
What are three facts about Plato?
What are three facts about Plato?
- Details of his early life are hearsay.
- He did time as a soldier of Greece.
- Plato wrote dialogues.
- Plato had a school.
- He had an interesting view on death.
- His family member almost had Socrates killed.
- He tutored royalty.
- His father was a descendant of Kings.
Who is Plato and what did he do?
The Athenian philosopher Plato (c.428-347 B.C.) is one of the most important figures of the Ancient Greek world and the entire history of Western thought. In his written dialogues he conveyed and expanded on the ideas and techniques of his teacher Socrates.
What are the four levels of knowledge for Plato?
- The Allegory of the Cave
- The Divided Line
- The Theory of Justice
- Plato's Theory of Philosophy as Dialectical Inquiry and Argumentation
What are the teachings of Plato?
Plato’s Ethics: An Overview. First published Tue Sep 16, 2003; substantive revision Wed Dec 6, 2017. Like most other ancient philosophers, Plato maintains a virtue-based eudaemonistic conception of ethics. That is to say, happiness or well-being ( eudaimonia) is the highest aim of moral thought and conduct, and the virtues ( aretê ...
See more
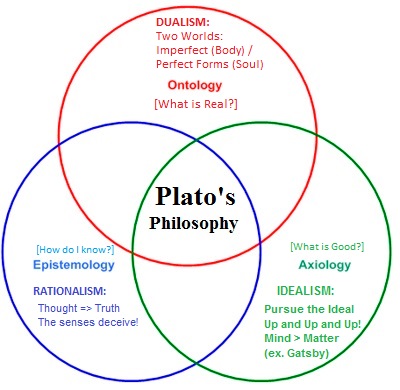
What did Plato do?
Plato was a philosopher during the 5th century BCE. He was a student of Socrates and later taught Aristotle. He founded the Academy, an academic pr...
What is Plato known for?
Plato’s most famous work is the Republic, which details a wise society run by a philosopher. He is also famous for his dialogues (early, middle, an...
What were Plato’s contributions to society?
Plato is one of history's most influential philosophers. His contributions range across numerous philosophical subfields, including (but not limite...
When was Plato alive?
Plato was born in 428/427 BCE to a noble family and died in 348/347 BCE. He lived primarily in Athens, Greece. Plato’s birth occurred near the end...
What was Plato’s family like?
Plato did not have children, and it is assumed based on textual evidence that he never married. He did have a number of siblings, however: three br...
Introduction
Plato is broadly viewed evenly one of the superlative and most operant philosophers in the western custom. His political school of thought is held in too difficult value, and is the originally comp political thought we believe.
Objectivity of values
Plato argued strongly in sustain of the objectiveness of values such equally nicety, excellent, and looker. honest values country those that live exterior of the mortal and are non composmentis subordinate abreast her/his insight or concept. … His hold accuracy contains his about noted averment; ‘humanity area the dispose of whole matters.’
Conclusion
Plato’s performance as a political philosopher may be seen in that he believed that there could be a organicstructure of cognition whose proficiency would make it proper to heal political problems, such as factionalism and the disgust of morality, which can confer a city to a extenuation.
Cite this Page
Philosophical Ideas And Concepts Of Plato. (2021, September 14). Edubirdie. Retrieved February 21, 2022, from https://edubirdie.com/examples/philosophical-ideas-and-concepts-of-plato/
Who was Plato in the Greek language?
Plato ( / ˈpleɪtoʊ / PLAY-toe; Greek: Πλάτων Plátōn, pronounced [plá.tɔːn] in Classical Attic; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was an Athenian philosopher during the Classical period in Ancient Greece, founder of the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world .
When was Plato born?
Thus, Nails dates Plato's birth to 424/423. According to Neanthes, Plato was six years younger than Isocrates, and therefore was born the same year the prominent Athenian statesman Pericles died (429 BC). Jonathan Barnes regards 428 BC as the year of Plato's birth.
Why did Socrates use geometrical examples?
In the Meno, Socrates uses a geometrical example to expound Plato's view that knowledge in this latter sense is acquired by recollection. Socrates elicits a fact concerning a geometrical construction from a slave boy, who could not have otherwise known the fact (due to the slave boy's lack of education).
What is Plato's nickname?
Although Platon was a fairly common name (31 instances are known from Athens alone), the name does not occur in Plato's known family line. The sources of Diogenes Laërtius account for this by claiming that his wrestling coach, Ariston of Argos, dubbed him "broad" on account of his chest and shoulders, or that Plato derived his name from the breadth of his eloquence, or his wide forehead. While recalling a moral lesson about frugal living Seneca mentions the meaning of Plato's name: "His very name was given him because of his broad chest."
Why is Plato's philosophy at odds with rhetoric?
Scholars often view Plato's philosophy as at odds with rhetoric due to his criticisms of rhetoric in the Gorgias and his ambivalence toward rhetoric expressed in the Phaedrus. But other contemporary researchers contest the idea that Plato despised rhetoric and instead view his dialogues as a dramatization of complex rhetorical principles.
How many letters did Plato write?
Thirty-five dialogues and thirteen letters (the Epistles) have traditionally been ascribed to Plato, though modern scholarship doubts the authenticity of at least some of these. Plato's writings have been published in several fashions; this has led to several conventions regarding the naming and referencing of Plato's texts.
What is Plato's family?
Due to a lack of surviving accounts, little is known about Plato's early life and education. Plato belonged to an aristocratic and influential family . According to a disputed tradition, reported by doxographer Diogenes Laërtius, Plato's father Ariston traced his descent from the king of Athens, Codrus, and the king of Messenia, Melanthus. According to the ancient Hellenic tradition, Codrus was said to have been descended from the mythological deity Poseidon.
What is Plato's philosophy?
Instead, the student of Plato's philosophy is encouraged to approach a topic in many different ways and repeatedly question the result . He would often revisit his own central ideas and provide more ways to examine and rethink the given topic. Let's look at some of the major ideas put forth by his dialogues.
What was Plato's life like?
Plato's Life and Accomplishments. Plato was a philosopher who was born in Greece somewhere around 428 BCE to a family of the political and social elite. Since Plato was somewhat associated with this group, he had the opportunity to study many different subjects from many different teachers until he famously became a disciple of Socrates.
What style of writing did Plato use?
Plato wrote predominantly in the style of dialogues. The characters in his writings debate a particular subject and examine it from multiple perspectives. Scholars typically organize Plato's works into three different eras: early, middle, and late.
What did Plato believe about the Academy?
Plato believed that this system would lead to social progress and a more stable government.
What are Plato's two parts?
Plato believed that reality is divided into two parts: the ideal and the phenomena. The ideal is the perfect reality of existence.
What were Plato's most famous works?
Plato's most famous works were written during this time, including the Republic, the Symposium, and Phaedo.
Which of Plato's earlier works tends to focus on lessons directly inherited from his teacher?
Plato's earlier works tend to focus on lessons directly inherited from his teacher. In fact, Socrates is usually the main character and the subjects usually center on Socrates' lessons. The most famous of the Socratic Dialogues is the Apology in which the character of Socrates defends his beliefs against the charges of the Athenian court.
What is Plato's philosophy?
Plato’s thought: A philosophy of reason. Plato was a Greek philosopher known and recognized for having allowed such a considerable philosophical work. The sensible world, according to Plato is the world of contingent, contrary to the intelligible world, which contains essences or ideas, intelligible forms, models of all things, ...
What dimension does Plato have in his work with dialogue?
In drafting his work with dialogue so, Plato has thus demonstrated an important dimension inherent in the search for truth: it takes two (or more) and this mediation is only able to move us beyond the particular views to us access to the universal.
What is the dialectic of ideas and theory of love?
The dialectic of ideas and theory of love leads to talk of a Platonic idealism (in the strong sense of the word idealism) as the doctrine of Ideas or Essences attributing an existence in itself, independence of mind and of individual things (NB: the word “idealism” is not Plato himself).
What is Plato's route to the Essences?
Plato, Love and Beauty: The route to the Essences can be understood as the dialectic of love, as Plato so aptly described in the Symposium.
What is Plato's answer to the problem and the formation of speculative dialectics based on?
Thus, the answer to the problem and the formation of speculative dialectics based on reminiscence also allows Plato to resolve the moral and political problem.
What is the first stage of rational knowledge?
The first stage of rational knowledge is the data entry math, but this is so, even beyond these mathematical truths, the culmination of the dialectic: the Ideas or essences and the Good.
What is virtue in science?
Virtue in this context refers to participation in Essences and true knowledge, a science of good and evil inseparable from the dialectic.
What did Plato think about the monarchy?
Nevertheless, Plato thought that the supreme power had to belong to only one ruler. Thus, he thought that monarchy could be the basis ...
What did Plato believe about social groups?
As for Plato, it is known that he was born in one of the richest and the most educated families of that time. Being a part of a group that had access to knowledge and power, he believed that the state needed to have some people who were cleverer than the others as it was one of the factors allowing the society to survive (Jackson 15). Reflecting on the ideal state, Plato singled out three functions of a state that he supposed to be the most important. They included control, production of material values, and protection. Taking into consideration these functions, he believed that it was necessary to have three social groups such as guardians, farmers, and rulers who had to be philosophers at the same time. Despite the differences between these social groups and various tasks that they were supposed to fulfill, Plato believed that such a structure would help the society to develop. To him, justice was impossible without allowing different types of people to devote their lives to the things that they liked the most.
What did Plato think about the division of power?
Moreover, Plato had a lot of ideas concerning the division of power in his ideal state. Although he believed that democracy could not help to create prosperity, it did not mean that his notion of justice was connected to the unlimited power of the rulers who were supposed to be driven by higher purposes, unlike other social classes. There is no doubt that Plato regarded the existence of social classes as a necessary division based on people’s primary values. Unlike guardians and farmers, rulers were supposed to possess the knowledge related to the meaning of life and the power of reason. The philosopher considered rulers to be not only the cleverest individuals but also the people who could promote moral values (Russell 14). Due to the power that they possessed, they had to be impeccable.
What did Plato pay attention to?
Speaking about the key values that such type of state could be based on, Plato paid special attention to the power of truth and the common good. Moreover, it is necessary to consider the great role ...
What did Plato think of social classes?
There is no doubt that Plato regarded the existence of social classes as a necessary division based on people’s primary values. Unlike guardians and farmers, rulers were supposed to possess the knowledge related to the meaning of life and the power of reason.
What did Plato believe about justice?
Despite the differences between these social groups and various tasks that they were supposed to fulfill, Plato believed that such a structure would help the society to develop. To him, justice was impossible without allowing different types of people to devote their lives to the things that they liked the most.
Why did Plato believe it was important to educate future monarchs?
Moreover, Plato believed that it was urgent to educate future monarchs to secure the future of the state; in his opinion, being a child of the ruling monarch was not enough for the person to accede to the throne.
What is Plato's theory of forms?
In basic terms, Plato's Theory of Forms asserts that the physical world is not really the 'real' world; instead, ultimate reality exists beyond our physical world. Plato discusses this theory in a few different dialogues, including the most famous one, called 'The Republic.'. It is also likely that Plato inherited some of this theory ...
Who was Plato's mentor?
It is also likely that Plato inherited some of this theory from his mentor, Socrates. Plato's philosophy asserts that there are two realms: the physical realm and the spiritual realm. The physical realm is the material stuff we see and interact with on a daily basis; this physical realm is changing and imperfect, as we know all too well.
Which philosopher proposed the idea that the spiritual realm is perfect and more real than the physical realm?
Greek philosopher Plato 's Theory of Forms explores the idea that the spiritual realm is perfect and more real than the physical realm. Discover more about the significance of the Theory of Forms, and see examples and comparisons of the Realm of Forms and the physical realm. Updated: 09/21/2021
Who is the father of Western philosophy?
The ideas of Plato have such significance that many contemporary scholars still credit Plato as the father of Western philosophy. Write an essay discussing why the theory of forms is still relevant today. Hint: consider current political and cultural views in your response.
Did Plato associate the forms with religion?
Plato did not associate the Forms with any particular deity or religion, but his theory did offer many thinkers a profound, rational defense of this belief. Learning Outcomes. Once you are finished, you should be able to: Summarize the point of Plato's Theory of Forms and discuss its significance to society.
Who is the founder of the theory of forms?
Definition of The Theory of Forms. The ancient Greek philosopher Plato (420s-340s BCE) did a lot to change the way we think about the world, in everything from mathematics to ethics to logic. But perhaps one of his most influential contributions to philosophy was the Theory of Forms. In basic terms, Plato 's Theory of Forms asserts ...
Did Plato deny the existence of the physical realm?
Plato did not deny the existence of the physical realm, but his Theory of Forms did insist that the Realm of Forms is 'more real' than what we see. The Forms themselves are unchanging and perfect; whatever happens in our chaotic, changing physical world, the Forms themselves will never change.
What is Plato's philosophy?
Plato’s style of reasoning and conversation is certainly Socratic, and in this manner he was able to deduce and develop his best known philosophical contributions. These include the theory of Forms, Platonic realism, ethics, philosophy of religion, and many more.
What are Plato's philosophical doctrines?
Plato’s philosophical doctrines rest upon a few distinct doctrines, one of the biggest being the concept of Forms. Knowledge is based on real things about which we come up with true propositions in the process of acquiring knowledge. These ideas or objects are universal in that they can be applied to a wide range of real objects to describe or characterize them.
What is Plato Theory of Knowledge?
Plato believed that truth is objective and that it results from beliefs which have been rightly justified by and anchored in reason. Thus, knowledge is justified and true belief. We can draw several conclusions from this statement:
Why is Plato's theory of knowledge so challenging?
Plato’s theory of knowledge is a massive challenge to most students because it involves a lot of introspection. Not many modern students have the time to sit around brooding and meditating, given how fast-paced the academic life is today. We’re here to help with your Plato’s theory of knowledge essay assignment.
Who was Plato's teacher?
Estimated to have been born in 428 or 427 BCE, Plato was a remarkable student of Socrates and a teacher of Aristotle who went on to become the most influential philosopher of all time.
Who is in the dialogue with Plato?
The dialogue is held between Glaucon, Plato’s brother, and Socrates.
Was Plato influenced by Socrates?
As a student of Socrates, Plato was heavily influenced by the former’s instruction as well as the circumstances of his life and death. We know much about Socrates, who never wrote, through prolific students of his such as Plato.

Overview
Influences
Although Socrates influenced Plato directly as related in the dialogues, the influence of Pythagoras upon Plato, or in a broader sense, the Pythagoreans, such as Archytas also appears to have been significant. Aristotle claimed that the philosophy of Plato closely followed the teachings of the Pythagoreans, and Cicero repeats this claim: "They say Plato learned all things Pythagorean." It is …
Biography
Little is known about Plato's early life and education. He belonged to an aristocratic and influential family. According to a disputed tradition, reported by doxographer Diogenes Laërtius, Plato's father Ariston traced his descent from the king of Athens, Codrus, and the king of Messenia, Melanthus. According to the ancient Hellenic tradition, Codrus was said to have been descended from the …
Philosophy
In Plato's dialogues, Socrates and his company of disputants had something to say on many subjects, including several aspects of metaphysics. These include religion and science, human nature, love, and sexuality. More than one dialogue contrasts perception and reality, nature and custom, and body and soul. Francis Cornford referred to the "twin pillars of Platonism" as being the theory of Form…
Themes of Plato's dialogues
The trial of Socrates and his death sentence is the central, unifying event of Plato's dialogues. It is relayed in the dialogues Apology, Crito, and Phaedo. Apology is Socrates' defence speech, and Crito and Phaedo take place in prison after the conviction.
Apology is among the most frequently read of Plato's works. In the Apology, S…
History of Plato's dialogues
Thirty-five dialogues and thirteen letters (the Epistles) have traditionally been ascribed to Plato, though modern scholarship doubts the authenticity of at least some of these. Plato's writings have been published in several fashions; this has led to several conventions regarding the naming and referencing of Plato's texts.
The usual system for making unique references to sections of the text by Plato derives from a 16…
Criticism
The most famous criticism of the Theory of Forms is the Third Man Argument by Aristotle in the Metaphysics. Plato had actually already considered this objection with the idea of "large" rather than "man" in the dialogue Parmenides, using the elderly Elean philosophers Parmenides and Zeno characters anachronistically to criticize the character of the younger Socrates who proposed the idea. The dialogue ends in aporia.
Legacy
Plato's Academy mosaic was created in the villa of T. Siminius Stephanus in Pompeii, around 100 BC to 100 CE. The School of Athens fresco by Raphael features Plato also as a central figure. The Nuremberg Chronicle depicts Plato and others as anachronistic schoolmen.
Plato's thought is often compared with that of his most famous student, Aristotle, …