What are the 6 steps of the scientific method in the correct order?
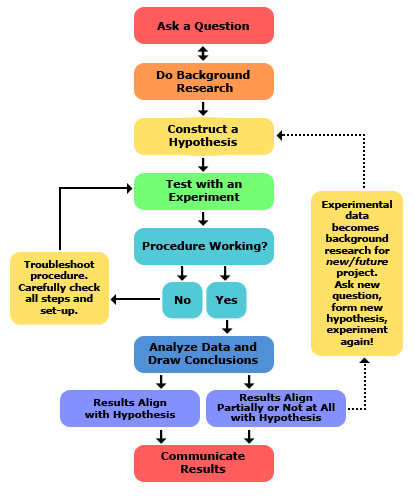
- Purpose/Question. Ask a question.
- Research. Conduct background research.
- Hypothesis. Propose a hypothesis.
- Experiment. Design and perform an experiment to test your hypothesis.
- Data/Analysis. Record observations and analyze the meaning of the data.
- Conclusion.
Full Answer
What are the 8 steps to a scientific method?
Scientific method eight steps. STUDY. Flashcards. Learn. Write. Spell. Test. PLAY. Match. Gravity. Created by. bjsmith4. Key Concepts: Terms in this set (8) Step 1. Make observation if the environment (Using thr five senses) Step 2. Ask a question (Based on the observations made) Step 3. Research your question
What are the four steps inthe scientific method?
The scientific method has four steps. Observation and description of a phenomenon. The observations are made visually or with the aid of scientific equipment. Formulation of a hypothesis to explain the phenomenon in the form of a causal mechanism or a mathematical relation. Test the hypothesis by analyzing the results of observations or by ...
What are the most important steps to the scientific method?
What are the two most important stages of the scientific method?
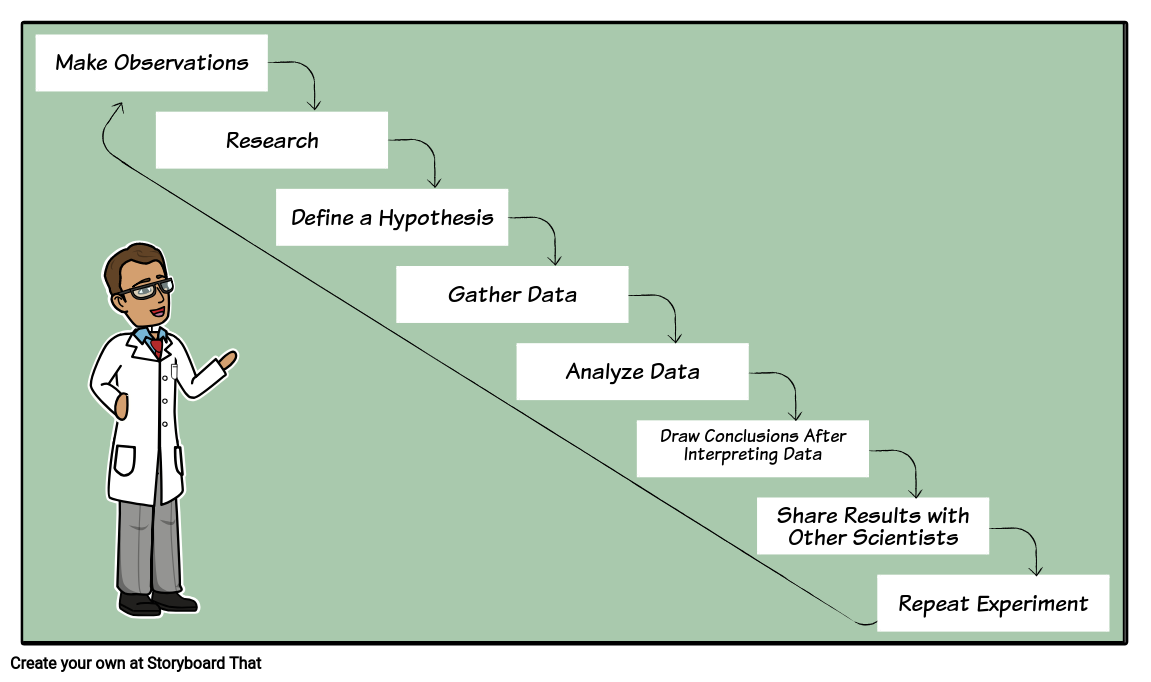
- Make an observation or observations.
- Ask questions about the observations and gather information.
- Form a hypothesis — a tentative description of what’s been observed, and make predictions based on that hypothesis.
- Test the hypothesis and predictions in an experiment that can be reproduced.
What is the sequence of steps of the scientific method?
What are the 7 steps of the scientific method?
- Ask a question. The first step in the scientific method is asking a question that you want to answer. …
- Perform research. …
- Establish your hypothesis. …
- Test your hypothesis by conducting an experiment. …
- Make an observation. …
- Analyze the results and draw a conclusion. …
- Present the findings.
What is the Scientific Method?
The scientific method is a process for experimentation that is used to explore observations and answer questions. Does this mean all scientists follow exactly this process? No. Some areas of science can be more easily tested than others. For example, scientists studying how stars change as they age or how dinosaurs digested their food cannot fast-forward a star's life by a million years or run medical exams on feeding dinosaurs to test their hypotheses. When direct experimentation is not possible, scientists modify the scientific method. In fact, there are probably as many versions of the scientific method as there are scientists! But even when modified, the goal remains the same: to discover cause and effect relationships by asking questions, carefully gathering and examining the evidence, and seeing if all the available information can be combined in to a logical answer.
How do scientists use the scientific method?
But scientists always strive to keep to the core principles of the scientific method by using observations, experiments, and data to support or reject explanations of how a phenomenon works. While experimenting is considered the best way to test explanations, there are areas of science, like astronomy, where this is not always possible.
What happens if an experiment is analyzed and a hypothesis is disproved?
If your hypothesis is disproved, then you can go back with the new information gained and create a new hypothesis to start the scientific process over again.
What happens if a scientist's prediction is not accurate?
Scientists often find that their predictions were not accurate and their hypothesis was not supported , and in such cases they will communicate the results of their experiment and then go back and construct a new hypothesis and prediction based on the information they learned during their experiment. This starts much of the process of the scientific method over again. Even if they find that their hypothesis was supported, they may want to test it again in a new way.
How to find evidence for an answer?
If you want to find evidence for an answer or an answer itself then you construct a hypothesis and test that hypothesis in an experiment. If the experiment works and the data is analyzed you can either prove or disprove your hypothesis.
Why do scientists go back and construct a new hypothesis?
Scientists often find that their predictions were not accurate and their hypothesis was not supported , and in such cases they will communicate the results of their experiment and then go back and construct a new hypothesis and prediction based on the information they learned during their experiment.
What is hypothesis in science?
A hypothesis is an educated guess about how things work. It is an attempt to answer your question with an explanation that can be tested. A good hypothesis allows you to then make a prediction:#N#"If _____ [I do this] _____, then _____ [this] _____ will happen."
What does a researcher come up with?
research, he comes up with a hypothesis.
What is the IV in research?
Make an Observation/Do Research, Ask a Question, Make a Hypothesis, Conduct an Experiment, Analyze Your Data, Draw Conclusion, Report Findings and Independent Variable which is also seen as (IV)
