flow (EOF) and can result in irreproducible changes in DNA migration from run to run.
How are DNA fragments hybridized?
DNA fragments are hybridized from a whole-genome library to complementary sequences that have been synthesized and combined into a mixture of probes designed with high specificity for the matching regions in the genome. Covalently linked biotin moieties enable a secondary capture by mixing the probe library complexes with streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. The targeted regions of the genome are selectively captured from solution by applying a magnetic field, whereas most of the remainder of the genome is washed away in the supernatant. Subsequent denaturation releases the captured library fragments from the beads into solution, ready for postcapture amplification, quantitation, and sequencing. Exome sequencing is performed when the probes are designed to capture essentially all of the known coding exons in a genome [143].