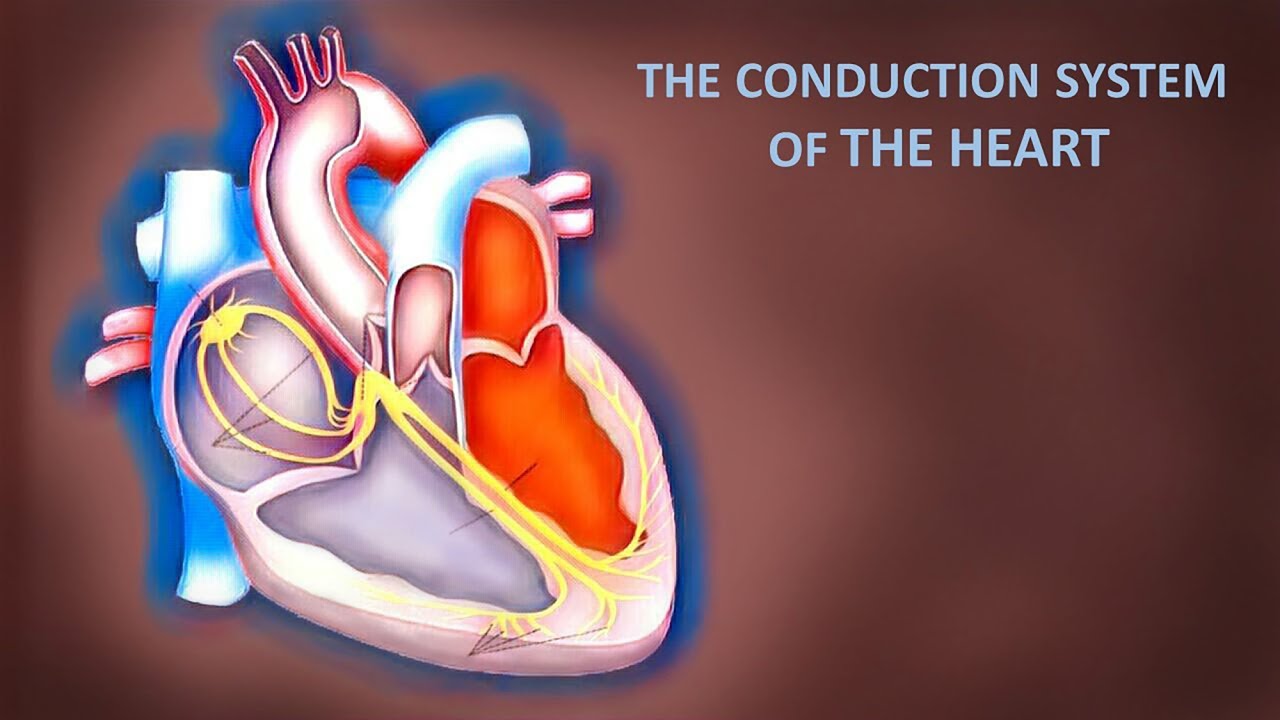
What are the components of the cardiac conduction system?
- SA node (sinoatrial node) – known as the heart’s natural pacemaker.
- AV node (atrioventricular node).
- His-Purkinje Network.
- The SA node fires another impulse and the cycle begins again.
What is the conductive system of the heart?
Your heart’s conduction system is the network of nodes (groups of cells that can be either nerve or muscle tissue), specialized cells and electrical signals that keep your heart beating. Two types of cells control your heartbeat: Conducting cells carry the electric signals. Muscle cells control your heart’s contractions.
What is the Order of electrical conduction in the heart?
What are the steps of the conduction pathway of the heart?
- Pacemaker Impulse Generation. The first step of cardiac conduction is impulse generation.
- AV Node Impulse Conduction.
- AV Bundle Impulse Conduction.
- Purkinje Fibers Impulse Conduction.
What are the steps of cardiac conduction?
What are the steps of the intrinsic conduction system? Intrinsic Conduction System of the Heart. Step 1: Stimulation of the sinoatrial node. SA node. … Step 2: Stimulation of the atrioventricular node. AV node. … Step 3: Propagation to the AV bundle. AV bundle. … Step 4: Splitting into the bundle branches. …

What is the purpose of the cardiac conduction system?
The cardiac conduction system is a network of specialized cardiac muscle cells that initiate and transmit the electrical impulses responsible for the coordinated contractions of each cardiac cycle. These special cells are able to generate an action potential on their own (self-excitation) and pass it on to other nearby cells (conduction), including cardiomyocytes.
Which part of the heart is responsible for impulse initiating and controlling heart contractions?
Although all parts have the ability to generate action potentials and thus heart contractions, the sinuatrial (SA) node is the primary impulse initiator and regulator in a healthy heart.
What is the inter-atrial conduction network?
The internodal conduction pathways are a part of the intra-atrial conduction network initially described by Thomas N. James in 1963. Not only do these pathways travel within the right atrium, but they also form direct points of communication between the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. The internodal conduction pathway is divided into anterior, middle and posterior branches.
Where does the SA node get its blood supply from?
The SA node receives its blood supply from the sinuatrial nodal branch of the coronary artery. In about 60% of individuals, this artery is a branch of the right coronary artery (therefore arising from the left coronary artery in the other 40%).
How do fibers affect the rate of conduction?
As a result, they are able to transmit impulses 6 times faster than ventricular muscles and 150 times faster than the AV nodal fibers. The increased number of gap junctions allow more ions to pass from one cell to the next, thus increasing the rate of conduction. Furthermore, there are fewer myofibrils in Purkinje cells, resulting in little to contraction (therefore shorter to absent refractory periods) within these cells. Consequently, the bundles can achieve almost instantaneous transmission of the action potential to the rest of the ventricle once it passes through the AV node. This compensates for the delay at the AV node and allows the ventricles to contract shortly after the atria.
Which layer of the heart is a hemi-oval-shaped node?
The hemi-oval-shaped node occupies the subendocardiac layer within Koch’s triangle.
Which branch of the pulmonary veins is in front of the left pulmonary veins?
Proximally, the superior part of the left branch passes in front of the openings of the left pulmonary veins. The inferior part continues caudally to the vestibule of the left atrium.
What is the function of the conduction system?
The conduction system of the heart controls its pumping action, which results in the delivery of blood to the different organs and tissues of the body. This conduction system is composed of a group of special cells found in the walls of the heart muscle, which send the electrical impulses and cause the heart muscle to contract.
What is the cycle of contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle?
The cycle of contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle is generated by electrical impulses that are controlled by the conduction system of the heart, which may be influenced by factors such as temperature, exercise, and hormonal changes.
What makes your heart beat?
What makes the heart beat? Your heart continues beating every moment of the day and night, even without you being aware of it. It may change its rate and rhythm for a few moments when you exercise or when you are excited, but it soon goes back to its regular pace without your conscious control. The cycle of contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle is generated by electrical impulses that are controlled by the conduction system of the heart, which may be influenced by factors such as temperature, exercise, and hormonal changes.
What happens when the sinus node changes its rate?
This may occur when: The sinus (SA) node changes its rate or rhythm. The conduction system of the heart is interrupted. Certain parts of the heart tissue take over the SA node and becomes another "pacemaker.". Arrhythmias cause heart palpitations and other symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, or fainting.
Which fibers pass on the action potential to the heart’s interventricular septum?
The bundle branches. These pass on the action potential to the heart’s interventricular septum. Purkinje fibres. These fibers begin at the interventricular septum down to the apex of your heart, and continue through the ventricular muscles (myocardium). They convey electrical impulses to the ventricles’ muscle cells.
What is the purpose of ECG?
It is a useful tool to monitor the heart’s conduction system and may be used to detect abnormalities in function.
Which system of the heart is known as a natural pacemaker?
The conduction system of the heart works this way: The SA node is known a natural pacemaker because it sets the pace of the heartbeat. It is where cardiac muscle contraction begins, from an impulse which causes the right and left atria to contract and push blood into the ventricles.
What are the components of the cardiac conduction system?
The cardiac conduction system involves the spread of electrical activity from the sinoatrial node, to the atrioventricular node, down the bundle of His and along the Purkinje fibres. As the electrical activity spreads along the heart’s conduction system it initiates myocardial contraction in ...
What are the two main types of cells in the heart?
The heart has two main types of cells: 1. Conducting cells: generate and propagate electrical impulses. Contractile (muscle) cells: contract following receipt of electrical impulses. These cells can also propagate and, on ...
Which bundle of His branches travels down the interventricular septum?
The bundle of His branches into the left and right bundle branches which travel down the interventricular septum. Branches of the bundle of His propagate impulses to the left and right ventricles respectively. Each branch terminates as several Purkinje fibres.
Where is the atrioventricular node located?
Atrioventricular node (AVN) The atrioventricular node (AVN) is a group of specialised cells situated in the atrioventricular septum just above the coronary sinus ostium. 1,4,5. The AVN receives electrical impulses from the atria and then transmits the electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles.