Reasoning is the ability to assess things rationally by applying logic based on new or existing information when making a decision or solving a problem. Reasoning allows you to weigh the benefits and disadvantages of two or more courses of action before choosing the one with the most benefit or the one that suits your needs.
Full Answer
What are the 4 types of reasoning?
Types of reasoning include: Abduction: the process of creating explanatory hypotheses. Backwards Reasoning: Start from what you want and work back. Butterfly Logic: How people often argue. Analogical Reasoning: relating things to novel other situations. Cause-and-Effect Reasoning: showing causes and resulting effect.
What are the four kinds of reasoning?
- Selective encoding – choosing what information matters
- Selective combination – choosing what’s important within chosen information
- Selective comparison – out of chosen information, how does it apply to the problem
How to explain your reasoning?
Types of Reasoning Statements
- Simple Statements. Simple statements are those which are direct and do not include any modifier. ...
- Compound Statement. With the help of certain connectives, we can club different statements. ...
- If-Then Statements. According to mathematical reasoning, if we encounter an if-then statement i.e. ...
What are the forms of reasoning?
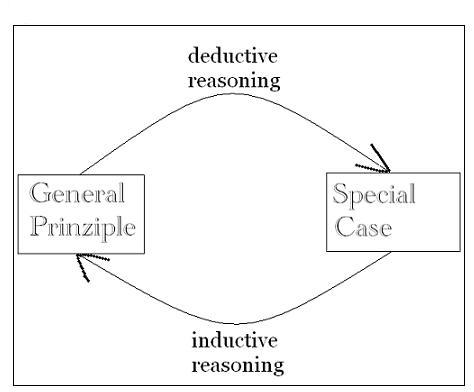
Reasoning may be subdivided into forms of logical reasoning, such as: deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and abductive reasoning. Aristotle drew a distinction between logical discursive reasoning (reason proper), and intuitive reasoning , [6] in which the reasoning process through intuition—however valid—may tend toward the personal ...

What is reasoning and example?
Example reasoning involves using specific instances as a basis for making a valid conclusion. In this approach, specific instances 1, 2, and 3 lead to a generalized conclusion about the whole situation. For example: I have a Sony television, a Sony stereo, a Sony car radio, a Sony video system, and they all work well.
What is reasoning explain?
Reasoning is the process of using existing knowledge to draw conclusions, make predictions, or construct explanations. Three methods of reasoning are the deductive, inductive, and abductive approaches. Deductive reasoning: conclusion guaranteed.
What is the definition of reasoning in writing?
Reasoning is the process for making clear how your evidence supports your claim. In scientific argumentation, clear reasoning includes using scientific ideas or principles to make logical connections to show how the evidence supports the claim.
What are the 4 types of reasoning?
Four types of reasoning will be our focus here: deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, abductive reasoning and reasoning by analogy.
What is a good example of reasoning?
For instance, it might be good reasoning to move from the belief that someone said that the store is open to the belief that the store is open, even if it is not good reasoning to make this move given the further belief that the person who said this is a liar.
What is the importance of reasoning?
Reasoning is essential for posing, exploring, making sense of, and patiently solving problems. It is the soil in which mathematical understanding is deepened and becomes more complex, multi-faceted and connected.
What is the most common form of reasoning?
The most common form of logic seen in argumentation is the syllogism: an argument with a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. Logical forms are either valid or not—as long as the form of the argument and the premises are true, then the conclusion must be true.
What is the meaning of reasoning in logic?
Logical reasoning is a form of thinking in which premises and relations between premises are used in a rigorous manner to infer conclusions that are entailed (or implied) by the premises and the relations.
What are the 8 elements of reasoning?
The critical thinking framework includes eight elements of thought: purpose, question at issue, information, inferences, concepts, assumptions, implications, and point of view.
What are the three elements of reasoning?
Elements of Thought (reasoning) All reasoning is based on assumptions. All reasoning is done from some point of view. All reasoning is based on data, information and evidence.
What are the 7 types of reasoning?
7 types of reasoningDeductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning is a type of reasoning that uses formal logic and observations to prove a theory or hypothesis. ... Inductive reasoning. ... Analogical reasoning. ... Abductive reasoning. ... Cause-and-effect reasoning. ... Critical thinking. ... Decompositional reasoning.
How do you explain the reasoning in math?
In mathematics, reasoning involves drawing logical conclusions based on evidence or stated assumptions. Sense making may be considered as developing understanding of a situation, context, or concept by connecting it with existing knowledge or previous experience.
What is the meaning of reasoning in education?
Reasoning is the generation or evaluation of claims in relation to their supporting arguments and evidence. The ability to reason has a fundamental impact on one's ability to learn from new information and experiences because reasoning skills determine how people comprehend, evaluate, and accept claims and arguments.
What is the study of reasoning?
logic, the study of correct reasoning, especially as it involves the drawing of inferences.
What is reasoning in a paragraph?
Reasoning is when the writer explains how and why the evidence supports the claim. How does one write reasoning? The reasoning should immediately follow the evidence in the paragraph. To incorporate reasoning, begin by explaining or summarizing what the evidence says.
What is an example of reasoning?
An example of reasoning is if x happens, then y will happen as a result. This is a cause and effect type of reasoning.
What is the act of reasoning?
The act of reasoning can be defined as taking new or existing information and using it to make a logical decision.
What does reasoning mean in writing?
Reasoning in writing happens from the brainstorming stage all the way through the conclusion of the process. Reasoning in writing is creating a com...
What is Reasoning?
Reasoning can best be defined as the basic action of thinking in a sensible and rational way about something. Sounds easy, right? Most of the time, reasoning happens automatically. But, when someone stops to think logically about something, rather than act impulsively or emotionally, that is using reasoning.
Reasoning Examples
Below are some examples of reasoning in a variety of situations. For the examples below, these are general examples. The types of reasoning mentioned above will be discussed and outlined in greater detail below.
Types of Reasoning
Below we will explore a variety of types of reasoning. The two main types are deductive and inductive.
Practicing the Skill of Reasoning
1. In the lesson, you read about our everyday use of reasoning in making decisions. Make a list of decisions you've been faced with recently, like deciding whether to go to a party or deciding what to wear to an important event. See if you can pinpoint the steps in making these decisions.
What is project management?
Project management utilizes decompositional reasoning in its division of a project into components. A manager assigns each component to an individual, who is responsible for completion and communication about integration into the project. This division ensures the success of each component and contributes to the operation of the whole.
What is decompositional reasoning?
Decompositional reasoning is the process of breaking things into constituent parts to understand the function of each component and how it contributes to the operation of the item as a whole. By analyzing each part independently, decompositional reasoning allows an observer to draw powerful conclusions about the whole. You find this approach in several disciplines, including science, engineering, marketing, product development, game development and software development.
What is the ability to assess things rationally?
Reasoning is the ability to assess things rationally by applying logic based on new or existing information when making a decision or solving a problem. Reasoning allows you to weigh the benefits and disadvantages of two or more courses of action before choosing the one with the most benefit or the one that suits your needs. It also helps you solve problems, handle uncertainty, verify claims and assess situations carefully to ensure the decision you make is in your best interest.
How many types of reasoning are there?
Here are seven types of reasoning and examples of situations when they're best used:
What is analogous reasoning?
Analogical reasoning is a form of thinking that finds similarities between two or more things and then uses those characteristics to find other qualities common to them. It's based on the brain's tendency to notice patterns and make associations. Once the brain recognizes a pattern, it can associate the pattern with specific things, and this leads to analogous reasoning. Analogous thinking can help you expand your understanding by looking for similarities between different things.
Why is it important to understand logic?
It's essential to success in positions from entry-level to corporate and help define your leadership abilities. Understanding the different types of reasoning and how to apply them can help you excel as a professional, contribute meaningfully at work and gain the respect of your superiors. In this article, we discuss the concept of reasoning, the seven types of reasoning and when to use each one.
When to use abductive reasoning?
For example, salespeople may use this type of reasoning when they receive a short correspondence from a client, asking them to reply quickly about an issue. When the client doesn't give enough information to understand before responding, a salesperson can use abductive reasoning to narrow down possible concerns. It's sometimes better to prepare answers for a few best guesses.
What is logic in philosophy?
Logic is a theme of philosophy that values the internal logic of a philosophical reasoning, that is, it measures the criterion of truth and certainty in a discourse . There are also mathematical reasonings, which have a numerical logic and show a scientific equation.
What is the essence of reason?
Reasoning refers to a person’s explanation of a particular subject. Therefore, the essence of it is understanding and understanding, since then, there is only communication when the receiver of a message really understands what the sender means.
Why is it important to present information in language according to the interlocutor's age?
To express good reasoning, it is important to present information in language according to the interlocutor’s age. For example, a teenager has a different language than a 70 year old.
Is silence valuable in communication?
Within an effective communication process, it is noteworthy that not only words are valuable, but silence is also valuable. On the other hand, a reasoning can be presented either in written form or orally.
What are the concepts used in the realms of reason?
The concepts employed in the realms of reason illustrate an inferential process of making conclusive arguments based on logical and clear thoughts. These concepts include co existential, cause, generalization, analogy and quasi-logical arguments.
What is critical thinking?
The term critical thinking refers to an individual’s ability to think logically, rationally, and clearly in given circumstances. It entails the ability of an individual to involve in both independent and reflective thinking.
What is the purpose of the chapter on reasoning?
This chapter develops on the first chapter that introduced the linkage between a claim and evidence in proposing an argument. This chapter seeks to explore the various forms of reasoning that commonly used in daily discussions.
Why is reasoning important in argumentation?
In simple terms, reasoning is a necessary element for any argumentation to remain relevant while withstanding the challenges of refutation observed on observed weaknesses.