
Precautions
LDL cholesterol is considered the “bad” cholesterol, because it contributes to fatty buildups in arteries ( atherosclerosis ). This narrows the arteries and increases the risk for heart attack, stroke and peripheral artery disease (PAD).
What is the worst kind of cholesterol?
What Are the Functional Groups in Cholesterol?
- Types of Functional Groups. Molecules are made from atoms, which sometimes combine to form a specific group of atoms. ...
- Group Characteristics. Four hydrocarbon rings form the middle of the molecule. ...
- Cholesterol in Cell Membranes. ...
- Digestive Support. ...
What are the functional groups in cholesterol?
for healthy cholesterol levels are as follows:
- total cholesterol below 200 mg/dL
- LDL cholesterol less than 100 mg/dL
- HDL cholesterol above 40 mg/dL
What are the two forms of cholesterol?
The types of cholesterol and lipoproteins include Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), Triglycerides and Lp(a) Cholesterol
What is the classification of cholesterol?
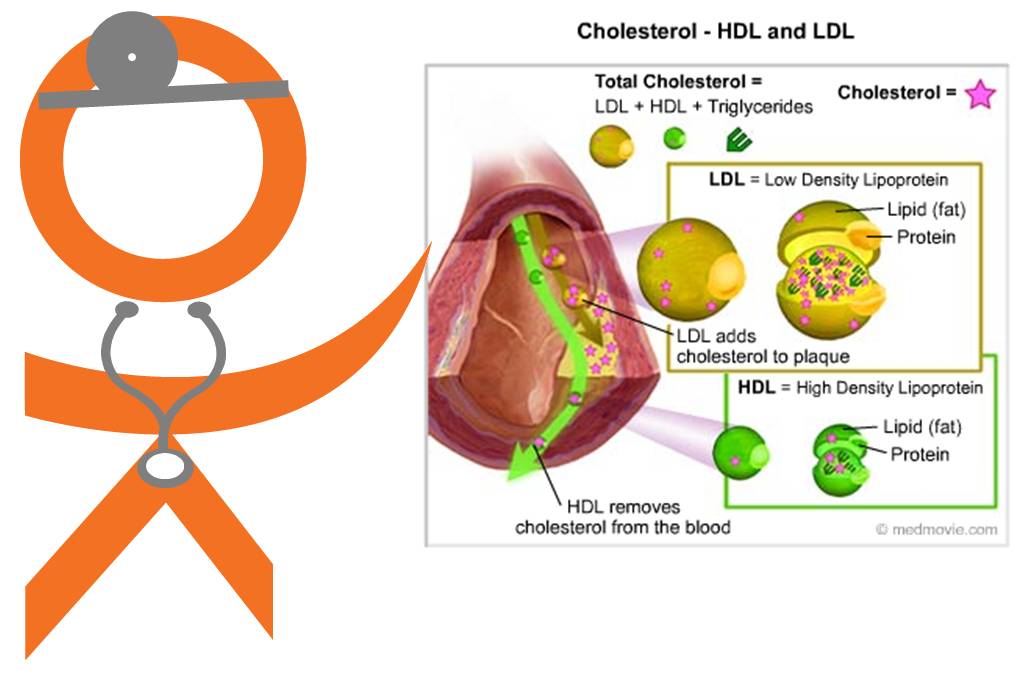
What does low HDL cholesterol do to the heart?
Low HDL levels cause the buildup of LDL in the blood and some of it gets deposited along the inner lining of the arteries. High levels of HDL protect the heart and blood vessels by reducing LDL cholesterol in the blood. High levels of HDL also produce other protective effects like antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-clot effects on heart ...
Why is HDL considered good cholesterol?
HDL is known as good cholesterol because having high levels can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. HDL cholesterol scavenges and removes LDL or bad cholesterol HDL reduces, reuses, and recycles LDL cholesterol by transporting it to the liver where it can be reprocessed.
What is the role of HDL cholesterol in blood vessels?
HDL cholesterol acts as a maintenance crew for the inner walls (endothelium) of blood vessels. Damage to the inner walls is the first step in the process of atherosclerosis, which causes heart attacks and strokes. HDL scrubs the wall clean and keeps it healthy.
What is the total cholesterol?
Total cholesterol is a measure of the total amount of cholesterol in your blood and is based on the HDL, LDL, and triglycerides number. Total cholesterol: less than 200 mg/dL.
Can high triglycerides cause heart attacks?
The combination of high levels of triglycerides with low HDL cholesterol or high LDL cholesterol can increase your risk of heart attack and stroke . Triglycerides: less than 150 mg/dL.
Can a diet cause CAD?
Unhealthy lifestyle and no control over diet will do the exact opposite of what is just written above. Our body would be unable to cope with dietary cholesterol. A diet that produces free radicals gives free permit to the excess cholesterol to flow into the bloodstream and oxidize. Subsequently, the cholesterol accumulates in the blood vessels and coronary arteries leading to CAD (Coronary Artery Disease).
Does HDL increase cholesterol?
High levels of HDL also produce other protective effects like antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-clot effects on heart and blood vessels. Many people look for a rise in good cholesterol. However, it is important to regulate both the good cholesterol and bad cholesterol.
What enzyme reduces mevalonate?
This molecule is then reduced to mevalonate by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Production of mevalonate is the rate-limiting and irreversible step in cholesterol synthesis and is the site of action for statins (a class of cholesterol-lowering drugs).
How does cholesterol affect the cell?
Cholesterol is also implicated in cell signaling processes, assisting in the formation of lipid rafts in the plasma membrane, which brings receptor proteins in close proximity with high concentrations of second messenger molecules . In multiple layers, cholesterol and phospholipids, both electrical insulators, can facilitate speed of transmission of electrical impulses along nerve tissue. For many neuron fibers, a myelin sheath, rich in cholesterol since it is derived from compacted layers of Schwann cell membrane, provides insulation for more efficient conduction of impulses. Demyelination (loss of some of these Schwann cells) is believed to be part of the basis for multiple sclerosis .
What is the role of cholesterol in the lipid rafts?
Cholesterol regulates the biological process of substrate presentation and the enzymes that use substrate presentation as a mechanism of their activation. ( PLD2) is a well-defined example of an enzyme activated by substrate presentation. The enzyme is palmitoylated causing the enzyme to traffic to cholesterol dependent lipid domains sometimes called " lipid rafts ". The substrate of phospholipase D is phosphatidylcholine (PC) which is unsaturated and is of low abundance in lipid rafts. PC localizes to the disordered region of the cell along with the polyunsaturated lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate ( PIP2 ). PLD2 has a PIP2 binding domain. When PIP2 concentration in the membrane increases, PLD2 leaves the cholesterol dependent domains and binds to PIP2 where it then gains access to its substrate PC and commences catalysis based on substrate presentation.
How much cholesterol is in a human body?
A human male weighing 68 kg (150 lb) normally synthesizes about 1 gram (1,000 mg) of cholesterol per day, and his body contains about 35 g, mostly contained within the cell membranes.
What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
Within the cell membrane, cholesterol also functions in intracellular transport, cell signaling and nerve conduction. Cholesterol is essential for the structure and function of invaginated caveolae and clathrin -coated pits, including caveola-dependent and clathrin-dependent endocytosis.
How many steps are there in the process of synthesizing cholesterol?
Physiology. Cholesterol is essential for all animal life, with each cell capable of synthesizing it by way of a complex 37- step process. This begins with the mevalonate or HMG-CoA reductase pathway, the target of statin drugs, which encompasses the first 18 steps.
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
It is required to build and maintain membranes and modulates membrane fluidity over the range of physiological temperatures. The hydroxyl group of each cholesterol molecule interacts with water molecules surrounding the membrane, as do the polar heads of the membrane phospholipids and sphingolipids, while the bulky steroid and the hydrocarbon chain are embedded in the membrane, alongside the nonpolar fatty-acid chain of the other lipids. Through the interaction with the phospholipid fatty-acid chains, cholesterol increases membrane packing, which both alters membrane fluidity and maintains membrane integrity so that animal cells do not need to build cell walls (like plants and most bacteria). The membrane remains stable and durable without being rigid, allowing animal cells to change shape and animals to move.
Did You Know?
Higher blood LDL – especially higher LDL concentrations and smaller LDL particle size – contributes more to this process than the cholesterol content of HDL particles, so LDL particles are often referred to as "poor cholesterol." High levels of functional HDL, which can extract cholesterol from cells and atheromas, provide safety and are referred to as "healthy cholesterol" by the general public. These equilibriums are often determined by genetics, but they can be influenced by body structure, drugs, diet, and other factors.
What is the most common type of cholesterol in the body?
Ans: Lipoproteins are two types of proteins that transport cholesterol in the body: the majority of your body's cholesterol is LDL (low-density lipoprotein), also known as "negative" cholesterol. High LDL cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
It is required for the construction and maintenance of membranes, as well as the modulation of membrane fluidity over a wide range of physiological temperatures. The hydroxyl groups of cholesterol molecules, as well as the polar heads of membrane phospholipids and sphingolipids, interact with water molecules surrounding the membrane, while the bulky steroid and hydrocarbon chains, as well as the nonpolar fatty-acid chains of the other lipids, are embedded in the membrane. Cholesterol enhances membrane packing by interacting with phospholipid fatty-acid chains, altering membrane fluidity, and maintaining membrane integrity so that animal cells do not need to erect cell walls (like plants and most bacteria). Animal cells can change shape and animals can move because the membrane is stable and strong without being rigid.
Why is cholesterol important in endocytosis?
Cholesterol controls the biological process of substrate presentation as well as the enzymes that use substrate presentation to activate themselves.
How does cholesterol affect the cell?
Cholesterol plays a role in cell signaling by assisting in the development of lipid rafts in the plasma membrane, which carry receptor proteins together with high concentrations of second messenger molecules. Cholesterol and phospholipids, both electrical insulators, can help speed up the propagation of electrical impulses along with nerve tissue in multiple layers. A myelin sheath, which is rich in cholesterol since it is derived from compacted layers of Schwann cell membrane, provides protection for many neuron fibres, allowing for more effective impulse conduction. Multiple sclerosis is thought to be caused by demyelination (the failure of some of these Schwann cells).
Is cholesterol soluble in water?
Cholesterol is only slightly soluble in water as an isolated molecule, making it hydrophilic. As a result, it dissolves in blood at very low concentrations. Cholesterol is packaged inside lipoproteins, complex discoidal particles with external amphiphilic proteins and lipids, whose outward-facing surfaces are water-soluble and inward-facing surfaces are lipid-soluble, in order to be transported effectively. This causes it to emulsify and pass through the bloodstream. Since unbound cholesterol is amphipathic, it is transported along with phospholipids and proteins in the monolayer surface of the lipoprotein particle. Cholesterol esters attached to fatty acids, on the other hand, are transported along with triglyceride within the lipoprotein.
Is cholesterol a precursor for steroid hormones?
Cholesterol is also a precursor for steroid hormones, bile acid, and vitamin D biosynthesis. Cholesterol is the most common sterol produced by all animals. Hepatic cells are the ones that generate the most in the vertebrates. With the exception of Mycoplasma, which needs cholesterol for growth, it is not present in prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea). This article will study cholesterol formula, cholesterol chemical name, Cholesterol Structure, properties of cholesterol, and cholesterol structure and function.
What causes atherosclerosis?
High levels of cholesterol in the bloodstream are an extremely important cause of atherosclerosis. In this disorder, deposits of cholesterol and other fatty substances circulating in the blood accumulate in the interior walls of the blood vessels. These fatty deposits build up, thicken, and become calcified, eventually converting the vessel walls to scar tissue. The deposits narrow the channels of the blood vessels and thus can constrict the blood flow, causing heart attacks and strokes. High levels of cholesterol in the blood (more than 240 mg of cholesterol per 100 cc of blood plasma) accelerate the buildup of cholesterol deposits in the vessel walls; people with high cholesterol levels thus eventually become more susceptible to coronary heart disease.
How much cholesterol is in blood?
High levels of cholesterol in the blood (more than 240 mg of cholesterol per 100 cc of blood plasma) accelerate the buildup of cholesterol deposits in the vessel walls; people with high cholesterol levels thus eventually become more susceptible to coronary heart disease. Read More on This Topic.
Where does cholesterol get broken down?
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) may possibly transport excess or unused cholesterol from the tissues back to the liver, where it is broken down to bile acids and is then excreted. Cholesterol attached to LDLs is primarily that which builds up in atherosclerotic deposits in the blood vessels.
What is the chemical formula for cholesterol?
Chemically, cholesterol is an organic compound belonging to the steroid family; its molecular formula is C 27 H 46 O. In its pure state it is a white, crystalline substance that is odourless and tasteless.
Is cholesterol a component of the cell membrane?
Cholesterol is essential to life; it is a primary component of the membrane that surrounds each cell, and it is the starting material or an intermediate compound from which the body synthesizes bile acids, steroid hormones, and vitamin D. Cholesterol circulates in the bloodstream and is synthesized by the liver and several other organs.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Which system regulates the amount of cholesterol synthesized by the liver?
A compensatory system regulates the amount of cholesterol synthesized by the liver, with the increased dietary intake of cholesterol resulting in the liver’s decreased synthesis of the compound.
Why is it important to have your cholesterol tested?
Too much of the bad kind, or not enough of the good kind, increases the risk cholesterol will slowly build up in the inner walls of the arteries ...
What happens if a blood clot forms and blocks one of these narrowed arteries?
If a blood clot forms and blocks one of these narrowed arteries, a heart attack or stroke can result. When it comes to cholesterol, remember: check, change and control. That is: Check your cholesterol levels. It’s key to know your numbers and assess your risk. Change your diet and lifestyle to help improve your levels.
What happens if you have a blood clot in your arteries?
If a blood clot forms and blocks one of these narrowed arteries, a heart attack or stroke can result.
Why does cholesterol matter?
Why cholesterol matters. Cholesterol circulates in the blood. As the amount of cholesterol in your blood increases, so does the risk to your health. High cholesterol contributes to a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease and stroke.
How to control cholesterol?
When it comes to cholesterol, remember: check, change and control. That is: 1 Check your cholesterol levels. It’s key to know your numbers and assess your risk. 2 Change your diet and lifestyle to help improve your levels. 3 Control your cholesterol, with help from your doctor if needed
Where does cholesterol come from?
Cholesterol comes from two sources. Your liver makes all the cholesterol you need. The remainder of the cholesterol in your body comes from foods from animals. For example, meat, poultry and dairy products all contain dietary cholesterol. Those same foods are high in saturated and trans fats.
Does palm oil raise cholesterol?
These fats cause your liver to make more cholesterol than it otherwise would. For some people, this added production means they go from a normal cholesterol level to one that’s unhealthy. Some tropical oils – such as palm oil, palm kernel oil and coconut oil – contain saturated fat that can increase bad cholesterol.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that's found in all the cells in your body. Your body needs some cholesterol to make hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help you digest foods. Your body makes all the cholesterol it needs. Cholesterol is also found in foods from animal sources, such as egg yolks, meat, and cheese.
What causes high cholesterol?
The most common cause of high cholesterol is an unhealthy lifestyle . This can include:
What health problems can high cholesterol cause?
If you have large deposits of plaque in your arteries, an area of plaque can rupture (break open). This can cause a blood clot to form on the surface of the plaque. If the clot becomes large enough, it can mostly or completely block blood flow in a coronary artery.
How is high cholesterol diagnosed?
There are usually no signs or symptoms that you have high cholesterol. There is a blood test to measure your cholesterol level. When and how often you should get this test depends on your age, risk factors, and family history. The general recommendations are:
Why is LDL considered bad?
LDL stands for low-density lipoprotein. It is sometimes called "bad" cholesterol because a high LDL level leads to the buildup of plaque in your arteries. VLDL stands for very low-density lipoprotein. Some people also call VLDL a "bad" cholesterol because it too contributes to the buildup of plaque in your arteries.
What does HDL stand for?
Different types of lipoproteins have different purposes: HDL stands for high-density lipoprotein. It is sometimes called "good" cholesterol because it carries cholesterol from other parts of your body back to your liver. Your liver then removes the cholesterol from your body. LDL stands for low-density lipoprotein.
What is the treatment for familial hypercholesterolemia?
Some people with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) may receive a treatment called lipoprotein apheresis. This treatment uses a filtering machine to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood. Then the machine returns the rest of the blood back to the person. NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
What Are Lipoproteins?
The HDL and LDL lipoproteins are tiny “packages” in your blood, with fat (lipid) on the inside and proteins on the outside, that carry cholesterol throughout your body. You will often see them called the good cholesterol and the bad cholesterol.
What is the main engine of cholesterol buildup and blockage in your arteries?
LDL (“bad”) cholesterol is the main “engine” of cholesterol buildup and blockage in your arteries.
Why does LDL cholesterol go up?
LDL cholesterol goes up if your diet is high in saturated and “trans” fat, also called trans-fatty acid. (This is the manufactured fat used to increase food products’ shelf life and flavor stability.)
What is total cholesterol?
Total cholesterol is the total amount of cholesterol in your blood. Your total cholesterol includes low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or “bad”) cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL, or “good”) cholesterol. Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in every cell in your body. Verywell / Cindy Chung.
How is total cholesterol measured?
How Total Cholesterol Is Measured. This is done using a blood test called a lipoprotein panel, which also measures your triglycerides. 1 For this test, you provide a blood sample that’s taken after you’ve fasted (not eaten anything and drunk only water) for 9 to 12 hours before your test.
Why is triglyceride considered a fat?
But it’s measured because elevated triglyceride levels increase your risk of developing atherosclerosis —a buildup of fatty plaques on artery walls—and increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
What is cholesterol in the body?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in every cell in your body. Verywell / Cindy Chung.
What happens when you have too much LDL?
When your body has too much LDL cholesterol, the LDL cholesterol can build up on the walls of your blood vessels. This buildup is called “plaque.”. As your blood vessels build up plaque over time, the insides of the vessels narrow. This narrowing blocks blood flow to and from your heart and other organs. When blood flow to the heart is blocked, it ...
What are the two types of cholesterol?
Cholesterol travels through the blood on proteins called “lipoproteins.” Two types of lipoproteins carry cholesterol throughout the body: 1 LDL (low-density lipoprotein), sometimes called “bad” cholesterol, makes up most of your body’s cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol raise your risk for heart disease and stroke. 2 HDL (high-density lipoprotein), or “good” cholesterol, absorbs cholesterol and carries it back to the liver. The liver then flushes it from the body. High levels of HDL cholesterol can lower your risk for heart disease and stroke.
What is the name of the cholesterol that is high in the body?
LDL (low-density lipoprotein), sometimes called “bad” cholesterol, makes up most of your body’s cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol raise your risk for heart disease and stroke.
What to do if you have high LDL cholesterol?
If you have high LDL cholesterol levels, your health care team may recommend cholesterol-lowering medicine and lifestyle changes to lower your risk for heart disease and stroke. If you have low HDL cholesterol levels, talk to your doctor about lifestyle changes that may help raise your levels.

Overview
This medication is a multivitamin product used to treat or prevent vitamin deficiency due to poor diet, certain illnesses, or during pregnancy.
Status: Discontinued
May Treat: Mineral deficiency · Mineral deficiency · Vitamin deficiency · Vitamin deficiency
Drug Class: Multivitamin and Mineral Combinations · Nutritional Product - Medical Condition Specific Formulation · Pharmaceutical Adjuvant - Surfactants
Availability: Prescription sometimes needed
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Does not adversely affect lactation
Clinical significance
Etymology
Physiology
According to the lipid hypothesis, elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood lead to atherosclerosis which may increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Since higher blood LDL – especially higher LDL concentrations and smaller LDL particle size – contributes to this process more than the cholesterol content of the HDL particles, LDL particles are often terme…
Biosynthesis and regulation
The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek chole- (bile) and stereos (solid), followed by the chemical suffix -ol for an alcohol.
Dietary sources
Cholesterol is essential for all animal life, with each cell capable of synthesizing it by way of a complex 37-step process. This begins with the mevalonate or HMG-CoA reductase pathway, the target of statin drugs, which encompasses the first 18 steps. This is followed by 19 additional steps to convert the resulting lanosterol into cholesterol.
Interactive pathway map
All animal cells (exceptions exist within the invertebrates) manufacture cholesterol, for both membrane structure and other uses, with relative production rates varying by cell type and organ function. About 80% of total daily cholesterol production occurs in the liver and the intestines; other sites of higher synthesis rates include the brain, the adrenal glands, and the reproductive organs.
Cholesteric liquid crystals
Animal fats are complex mixtures of triglycerides, with lesser amounts of both the phospholipids and cholesterol molecules from which all animal (and human) cell membranes are constructed. Since all animal cells manufacture cholesterol, all animal-based foods contain cholesterol in varying amounts. Major dietary sources of cholesterol include red meat, egg yolks and whole eggs, liver, kidney, giblets, fish oil, and butter. Human breast milk also contains significant quantities of cholest…