Demand is an economic concept that relates to a consumer's desire to purchase goods and services and willingness to pay a specific price for them. An increase in the price of a good or service tends to decrease the quantity demanded. Likewise, a decrease in the price of a good or service will increase the quantity demanded.
What does demand mean in economics?
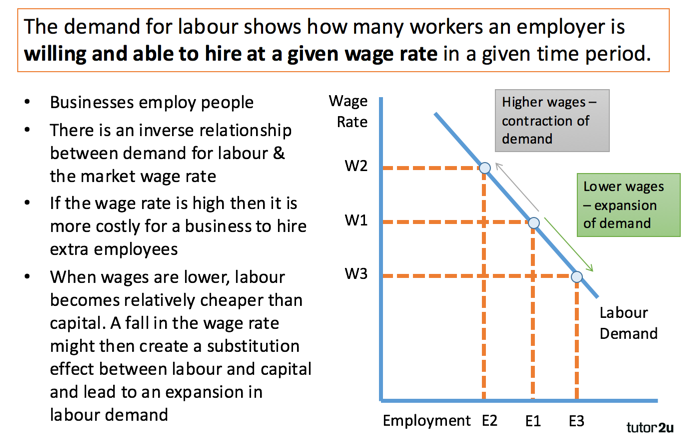
- Price and Demand are inversely related to each other
- When price of a product increases it’s demand falls
- When price of a product decreases it’s demand rise
What is the definition of demand in economics?
Demand is an economic principle referring to a consumer's desire to purchase goods and services and willingness to pay a price for a specific good or service. Holding all other factors constant, an increase in the price of a good or service will decrease the quantity demanded, and vice versa.
What are the determinants of demand in economics?
Top 10 Determinants of Demand for an Economy
- The Prices of Goods or Services. When the price of goods & services rises, the quantity demand falls & when the price of goods & services falls, the ...
- Price of Substitute/Complementary Goods & Services. Substitute goods are goods that satisfy the same needs. ...
- Buyers’ Tastes and Preferences. ...
- Buyers’ Expectations of the Goods’ Future Price. ...
What is an example of demand in economics?
Types of Demand in Economics
- Price Demand. Price demand is a demand for different quantities of a product or service that consumers intend to purchase at a given price and time period assuming other factors, ...
- Income Demand. ...
- Cross Demand. ...
- Individual demand and Market demand. ...
- Joint Demand. ...
- Composite Demand. ...
- Direct and Derived Demand. ...

What are the 3 concepts of demand?
An effective demand has three characteristics namely, desire, willingness, and ability of an individual to pay for a product.
What is the concept of demand and supply?
The law of supply and demand combines two fundamental economic principles describing how changes in the price of a resource, commodity, or product affect its supply and demand. As the price increases, supply rises while demand declines. Conversely, as the price drops supply constricts while demand grows.
How many concepts of demand are there?
Two main classifications of demand are elastic demand, a considerable change in the quantity demanded, and inelastic demand, a slight or no change in quantity demanded.
What is demand defined by?
Demand refers to the consumer's desire and willingness to buy a product or service at a given period or over time. Consumers must also have the ability to pay for something they want or need as determined by their disposable income budget. Therefore, demand is a force that affects economic growth and market expansion.
Who gave the concept of demand?
Alfred Marshall After Smith's 1776 publication, the field of economics developed rapidly, and the law of supply and demand was refined. In 1890, Alfred Marshall's Principles of Economics developed a supply-and-demand curve that is still used to demonstrate the point at which the market is in equilibrium.
What are the 4 types of demand?
The different types of demand are as follows:i. Individual and Market Demand: ... ii. Organization and Industry Demand: ... iii. Autonomous and Derived Demand: ... iv. Demand for Perishable and Durable Goods: ... v. Short-term and Long-term Demand:
What is the types of demand?
Individual demand and Market demand. Joint demand. Composite demand. Direct and Derived demand.
What is the importance of demand?
Demand is a representation of a consumer's desire to purchase goods and services; it acts as a measurement of a consumer's willingness to purchase a specific good or service at a given price.
What are the factors of demand?
The 5 Determinants of Demand The price of the good or service. The income of buyers. The prices of related goods or services—either complementary and purchased along with a particular item, or substitutes bought instead of a product. The tastes or preferences of consumers will drive demand.
What is demand and its example?
When there are more buyers available in a market, overall demand increases. For example, if more people can afford yachts, the market size and demand for yachts will increase. If there are fewer people able to afford yachts, the market and demand decrease.
What is meant by demand and examples?
Definition: Demand is an economic term that refers to the amount of products or services that consumers wish to purchase at any given price level. The mere desire of a consumer for a product is not demand. Demand includes the purchasing power of the consumer to acquire a given product at a given period.
What is demand give a simple example?
For example, if a consumer is hungry and buys a slice of pizza, the first slice will have the greatest benefit or utility. With each additional slice, the consumer becomes more satisfied, and utility declines. In theory, the first slice might fetch a higher price from the consumer.
What is the concept of supply?
Supply is a fundamental economic concept that describes the total amount of a specific good or service that is available to consumers. Supply can relate to the amount available at a specific price or the amount available across a range of prices if displayed on a graph.
What are the 4 basic laws of supply and demand?
1) If the supply increases and demand stays the same, the price will go down. 2) If the supply decreases and demand stays the same, the price will go up. 3) If the supply stays the same and demand increases, the price will go up. 4) If the supply stays the same and demand decreases, the price will go down.
What are the types of demand and supply?
Here are seven types of economic demand:Joint demand. The demand for products and services that are complementary is called joint demand. ... Composite demand. ... Short-run and long-run demand. ... Price demand. ... Income demand. ... Competitive demand. ... Demand from direct and derived sources.
What factors determine demand and supply?
Market prices are dependent upon the interaction of demand and supply. An equilibrium price is a balance of demand and supply factors. There is a tendency for prices to return to this equilibrium unless some characteristics of demand or supply change.
What is Demand?
Demand is an economic principle referring to a consumer's desire to purchase goods and services and willingness to pay a price for a specific good or service. Holding all other factors constant, an increase in the price of a good or service will decrease the quantity demanded, and vice versa. Market demand is the total quantity demanded across all consumers in a market for a given good. Aggregate demand is the total demand for all goods and services in an economy. Multiple stocking strategies are often required to handle demand.
What is demand in retail?
Demand refers to consumers' desire to purchase goods and services at given prices.
Why do equilibrium prices remain in flux?
Equilibrium prices typically remain in a state of flux for most goods and services because factors affecting supply and demand are always changing. Free, competitive markets tend to push prices toward market equilibrium.
How does demand affect supply?
If suppliers charge too much, the quantity demanded drops and suppliers do not sell enough product to earn sufficient profits. If suppliers charge too little, the quantity demanded increases but lower prices may not cover suppliers’ costs or allow for profits. Some factors affecting demand include the appeal of a good or service, the availability of competing goods, the availability of financing, and the perceived availability of a good or service.
How does the Fed reduce demand?
If the Fed wants to reduce demand, it will raise prices by curtailing the growth of the supply of money and credit and increasing interest rates. Conversely, the Fed can lower interest rates and increase the supply of money in the system, therefore increasing demand. 1 In this case, consumers and businesses have more money to spend. But in certain cases, even the Fed can’t fuel demand. When unemployment is on the rise, people may still not be able to afford to spend or take on cheaper debt, even with low interest rates.
What is demand curve?
A demand curve slopes downward, from left to right. As prices increase, consumers demand less of a good or service. A supply curve slopes upward. As prices increase, suppliers provide more of a good or service.
Why do businesses spend money?
Businesses often spend a considerable amount of money to determine the amount of demand the public has for their products and services. How much of their goods will they actually be able to sell at any given price? Incorrect estimations either result in money left on the table if demand is underestimated or losses if demand is overestimated. Demand is what helps fuel the economy, and without it, businesses would not produce anything.
What is Demand in Economics?
Demand in Economics is an economic principle can be defined as the quantity of a product that a consumer desires to purchase goods and services at a specific price and time.
What is the demand for anything at a given price?
According to Benham “ The demand for anything at a given price, is the amount of it which will be bought per unit of time at that price. ”
How does price demand relate to price?
Price demand is inversely proportional to the price of a commodity or service. As the price of a commodity or service rises, its demand falls and vice versa.
What factors influence the demand for a product?
Factors such as the price of the product, the standard of living of people and change in customers’ preferences influence the demand. The demand for a product in the market is governed by the Laws of Economics
How does credit policy affect demand?
Credit policy: The credit policy of suppliers or banks also affects the demand for a commodity. Size and composition of the population: An increase in the size of a population increases the demand for commodities as the number of consumers would increase.
What is demand in terms of a time period?
Demand is always referred in terms of a time period and bears no meaning if it is not expressed in relation to a time period. For example, a garment manufacturer has a demand for 200 metres of cloth in a month or 2400 metres of cloth in a year. A statement referring to demand for a commodity or service must include the following three key factors: ...
Why is demand important?
Demand is considered the basis of the entire process of economic development, hence demand plays an important role in the economic, social and political fields. The importance of demand are: Importance in Consumption. Advantageous to producers.
What is demand in economics?
Demand can be defined as the quantity of a commodity (goods and services) that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price and at a particular place and time . Demand is quite different from wants, need or desire. ‘Effective Demand’ in economics must meet three conditions which are:
Why is demand related to price?
Demand must be related to price because to a great extent, price determines the quantity which consumers are willing to buy
What is competitive demand?
Competitive (Substitute) Demand: This is the demand that occurs when two goods are close substitutes and serves the same purpose. In this case, when there is an increase in the price of one commodity that has a close substitute to another, its demand will fall as consumers will shift to the other close substitute goods with lower price and the demand for the close substitute goods will increase, eg fish and meat, tea and coffee, butter and margarine, pen and biro.
What is derived demand?
Derived Demand: This is the demand that occurs when the demand for a commodity is not for its immediate consumption but for the demand for another commodity. For example, there is a demand (derived) for flour to satisfy the demand for bread and cake.
What is demand curve?
The demand curve is the graphical representation of the information contained in the demand schedule. The price is plotted on the vertical axis and the quantity demanded is plotted on the horizontal axis. The normal demand curve slopes downwards from left to right. From Mr Tunde’s demand schedule, a demand curve is drawn as follows.
What influences the demand for particular commodities?
Weather: The weather condition prevailing at a particular time influences the demand for particular commodities e.g. umbrella has a high demand during the rainy season.
What is abnormal demand?
Exceptional or Abnormal Demand – is a demand pattern that does not abide by the law of demand, and therefore gives rise to the reverse of the basic law of demand which states that the higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded of a commodity, and vice-versa. In a case of abnormal demand, a higher price may mean a higher demand or no change in demand, while a lower price may mean a lower demand or no change in demand. Conditions for these exceptional cases are:
What is demand in economics?
The economy relies on the willingness of consumers to make purchases and the ability of companies to supply them. When consumers make more purchases, inflation and interest rates decrease. When consumers decrease their purchases or if producers are unable to supply, ...
What is the definition of demand in economics?
Economic demand is the number of consumers willing to purchase goods or services at a certain price. Supply is the other side of demand. Businesses that accurately meet demand with their supply of products or services greatly benefit in profits and heightened brand awareness.
What is equilibrium price?
When the supply is low and the demand is high, the price will increase. When supply is high and the demand is low, the price will decrease. The equilibrium price is the price where the quantity consumers purchase equals the quantity producers supply.
How is the price of goods and services determined?
The price of goods and services is determined by the supply in the market and the demand for it. When the supply is low and the demand is high, the price will increase. When supply is high and the demand is low, the price will decrease. The equilibrium price is the price where the quantity consumers purchase equals the quantity producers supply.
Why do consumers buy products?
Consumers will often buy a product or service because it is what they can afford but may deem lower quality. The demand for those lower-quality products will decrease as income increases.
What is composite demand?
Composite demand happens when there are multiple uses for a single product. For example, corn can be used as animal feed, ethanol and food in its whole form. The rise in demand for any of these products leads to a shortage in supply for the others. This shortage can lead to a rise in price.
What is joint demand?
Joint demand is the demand for complementary products and services. These can be products that are accessories for others or that people commonly purchase together. For example, cereal and milk or peanut butter and jelly. The two are linked but demand for one is not necessarily dependent on the demand for the other.
What Is Demand?
Demand refers to the consumer’s desire and willingness to buy a product or service at a given period or over time. Consumers must also have the ability to pay for something they want or need as determined by their disposable income budget. Therefore, demand is a force that affects economic growth and market expansion.
Understanding Demand
There are two factors involved in economic demand. First, it is based on the willingness of consumers to buy a commodity. It can be described as consumer preference and taste. Second, demand is also determined by the consumers’ ability to buy the product or service at a certain price.
Demand FAQs
MoneyGeek answers some frequently asked questions to help you better understand what demand is and how it impacts the economy.
Expert Insights
Understanding demand will give you an idea of how prices move. MoneyGeek interviewed an industry leader and an academic to provide expert insight about this concept.
What is demand derived from?
Demand is derived from the law of diminishing marginal utility, the fact that consumers use economic goods to satisfy their most urgent needs first.
What Is the Law of Demand?
The law of demand is one of the most fundamental concepts in economics. It works with the law of supply to explain how market economies allocate resources and determine the prices of goods and services that we observe in everyday transactions.
What Is a Simple Explanation of the Law of Demand?
The Law of Demand tells us that if more people want to buy something, given a limited supply, the price of that thing will be bid higher. Likewise, the higher the price of a good, the lower the quantity that will be purchased by consumers.
Why Is the Law of Demand Important?
Together with the Law of Supply, the Law of Demand helps us understand why things are priced at the level that they are, and to identify opportunities to buy what are perceived to be underpriced (or sell overpriced) products, assets, or securities. For instance, a firm may boost production in response to rising prices that have been spurred by a surge in demand.
What does it mean when the quantity demanded changes?
Changes in quantity demanded just mean movement along the demand curve itself because of a change in price . These two ideas are often conflated, but this is a common error; rising (or falling) prices do not decrease (or increase) demand, they change the quantity demanded.
How to describe a demand curve?
By adding up all the units of a good that consumers are willing to buy at any given price we can describe a market demand curve, which is always downward-sloping, like the one shown in the chart below. Each point on the curve (A, B, C) reflects the quantity demanded (Q) at a given price (P). At point A, for example, the quantity demanded is low (Q1) and the price is high (P1). At higher prices, consumers demand less of the good, and at lower prices, they demand more.
Why do rising incomes increase demand for normal economic goods?
Rising incomes tend to increase demand for normal economic goods, as people are willing to spend more. The availability of close substitute products that compete with a given economic good will tend to reduce demand for that good, since they can satisfy the same kinds of consumer wants and needs.
What does demand mean in a market?
As per Prof Hibdon, “Demand means the various quantities of goods that would be purchased per time period at different prices in a given market.”
What is demand and supply in economics?
Demand and Supply & Concept of Demand. Economics is a study of market that comprises a group of buyers and sellers of a particular product or service. The working of the market system is governed by two forces, demand and supply. These two forces play a crucial role in determining the price of a product and size of the market.
What is equilibrium price?
Equilibrium price refers to the price where the quantity demanded of a product by buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by sellers. In other words, equilibrium price is a price when there is a balance between market demand and supply.
What is demand in advertising?
ADVERTISEMENTS: Demand refers to the willingness or ability of a buyer to pay for a particular product. In other words demand can be defined as the quantity of a product that a buyer desires to purchase at a specific price and time period The’ demand for a product is influenced by a number of factors, such as price of the product, ...
What is the law of demand?
The demand for a product in the market is governed by the law of demand, which states that the demand for a product decreases with increase in its prices and vice versa, while other factors are constant. In the market system, buyers constitute the demand for a product, while sellers represent the supply side of the product in the market.
What is the difference between supply and demand?
In the market system, buyers constitute the demand for a product, while sellers represent the supply side of the product in the market. Supply refers to the quantity of a product that a seller agrees to sell in the market at a particular price within a specific point of time. There are various determinants of supply, including price of a product, ...
What are the three key factors that determine the demand for a product?
The demand for a product is always defined in reference to three key factors, price, point of time, and market place . These three factors contribute a major part in understanding the concept of demand. The omission of any of these factors would make the concept of demand meaningless and vague. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the law of demand?
Demand. The law of demand states that, if all other factors remain equal, the higher the price of a good, the less people will demand that good. In other words, the higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded. The amount of a good that buyers purchase at a higher price is less because as the price of a good goes up, ...
What is the relationship between price and demand?
The theory defines the relationship between the price of a given good or product and the willingness of people to either buy or sell it. Generally, as price increases, people are willing to supply more and demand less and vice versa when the price falls. The theory is based on two separate "laws," the law of demand and the law of supply.
What Is the Law of Supply and Demand?
The law of supply and demand is a theory that explains the interaction between the sellers of a resource and the buyers for that resource. The theory defines the relationship between the price of a given good or product and the willingness of people to either buy or sell it. Generally, as price increases, people are willing to supply more and demand less and vice versa when the price falls.
Why Is the Law of Supply and Demand Important?
The Law of Supply and Demand is essential because it helps investors, entrepreneurs, and economists understand and predict market conditions. For example, a company launching a new product might deliberately try to raise the price of its product by increasing consumer demand through advertising.
How does the supply curve change over time?
Over longer intervals of time, however, suppliers can increase or decrease the quantity they supply to the market based on the price they expect to charge . So over time, the supply curve slopes upward; the more suppliers expect to charge , the more they will be willing to produce and bring to market.
Why is time important in supply and demand?
It is important for both supply and demand to understand that time is always a dimension on these charts. The quantity demanded or supplied, found along the horizontal axis, is always measured in units of the good over a given time interval. Longer or shorter time intervals can influence the shapes of both the supply and demand curves.
How does willingness affect supply and demand?
In practice, people's willingness to supply and demand a good determines the market equilibrium price, or the price where the quantity of the good that people are willing to supply just equals the quantity that people demand. However, multiple factors can affect both supply and demand, causing them to increase or decrease in various ways.

What Is Demand?
Understanding Demand
- Businesses can spend a considerable amount of money to determine the amount of demand the public has for their products and services. How many of their goods will they actually be able to sell at any given price? Incorrect estimations can result in lost sales from willing buyers if demand is underestimated or losses from leftover inventory if demand is overestimated. Demand helps fu…
Determinants of Demand
- There are five main factors that drive demand: 1. Product/service price 2. Buyer's income 3. Prices of substitute goods 4. Consumer preferences 5. Consumer expectations for a change in price As these factors change, so can the demand for a product or service. In fact, they change all the time, so demand can be constantly in flux.
The Law of Demand
- The law of demand states that when prices rise, demand will fall. When prices fall, demand will rise. The law of demand is simply an expression of the inverse relationship between price and demand. It involves price only. None of the other drivers of demand mentioned above are involved. If they do come into play, the functioning of the law can be affected. Demand can be s…
Demand Curve
- A demand curveis a graph that displays the change in demand resulting from a change in price. It's a visual representation of the law of demand. The demand curve can be a useful tool for businesses because it can show them the prices at which consumers start buying less or more. It can point out prices at which a company can maintain consumer demand and support reasonabl…
Market Equilibrium
- The point where supply and demand curves intersect represents the market clearing or market equilibrium price. An increase in demand shifts the demand curve to the right. The two curves then intersect at a higher price, which means consumers are willing to pay more for the product. Equilibriumprices typically change for most goods and services because factors affecting supply …
Market Demand vs. Aggregate Demand
- The market for each good in an economy faces a different set of circumstances, which vary in type and degree. In macroeconomics, we also look at aggregate demand in an economy. Aggregate demandrefers to the total demand by all consumers for all goods and services in an economy across all the markets for individual goods. Since aggregate demand includes all good…
Macroeconomic Policy and Demand
- Fiscal and monetary authorities, such as the Federal Reserve, devote much of their macroeconomic policy-making to managing aggregate demand. If the Fed wants to reduce demand, it can raise interest rates and increase prices by curtailing the growth of the money supply and credit. If it needs to increase demand, the Fed can lower interest rates and increase t…
What Is The Definition of Demand in Economics?
The Relationship Between Supply and Demand
- If demand is the quantity consumers are willing to buy at a given price, supply is the quantity producers are willing to offer. The price of goods and services is determined by the supply in the market and the demand for them. When the supply is low and the demand is high, the price will increase. When supply is high and the demand is low, the price will decrease. The equilibrium pr…
7 Types of Demand
- As a business, you need to understand the different types of demand to be able to best anticipate how much product you need. Demand characteristics provide a picture of how well the industry is thriving and offers ideas as to where new service can be introduced. The following list details seven types of demand in economics:
Factors That Influence Demand
- Demand is influenced by the activities of consumers and businesses. Businesses attempt to drive demand through marketing efforts. Consumers drive demand through their tastes, income levels and resistance to price increases. Here are the most common determinants of demand: