
Precautions

What is the composition of urea fertilizer?
Urea is applied alone or in combination with other fertilizers. It is available in solid prills and in water solution. The latter includes a 50-50 mix of urea and ammonium nitrate, which is sold under various trade names and is guaranteed at 32% nitrogen (32-0-0).
What type of compound is urea?
nitrogenous compoundUrea is a nitrogenous compound containing a carbonyl group attached to two amine groups with osmotic diuretic activity. In vivo, urea is formed in the liver via the urea cycle from ammonia and is the final end product of protein metabolism.
Does urea have another name?
Urea, also known as carbamide, is a safe, useful compound with a significant history. It is a naturally occurring molecule that is produced by protein metabolism and found abundantly in mammalian urine.
Where does urea made?
Urea is naturally produced when the liver breaks down protein or amino acids, and ammonia. The kidneys then transfer the urea from the blood to the urine.
Is urea ionic or covalent?
Covalent compoundsCovalent compounds:- Urea, Cane sugar, Hydrogen chloride, Carbon tetrachloride , Ammonia, Alcohol.
Why urea is an organic compound?
Urea is an organic compound that consists of two different NH_{2} groups which are in relation to the carbonyl functional group. Urea dissolves In water as it is a non-toxic substance. Not only urea is colourless but also it has no smell. The carbonyl Group of ammonia has two Amide groups.
What kind of compound is urea quizlet?
Urea is a nitrogen-containing compound with a relatively simple molecular structure. It is a component of urine. It is produced when there is an excess of amino acids in the body, as a means of excreting the nitrogen from the amino acids.
What is the functional group of urea?
Urea (carbamide): A functional group containing a carbonyl group bonded to two nitrogen atoms, or a molecule containing this functional group. The simplest member of this family is also called urea.
What is urea?
Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. It occurs not only in the urine of...
What is the chemical name of urea?
The chemical name of urea is carbamide, the diamide of carbonic acid. Its formula is H2NCONH2.
Who first synthesized urea?
German chemist Friedrich Wöhler first synthesized urea from ammonium cyanate in 1828. It was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a...
What is urea used for?
Urea is used as a fertilizer and feed supplement, as well as a starting material for the manufacture of plastics and drugs.
What is urea used for?
Urea is used for a variety of purposes. Its main industrial use is in fertilizer. It is also used to make adhesives, as an ingredient in skin cream...
What is urea and how is it made?
Urea is a nitrogen-containing compound and waste product. It is made as the final product in protein metabolism through the urea cycle.
What are the components of urea?
The components of urea are: one carbon, four hydrogens, two nitrogens, and one oxygen. It is made of up one carbonyl group and two nitrogen groups.
What are the properties of urea?
Urea is an organic, colorless, odorless, solid compound that is highly soluble in water. It has a melting point of 133-135 degrees Celcius.
What is the IUPAC name of urea?
Carbamide. Urea is an amide because it contains nitrogen that is bound to a carbonyl carbon. It was named carbamide because it has a carbonyl carbo...
What is the structure of urea and where is it found?
Urea contains one carbon, four hydrogens, two nitrogens, and one oxygen. It consists of one carbonyl group and two nitrogen groups (-NH2). It is ma...
What is the formula for urea?
Urea, also called carbamide, the diamide of carbonic acid. Its formula is H 2 NCONH 2. Urea has important uses as a fertilizer and feed supplement, as well as a starting material for the manufacture of plastics and drugs. It is a colourless, crystalline substance that melts at 132.7° C (271° F) and decomposes before boiling.
What is the formula for urea in encyclopedia?
See Article History. Alternative Title: carbamide. Urea, also called carbamide, the diamide of carbonic acid. Its formula is H 2 NCONH 2.
What is the end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes?
Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. It occurs not only in the urine of mammals but also in their blood, bile, milk, and perspiration.
What is the purpose of urea?
Urea is used as a fertilizer and feed supplement, as well as a starting material for the manufacture of plastics and drugs. Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. The material occurs not only in the urine of all mammals but also in their blood, bile, milk, and perspiration.
When was urine first isolated?
Urea was first isolated from urine in 1773 by the French chemist Hilaire-Marin Rouelle. Its preparation by the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler from ammonium cyanate in 1828 was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a naturally occurring organic compound from inorganic materials.
Who made urea?
German chemist Friedrich Wöhler first synthesized urea from ammonium cyanate in 1828. It was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a naturally occurring organic compound from inorganic materials. Urea is now prepared commercially in vast amounts from liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide.
Is urea nitrogen a protein?
Although urea nitrogen is in nonprotein form, it can be utilized by ruminant animals (cattle, sheep), and a significant part of these animals’ protein requirements can be met in this way. The use of urea to make urea–formaldehyde resin is second in importance only to its use as a fertilizer.
What is the chemical formula for urea?
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO (NH 2) 2. This amide has two –NH 2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group .
How is urea produced?
For use in industry, urea is produced from synthetic ammonia and carbon dioxide. As large quantities of carbon dioxide are produced during the ammonia manufacturing process as a byproduct from hydrocarbons (predominantly natural gas, less often petroleum derivatives), or occasionally from coal (steam shift reaction), urea production plants are almost always located adjacent to the site where the ammonia is manufactured. Although natural gas is both the most economical and the most widely available ammonia plant feedstock, plants using it do not produce quite as much carbon dioxide from the process as is needed to convert their entire ammonia output into urea. In recent years new technologies such as the KM-CDR process have been developed to recover supplementary carbon dioxide from the combustion exhaust gases produced in the fired reforming furnace of the ammonia synthesis gas plant, allowing operators of stand-alone nitrogen fertilizer complexes to avoid the need to handle and market ammonia as a separate product and also to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere.
How much protein is in a gram of nitrogen?
Furthermore, 1 gram of nitrogen is roughly equivalent to 6.25 grams of protein, and 1 gram of protein is roughly equivalent to 5 grams of muscle tissue.
What is urea used for?
Automobile systems. Urea is used in Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) reactions to reduce the NO x pollutants in exhaust gases from combustion from diesel, dual fuel, and lean-burn natural gas engines.
How are amino acids oxidized?
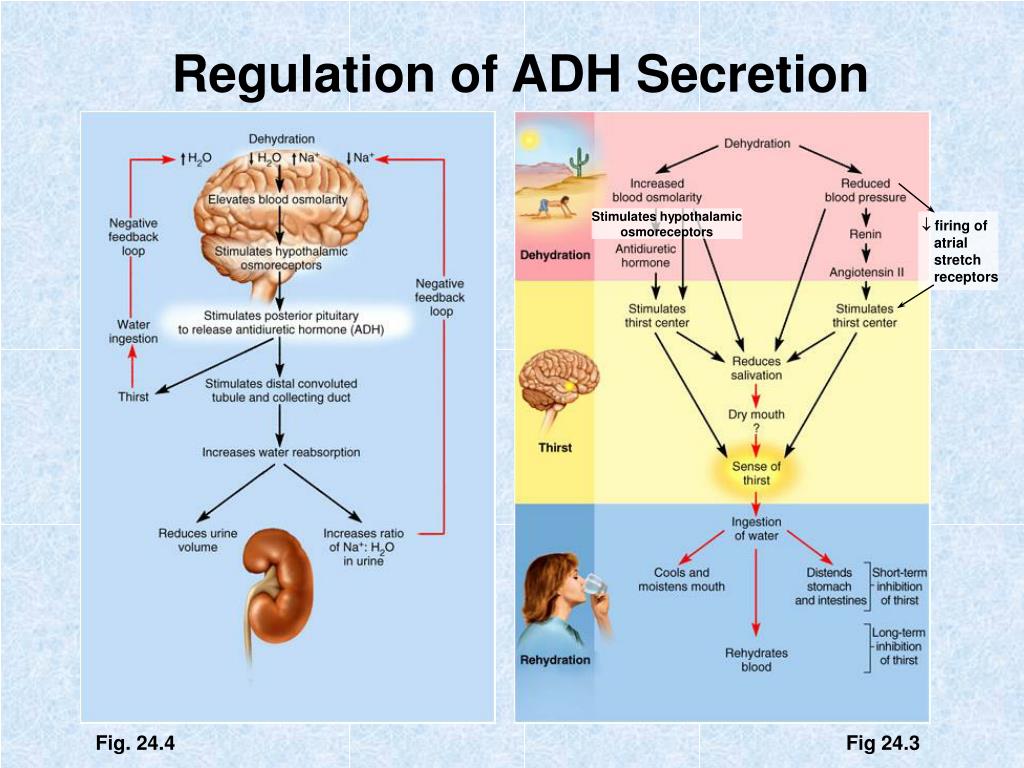
Amino acids from ingested food that are used for the synthesis of proteins and other biological substances — or produced from catabolism of muscle protein — are oxidized by the body as an alternative source of energy, yielding urea and carbon dioxide . The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a transaminase; the amino group is then fed into the urea cycle. The first step in the conversion of amino acids from protein into metabolic waste in the liver is removal of the alpha-amino nitrogen, which results in ammonia. Because ammonia is toxic, it is excreted immediately by fish, converted into uric acid by birds, and converted into urea by mammals.
What happens when urae breaks down?
In some soils, the ammonium is oxidized by bacteria to give nitrate, which is also a plant nutrient. The loss of nitrogenous compounds to the atmosphere and runoff is both wasteful and environmentally damaging.
How does the liver use urea?
The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules (NH 3) with a carbon dioxide (CO 2) molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry .
What is urea made of?
Urea is now prepared commercially in vast amounts from liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide. Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes.
How to use urea in soil?
How to Use UreaWhen urea is placed on the surface of the soil, a chemical reaction takes place that changes the urea to ammonium bicarbonate. This may be done either by broadcasting the urea then plowing it into the soil immediately or by injecting the urea into the soil.
What is urea fertilizer?
UREA (46% N)Fertilizers provide three primary nutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Potassium (K). The main function of Urea fertilizer is to provide the plants with nitrogen to promote green leafy growth and make the plants look lush. Since urea fertilizer can provide only nitrogen and not phosphorus or potassium, it’s primarily used for bloom growth. Advantages of Urea FertilizerSuperior Nitrogen contentLow production cost, as source is naturalNon-flammable and risk-free storageWide application range, for all types of crops and soilsNeutral pH and harmless to crops and soilHow to Use Urea Fertilizer? However, Urea must not be mixed with any superphosphate unless applied immediately after blending as Urea reacts with superphosphate liberating water molecules. .
What are the different types of coated urea fertilizers?
The types of coated urea fertilizers were as follows: linear release types CU70, CU100 and CU140, and sigmoid release types CUS80, CUS100 and CUS120. In addition, in Enrei the seed yield increased significantly in each coated urea treatment and the largest increase was induced by CUS120 (498 g m−2) compared with the control (363 g m−2). .
Is urea harmful to the respiratory tract?
Miscellaneous uses Adverse effects Urea can be irritating to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. In water, the amine groups undergo slow displacement by water molecules, producing ammonia, ammonium ion, and bicarbonate ion.
Is urea nitrogen a protein?
Urea is now prepared commercially in vast amounts from liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide. Although urea nitrogen is in nonprotein form, it can be utilized by ruminant animals (cattle, sheep), and a significant part of these animals’ protein requirements can be met in this way.
What are the properties of urea?
Other properties of urea include: Solid. Odorless. Usually white or colorless. Crystalline. Dissolves easily in water. Organic compound (meaning it contains carbon)
What Is Urea?
What is this substance? Urea! Urea, which is sometimes referred to as carbamide, is a solid compound that contains nitrogen.
How many amide groups are in urea?
The amide group in urea contains nitrogen attached to two hydrogen atoms. So, you put two amide groups with a carbonyl group and you have urea! To figure out the formula, you need to count up how many of each atom urea contains: 1 carbon. 4 hydrogen. 2 nitrogen. 1 oxygen.
Why is urea called carbamide?
Structure and Formula of Urea. Urea is also known as carbamide because of the groups it contains. Groups? Yes. In chemistry, certain elements bond together and are referred to as groups. In urea, there is a carbonyl group attached to two amide groups. Now you can see how it gets the name carbamide (carboxyl + amide).
Why is urea used in diesel engines?
But, there's more! Urea can be used in diesel engines to reduce nitrous oxide emissions (nitrous oxide is a pollutant). In fact, when urea is injected into the vehicle, the release of nitrous oxide is reduced by 80%.
What is urea in spandex?
Urea can be a component in polyurethane, a substance used in a variety of products from paints to foam to spandex pants. The spandex you may be wearing is made of a special polyurethane that contains urea, which helps with its unique properties (a fabric that stretches!).
How does urea work?
Our bodies use urea to get rid of the products of proteins that have been broken down. When the body breaks down proteins, they are turned in to carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. Ammonia is toxic and would destroy your cells, so your body must convert it into something less toxic. Through the beauty of chemistry, your liver turns the ammonia into urea, which can then be safely transported to your kidneys and removed through the urine.
What are the properties of urea?
Properties of Urea. Urea consists of Nitrogen, Carbon, and Oxygen. As mentioned, you can find it in the milk, blood, and sweat of mammals. When in concentrated form, it is turned into urine. Urea is basically a crystalline compound whose nitrogen content is around 46%, in the dry state.
How is urea formed?
An amide group is where a nitrogen atom is attached to two different hydrogen atoms. When you put two such amide groups bonded with the carbonyl group , urea is formed.
Why is Urea produced in large quantities?
Why is there such a significant amount of urea produced? The reason is that, aside from ammonia, urea is the industrial chemical with the highest nitrogen content and is in high demand as a fertilizer. It decomposes into ammonia (really ammonium ions) and carbon dioxide in the soil. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert ammonium to nitrate, which is easily absorbed by plant roots. Aside from its high nitrogen concentration, urea is particularly beneficial because it can be applied as a solid in the form of pellets and because of its very high water solubility, which allows it to be mixed with other plant nutrients in solutions.
How is a urea breath test used?
It is used to detect the bacteria in the stomach through the urea breath test.
What is urea nitrate used for?
It is used in manufacturing high explosive materials like urea nitrate (CH5N3O4) It is used as an important reagent in lanthanide chemistry. It is used in creams/ointments that are used for rehydration. It is used in hair removal creams and dish soaps. It is used as a browning agent for pretzels.
How much urea is used in fertilizer?
About 1 million pounds of urea is processed in the United States every year. Most of it is used in the fertilizers to make their nitrogen content, water-soluble. Urea is also used in plastics and glues, animal feedstock, expensive commercial products, and explosive components.
What temperature does urea melt?
It is a colorless substance existing in the crystalline form, which melts at 132.7°C (271° F) and which decomposes even before the Urea boiling point. Urea is also the chief end product of the metabolic protein breakdown in all the mammals and few fishes.
How is urea made?
In the industry, urea is produced from carbon dioxide and ammonia. Usually, a large amount of carbon dioxide is produced during the process of producing ammonia from coal, natural gas, or oil. This causes direct urea from the combination of these materials. The basis for the production of urea was made in 1922 under the name of the Urea Process by Bosch-Meiser. There are various processes for the production of urea in different conditions, all of which have more production losses than the process.
What are the two reactions that produce urea?
This process involves two major equilibrium reactions: _ No reaction of dry ammonia liquid with dry ice. _The second reaction is the conversion of ammonia carbamide to urea in water.
What are the different types of nitrogen fertilizers?
The main common types of nitrogen fertilizers are urea fertilizer, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate. Nitrogen can be found in many different forms and from a number of sources as listed in Table. Among these sources urea tends to be the dominant nitrogen fertilizer used in agriculture. Forms of nitrogen.
What is the ratio of urea fertilizer?
About Urea Fertilizer. Urea is nitrogen fertilizer with an NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) ratio of 46-0-0. The chemical formula of the urea is close in composition to the organic formulation of the urea, which also provides a number of advantages in the mass use for feeding crops. Although urea is naturally produced in humans and animals, ...
What is the most important nutrient for plants?
Nitrogen (Nitrogen) is one of the most important nutrient requirements for plants and common types of chemical fertilizers .Farmers use N fertilizers to accelerate the growth and increase the yield of their agricultural products. The main common types of nitrogen fertilizers are urea fertilizer, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate.
What happens when you put urea on your skin?
Urea causes skin and eye irritation and has respiratory complications. Continuous exposure to the skin causes swelling in the skin. Its high concentration in the blood causes damage to the organs of the body. Heat it above the melting point causes it to decompose and generates toxic vapors.
How to store urea?
Also, if you need to store it in bulk, it should be covered with a special cover and water insulator. It is also recommended that urea be stored, as well as many other solid fertilizers, in a cool and dry place, where the ventilation is well done.
What is urea used for?
The agricultural industry widely uses urea, a white crystalline solid containing 46 percent nitrogen as an animal feed additive and fertilizer. Here, we’ll focus on its role as a nitrogen fertilizer. In the past decade, urea has surpassed and nearly replaced ammonium nitrate as a fertilizer.
What happens to urea after it is applied to soil?
After application to the soil, urea undergoes chemical changes and ammonium (NH4 +) ions form. Soil moisture determines how rapidly this conversion takes place. When an urea particle dissolves, the area around it becomes a zone of high pH and ammonia concentration. This zone can be quite toxic for a few hours.
How to use urea efficiently?
The key to most efficiently using urea is to incorporate it into the soil during a tillage operation.
How does urea breakdown occur?
Losing urea to air. Urea breakdown begins as soon as it’s applied to the soil. If the soil is totally dry, no reaction happens. But with the enzyme urease, plus any small amount of soil moisture, urea normally hydrolyzes and converts to ammonium and carbon dioxide.
Can you use urea fertilizer on corn?
If applying urea-based fertilizer in a band, separate it from the seed by at least 2 inches of soil. Under no circumstances should urea or urea-based fertilizer be seed-placed with corn.
Can fertilizer urea be granulated?
You can purchase fertilizer urea as prills or as a granulated material. In the past, it was usually produced by dropping liquid urea from a prilling tower while drying the product. The prills formed a smaller and softer substance than other materials commonly used in fertilizer blends. Today, considerable urea is manufactured as granules.
Is urea a fertilizer?
In the past decade, urea has surpassed and nearly replaced ammonium nitrate as a fertilizer. This has brought up new questions about urea and how to use it.
What is the ratio of urea to nitrogen?
Urea is an inexpensive form of nitrogen fertilizer with an NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) ratio of 46-0-0. Although urea is naturally produced in humans and animals, synthetic urea is manufactured with anhydrous ammonia.
What happens when urea is mixed with soil?
When urea is placed on the surface of the soil, a chemical reaction takes place that changes the urea to ammonium bicarbonate. The ammonium will convert into a gas, which is then lost if not protected. This means that urea should be mixed in with the soil for maximum effectiveness.
What are the disadvantages of urea?
Disadvantages of Urea. As a result of the chemical reaction that takes place when urea is applied to the soil, special care must be taken to ensure that the nitrogen is not lost when the ammonium evaporates. This can make urea impractical for gardeners dealing with large plots of land.
Why is urea used in soil?
As a result of the chemical reaction that takes place when urea is applied to the soil, special care must be taken to ensure that the nitrogen is not lost when the ammonium evaporates. This can make urea impractical for gardeners dealing with large plots of land. The high solubility of urea also makes dry storage conditions imperative.
How to mix urea into soil?
This may be done either by broadcasting the urea then plowing it into the soil immediately or by injecting the urea into the soil. This may also be done by broadcasting urea then irrigating heavily to push dissolved urea into the soil.
What temperature does urea take?
This process happens under intense pressure, at 350 degrees Fahrenheit. Urea is processed to take the form of granules or solid globules known as prills. Dry urea is very soluble and must be kept away from moisture until its use.
Does urea help with nitrogen loss?
Although urea often offers gardeners the most nitrogen for the lowest price on the market, special steps must be taken when applying urea to the soil to prevent the loss of nitrogen through a chemical reaction .
Overview
Urea is used to treat dry/rough skin conditions (such as eczema, psoriasis, corns, callus) and some nail problems (such as ingrown nails). It may also be used to help remove dead tissue in some wounds to help wound healing.
May Treat: Hyperkeratosis
Brand Names: Kerafoam · Keralac · Kerol · Umecta · Hydro 35 and more
Drug Class: Dermatological - Emollient Mixtures · Dermatological - Emollients · Dermatological - Keratolytic-Antimitotic Single Agents · Diuretic - Osmotic
Availability: Prescription sometimes needed
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
Production
Uses
Adverse effects
Physiology
Urea is produced on an industrial scale: In 2012, worldwide production capacity was approximately 184 million tonnes.
For use in industry, urea is produced from synthetic ammonia and carbon dioxide. As large quantities of carbon dioxide are produced during the ammonia manufacturing process as a byproduct from hydrocarbons (predominantly natu…
Analysis
More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined for use as a nitrogen-release fertilizer. Urea has the highest nitrogen content of all solid nitrogenous fertilizers in common use. Therefore, it has a low transportation cost per unit of nitrogen nutrient. The most common impurity of synthetic urea is biuret, which impairs plant growth. Urea breaks down in the soil to give ammo…
Related compounds
Urea can be irritating to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Repeated or prolonged contact with urea in fertilizer form on the skin may cause dermatitis.
High concentrations in the blood can be damaging. Ingestion of low concentrations of urea, such as are found in typical human urine, are not dangerous with additional water ingestion within a reasonable time-frame. Many animals (e.g. dogs) have a much more concentrated urine and it c…
History
Amino acids from ingested food that are used for the synthesis of proteins and other biological substances — or produced from catabolism of muscle protein — are oxidized by the body as an alternative source of energy, yielding urea and carbon dioxide. The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a transaminase; the amino group is then fed into the urea cycle. The first step in the conversion of amino acids from protein into metabolic waste in the liver is re…