
postmodernism, also spelled post-modernism, in Western philosophy
Western philosophy
Western philosophy is the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics such as Thales and Pythagoras, and eventually covering a large area of the globe. The word philosophy itself originated from the Ancient Greek philosophía, literally, "the love of wisdom".
What are the best things about postmodernism?
Postmodernism is related to the human sciences. History (as per Hegel’s owl) is vitally important in helping us understand ideas because ideas do not arise in a vacuum. Much of the framework for postmodernism was laid in the work of historian-philosopher Wilhelm Dilthey. Dilthey made a famous and important distinction between the natural ...
What is exactly is postmodernism?
Postmodernism was a sweeping movement that developed in the mid- to late 20th century, and touched on philosophy, the arts, architecture, and criticism, marking a full departure from modernism. Postmodernism is basically applied to the historical era which followed modernity.
What are some examples of postmodernism?
- Simulacra and Simulations, by Baudrillard, is a hugely important work in PM. ...
- Neo’s story is a revision of Jesus’ story (indicated with Zion, death and rebirth, ascension, and so on). ...
- Cypher’s discussion about being a happy brain in a jar is very PM, from the American rather than European perspective.
What are some characteristics of postmodernism?
postmodernism, also spelled post-modernism, in Western philosophy, a late 20th-century movement characterized by broad skepticism, subjectivism, or relativism; a general suspicion of reason; and an acute sensitivity to the role of ideology in asserting and maintaining political and economic power.

What is the main concept of postmodernism?
Definition. Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or mode of discourse which challenges worldviews associated with Enlightenment rationality dating back to the 17th century. Postmodernism is associated with relativism and a focus on ideology in the maintenance of economic and political power.
How do you identify postmodernism?
Some of the things that distinguish postmodern aesthetic work from modernist work are as follows: extreme self-reflexivity. ... irony and parody. ... a breakdown between high and low cultural forms. ... retro. ... a questioning of grand narratives. ... visuality and the simulacrum vs. ... late capitalism.More items...
What are the key features of postmodernism?
Its main characteristics include anti-authoritarianism, or refusal to recognize the authority of any single style or definition of what art should be; and the collapsing of the distinction between high culture and mass or popular culture, and between art and everyday life.
Who is the father of postmodernism?
French post-structuralist philosopher, best known for his highly influential formulation of postmodernism in The Postmodern Condition. Despite its popularity, however, this book is in fact one of his more minor works.
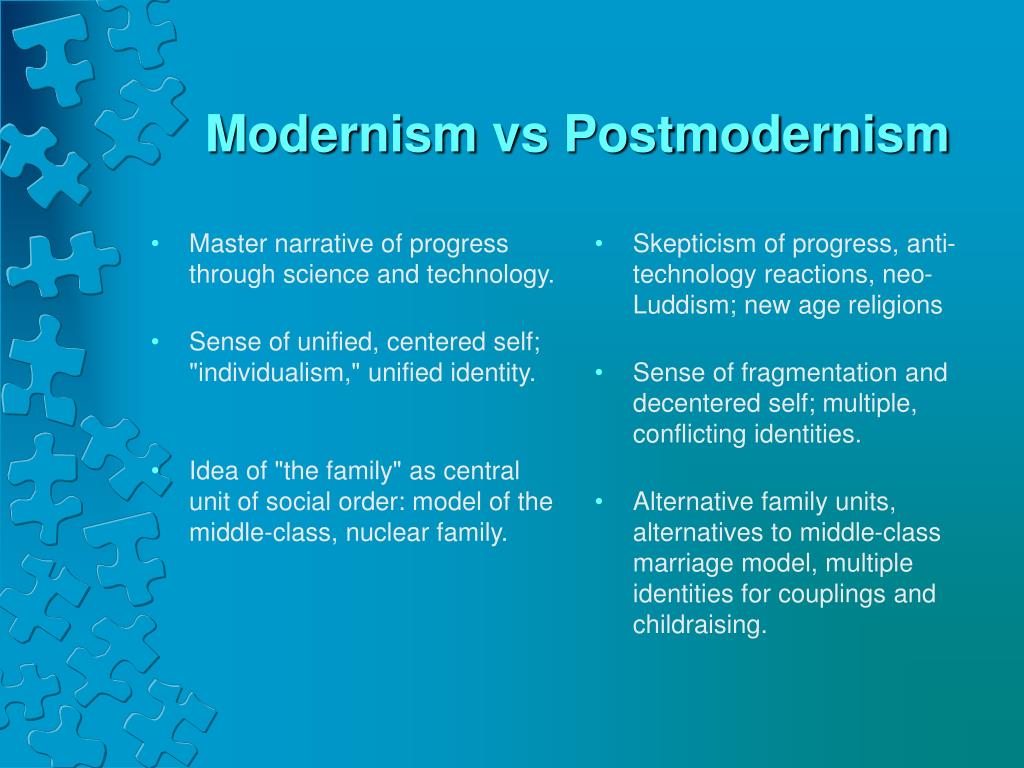
What's the difference between modernism and postmodernism?
The main difference between modernism and postmodernism is that modernism is characterized by the radical break from the traditional forms of prose and verse whereas postmodernism is characterized by the self-conscious use of earlier styles and conventions.
How does postmodernism affect society?
Postmodernism affects views and lifestyles, which in turn affects the young adult's performance of roles and his interactions within all his different social systems. A strong attachment to family and home, as well as the importance of roles as sons/daughters were found.
Which is an example of postmodern culture?
TWO EXAMPLES OF POSTMODERN POPULAR CULTURE I will consider here two prime examples: pop music and television.
What is the importance of postmodernism?
It collapsed the distinction between high culture and mass or popular culture, between art and everyday life. Because postmodernism broke the established rules about style, it introduced a new era of freedom and a sense that 'anything goes'.
What is postmodernism?
Postmodernism is a late 20th-century movement in philosophy and literary theory that generally questions the basic assumptions of Western philosoph...
What are some general characteristics of postmodernism?
Postmodern philosophy is characterized by broad skepticism or relativism and a general suspicion of reason. It also broadly asserts that Western in...
What do postmodernists believe?
Many postmodernists hold one or more of the following views: (1) there is no objective reality; (2) there is no scientific or historical truth (obj...
How is postmodernism related to relativism?
Although some postmodernists reject the relativist label, many postmodern doctrines constitute or imply some form of relativism. Many postmodernist...
Who are some famous postmodernists?
Some famous thinkers associated with postmodernism are Jean Baudrillard, Gilles Deleuze, Jacques Derrida, Michel Foucault, Pierre-Félix Guattari, F...
What is postmodernism?
Postmodernism is generally defined by an attitude of skepticism, irony, or rejection toward what it describes as the grand narratives and ideologies associated with modernism, often criticizing Enlightenment rationality and focusing on the role of ideology in maintaining political or economic power. Postmodern thinkers frequently describe knowledge ...
What is postmodernism in philosophy?
These developments—re-evaluation of the entire Western value system ( love, marriage, popular culture, shift from an industrial to a service economy) that took place since the 1950s and 1960s, with a peak in the Social Revolution of 1968 —are described with the term postmodernity, as opposed to postmodernism, a term referring to an opinion or movement. Post-structuralism is characterized by new ways of thinking through structuralism, contrary to the original form.
Why is postmodernism meaningless?
The linguist and philosopher Noam Chomsky has said that postmodernism is meaningless because it adds nothing to analytical or empirical knowledge. He asks why postmodernist intellectuals do not respond like people in other fields when asked, "what are the principles of their theories, on what evidence are they based, what do they explain that wasn't already obvious, etc.?...If [these requests] can't be met, then I'd suggest recourse to Hume 's advice in similar circumstances: 'to the flames'."
What are the characteristics of postmodernism?
The primary features of postmodernism typically include the ironic play with styles, citations and narrative levels, a metaphysical skepticism or nihilism towards a " grand narrative " of Western culture, and a preference for the virtual at the expense of the Real (or more accurately, a fundamental questioning of what 'the real' constitutes).
What is the role of critical theory in postmodernism?
Postmodernism and critical theory commonly criticize universalist ideas of objective reality, morality, truth, human nature, reason, language, and social progress.
What is postmodernism? What are its characteristics?
It questions or criticizes viewpoints associated with Enlightenment rationality dating back to the 17th century, and is characterized by irony, eclecticism, and its rejection of the "universal validity" of binary oppositions, stable identity, hierarchy, and categorization. Postmodernism is associated with relativism and a focus on ideology in the maintenance of economic and political power. Postmodernists are generally "skeptical of explanations which claim to be valid for all groups, cultures, traditions, or races," and describe truth as relative. It can be described as a reaction against attempts to explain reality in an objective manner by claiming that reality is a mental construct. Access to an unmediated reality or to objectively rational knowledge is rejected on the grounds that all interpretations are contingent on the perspective from which they are made; as such, claims to objective fact are dismissed as "naive realism ."
When did postmodernism start?
However, most scholars today agree postmodernism began to compete with modernism in the late 1950s and gained ascendancy over it in the 1960s.
WHAT COMES AFTER POSTMODERNISM?
Films like Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind and Inception both challenged universal truths related to memory and how we perceive the world around us.
Why are postmodern movies considered postmodern?
Postmodern movies aim to subvert highly-regarded expectations, which can be in the form of blending genres or messing with the narrative nature of a film. For example, Pulp Fiction is a Postmodern film for the way it tells the story out of the ordinary, upending our expectations of film structure. Naturally, Postmodern cinema is more complex ...
Why is postmodernism so difficult to pin down?
Postmodernism can be difficult to pin down, specifically because the philosophy aims to reject typically-held notions of criticism and definition. If you need a more concise Postmodernism definition, then just listen to Moe Szyslak.
What is the philosophy of modernism?
It’s typically characterized as artists being self-conscious about traditional forms of art and seeking to experiment with established forms.
When did postmodernism take off?
Postmodernism in the 1980 s and '90s. Postmodernism really took off in the 1980s. More films were becoming experimental and playing with typical genre conventions. First, let’s look at the interplay between Blade Runner and Postmodernism.
Is Scream a postmodern movie?
Scream and Austin Powers: International Man of Mystery are both Postmodern works for how they subvert the viewer’s expectations of the horror and spy genres, respectively. Consider this opening sequence from Austin Powers in Goldmember and how director Jay Roach brought multiple movie genres into the mix (spy, action, music video).
Is Monty Python the Holy Grail a postmodern movie?
Let’s look at another early adopter of postmodern film characteristics, Monty Python and the Holy Grail, which is more than just one of the funniest films ever made. It’s a very different film from 8 ½, but it takes us one step closer to a more Postmodern Hollywood.
What is postmodernism?
For philosopher Jean-François Lyotard, the postmodern condition was defined as “incredulity towards metanarra tives”; that is, a loss of faith in science and other emancipatory projects within modernity, such as Marxism.
What is the relationship between postmodernism and modernism?
Postmodernism describes not only a period but also a set of ideas, and can only be understood in relation to another equally complex term: modernism.
What did Jencks argue about modern architecture?
Jencks argued that while modern ist architects were interested in unified meanings, universal truths, technology and structure, postmodernists favoured double coding (irony), vernacular contexts and surfaces. The city of Las Vegas became the ultimate expression of postmodern architecture.
What was postmodernism associated with in the 1980s?
By the 1980s postmodernism had become the dominant discourse, associated with “anything goes” pluralism, fragmentation, allusions, allegory and quotations. It represented an end to the avant-garde’s faith in originality and the progress of art.
What is postmodernism in the Simpsons?
Postmodernism is often viewed as a culture of quotations. Take Matt Groening’s The Simpsons (1989–). The very structure of the television show quotes the classic era of the family sitcom.
What is modernism in art?
Modernism was a diverse art and cultural movement in the late 19th and early 20th centuries whose common thread was a break with tradition, epitomised by poet Ezra Pound ’s 1934 injunction to “make it new!”.
When did postmodernism start?
The shift from modernism to postmodernism is seen most dramatically in the world of architecture, where the term first gained widespread acceptance in the 1970s.
What is Postmodernism?
Postmodernism is a philosophical , cultural and artistic movement that emerged at the end of the 20th century , as a reaction to the intellectual and philosophical ideas of the Enlightenment period and the rest of the modern period (between the 17th and 19th centuries). It was a movement that succeeded modernism , hence the origin of its name.
Postmodern literature
Postmodern literature rejects the distinction between genres and forms of writing.
What is postmodernism?
Some theorists suggest that ‘postmodernism’ refers to a mood or an attitude of mind, others define it as a literary, cultural, or philosophic phenomenon.Either way, critics haven’t agreed on a common definition for the concept.
What is the relationship between postmodernism and architecture?
1. Postmodern Architecture Postmodernism and architecture share a long and productive relationship, since the field of architecture was the one to offer postmodernism its theoretical roots.
What was the postmodern culture of the 60s?
In the 60s the radical and critical postmodern culture represented the opposition of a minority (the artists and theoreticians of Pop Art, against the reductionism of modern art). The seventies transformed this perspective, which became more conservatory, rational and academic, losing some of its critical functions.
When did postmodernism become clear?
On the other hand, he claimed that the concept of postmodernism itself suffered some changes during the decades and became clear in its meaning only in the ‘80s.. But not all theorists see such a contrast between modernism and postmodernism.
Is postmodernism a cliche?
The concept of ‘Postmodernism’- A Theoretical Approach It is a cliche by now to say that we live in a postmodern world, and it is true that the word ’postmodern’ has become one of the most used, and abused, words in the language. Still, it is striking that not many people can say with assurance what this term actually means and involves.
Who is the architect who popularized postmodernism?
The architectural theorist Charles Jenks has done more than anyone to popularise postmodernism as a theoretical concept, particulary in the series of his book The Language of Postmodern Arhitecture (first edition 1977). But its roots lie in the sphere in which the term “postmodern” first found general usage: architecture.
Is poststructuralism a part of postmodernism?
Poststructuralism has been an influential part of the cultural scene since the 1960s, but nowadays it can be included to a more general reaction to author itarian ideologi es and political systems that we define as postmodernism.It can be said that postmodernism subsumes poststructuralism.
What is postmodernism?
Postmodernism would claim that such a view might pertain to Christians but not to those who don't follow Jesus Christ; therefore, sexual morality has become much more permissive in our society in recent decades. Taken to extremes, postmodernism argues that what society says is illegal, such as drug use or stealing, ...
What is postmodernism philosophy?
Postmodernism Definition. Postmodernism is a philosophy that says absolute truth does not exist. Supporters of postmodernism deny long-held beliefs and conventions and maintain that all viewpoints are equally valid. In today's society, postmodernism has led to relativism, the idea that all truth is relative.
What is postmodernism theory?
1. A Brief Introduction to Postmodern Theory. Postmodernism is a word used to describe a range of areas in society. It derives from the term Modernism, which was the previous movement that surrounded modern thought, character, and practice, but more specifically, the Modernist movement in the arts and its cultural tendencies.
What is the difference between modernism and postmodernism?
Under Modernism, we have words like Form, Distance, Interpretation and Grande Histoire, while under Postmodernism we have Anti-form, Participation, Against Interpretation and Petite Histoire. The distinctions are clear, but how do they relate to both Modernism and Postmodernism?
What is the term for the movement that describes the social, political, and economic conditions of an industrialized world?
In general, the term Modernism encompasses the actions of those who felt the traditional forms of art, architecture, literature, and social organization were becoming outdated in the new economic, social, and political conditions of an incipient, fully industrialized world. Postmodernism is, thus, a movement that describes social, political, ...
What is postmodern art?
Postmodernist art, however, is complex and eclectic. Taking different genres of artistic technique and juxtaposing it. It can also be described as kitsch or ironic . Postmodern art uses pastiche and parody to comment on the original piece of art that it represents. Literature has also come under the scrutiny of postmodern thought as it combined elements of previous genres and styles of literature to create a new narrative voice.
What is the family of words that are connected to Postmodernism?
He builds a “family” of words connected to Postmodernism, such as “Fragments, hybridity, relativism, play, parody…an ethos bordering on kitsch and camp". This list begins to build a context around Postmodernism, a way of describing, yet not defining the word. What this implies is that fragments of previous genres are combined with irony and pastiche to create the Postmodern. What it also implies is that, after the Postmodern era, nothing can be taken from the previous as nothing original was designed.
Who is the author of The Postmodern Condition?
Jean Francois Lyotard takes a completely different stance on Postmodernism in his analysis The Postmodern Condition (Lyotard, 1984). Lyotard’s epistemological examination of knowledge in the postmodern era portrays how it has changed from knowledge to " information ".
Is postmodernism a movement?
According to theorists, it describes a hectic era of simulations, recycling, capitalism and mass production, and consumerism. Postmodernism, therefore, cannot be seen as a movement, like some of the earlier periods, rather a condition of the current window in time.
What is the best definition of postmodernism?
Instead, postmodernism is better defined by the styles, attitudes, and response to modernism. Its general ideology reflects a widespread disillusionment with life, the power of existing value systems, and/or technology to effect change. Other factors of postmodernism include:
What Is Postmodern Art?
Postmodern art rejected the traditional values of modernism, and instead embraced experimentation with new media and art forms including intermedia, installation art, conceptual art, multimedia, performance art, and identity politics. Using these new forms, postmodernist artists have stretched the definition of art to embrace the idea that “anything can be art”.
What Are the Characteristics of Postmodern Art?
There is no list of ‘agreed’ characteristics of postmodern art, but could include bricolage, prominent text as the central artistic element, collage, simplification, appropriation, performance art, and the breakdown of high and low culture. It undermines concepts of authenticity and originality and has an emphasis on image and spectacle.
How does postmodernism affect art?
A new focus on low culture: Postmodernism democratizes art , making it more accessible and recognizable to the public. Many postmodern artists believe that art can have multiple meanings and the spectator is a judge of meaning.
What was the Neo-Dada style?
This Neo-Dada style was the first of the postmodern art movements and many of their experiments would give rise to pop art and minimalism.
Who wrote the book The Physical Impossibility of Death in the Mind of Someone Living?
Damien Hirst (The Physical Impossibility Of Death In The Mind Of Someone Living)
Overview
Philosophy
In the 1970s a group of poststructuralists in France developed a radical critique of modern philosophy with roots discernible in Nietzsche, Kierkegaard, and Heidegger, and became known as postmodern theorists, notably including Jacques Derrida, Michel Foucault, Jean-François Lyotard, Jean Baudrillard, and others. New and challenging modes of thought and writing pushed the development of new areas and topics in philosophy. By the 1980s, this spread to America (Richa…
Definition
Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or mode of discourse which challenges worldviews associated with Enlightenment rationality dating back to the 17th century. Postmodernism is associated with relativism and a focus on ideology in the maintenance of economic and political power. Postmodernists are "skeptical of explanations which claim to be valid for all groups, cultures, traditions, or races, and instead focuses on the relative truths of each person". It consid…
Origins of term
The term postmodern was first used in 1870. John Watkins Chapman suggested "a Postmodern style of painting" as a way to depart from French Impressionism. J. M. Thompson, in his 1914 article in The Hibbert Journal (a quarterly philosophical review), used it to describe changes in attitudes and beliefs in the critique of religion, writing: "The raison d'être of Post-Modernism i…
History
The basic features of what is now called postmodernism can be found as early as the 1940s, most notably in the work of artists such as Jorge Luis Borges. However, most scholars today agree postmodernism began to compete with modernism in the late 1950s and gained ascendancy over it in the 1960s.
The primary features of postmodernism typically include the ironic play with styles, citations, an…
Theories and derivatives
Structuralism was a philosophical movement developed by French academics in the 1950s, partly in response to French existentialism, and often interpreted in relation to modernism and high modernism. Thinkers who have been called "structuralists" include the anthropologist Claude Lévi-Strauss, the linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, the Marxist philosopher Louis Althusser, and the semiotician Algirdas Greimas. The early writings of the psychoanalyst Jacques Lacan and the lite…
Manifestations
Modern Architecture, as established and developed by Walter Gropius and Le Corbusier, was focused on:
• the attempted harmony of form and function; and,
• the dismissal of "frivolous ornament."
Criticisms
Criticisms of postmodernism are intellectually diverse, including the argument that postmodernism is meaningless and promotes obscurantism.
In part in reference to post-modernism, conservative English philosopher Roger Scruton wrote, "A writer who says that there are no truths, or that all truth is 'merely relative,' is asking you not to believe him. So don't." Similarly, Dick Hebdige criticized the vagueness of the term, enumerating …
Relationship to Modernism
Postmodern Architecture
- The shift from modernism to postmodernism is seen most dramatically in the world of architecture, where the term first gained widespread acceptance in the 1970s. One of the first to use the term, architectural critic Charles Jencks suggested the end of modernism can be traced to an event in St Louis on July 15, 1972 at 3:32pm. At that moment, the derelict Pruitt-Igoepubli…
Famous Theorists
- Theorists associated with postmodernism often used the term to mark a new cultural epoch in the West. For philosopher Jean-François Lyotard, the postmodern condition was defined as “incredulity towards metanarratives”; that is, a loss of faith in science and other emancipatory projects within modernity, such as Marxism. Marxist literary theorist Fredric Jameson famously …
Postmodern Visual Art
- In the visual arts, postmodernism is associated with a group of New York artists – including Sherrie Levine, Richard Prince and Cindy Sherman – who were engaged in acts of image appropriation, and have since become known as The Pictures Generationafter a 1977 show curated by Douglas Crimp. By the 1980s postmodernism had become the dominant discourse, a…
Postmodern Cultural Identity
- Postmodernism can also be a criticalproject, revealing the cultural constructions we designate as truth and opening up a variety of repressed other histories of modernity. Such as those of women, homosexuals and the colonised. The modernist canon itself is revealed as patriarchal and racist, dominated by white heterosexual men. As a result, one of the most common themes addressed …
Characteristics of Postmodernism
- Postmodernism was an anti-authoritarian current by nature. Postmodernism was characterized by breaking with the established rules about artand by introducing a new era of freedom in which “anything goes”. It was an anti-authoritarian current by nature because it refused to recognize the influence of any style. The movement was shown with a humorous...
Postmodern Architecture
- New Orleans’ Piazza d’Italia public square is a postmodern work. Postmodern architecture stood out for being of an indefinite type, without opposing any of the known styles, although it managed to differentiate itself from them. It replaced modern aesthetics without ornamentation and right angles, with irregular lines and unusual surfaces. Some examples of postmodern architecture ar…
Postmodern Literature
- Postmodern literature rejects the distinction between genres and forms of writing. Postmodern literature was characterized by an ideology and style that appealed to fragmentation, diversity, paradox, little-known storytellers, parody, and “black humor.” It rejects the distinction between genres and forms of writing . The literature of the 1990s in Latin America evidenced a trend tow…
Postmodern Society
- Postmodernism raised a revaluation of planet Earth. During the development of postmodern society, it went from a production economy to a consumer economy, including a compulsive consumerism that caused harmful consequences that can be seen today. To counteract the negative consequences, postmodernism began to question the environmental disasterscaused …