
What is the CPR in court?
What is the purpose of CPR?
What is the purpose of pre action protocols in CPR?
What is the Civil Procedure Act?
How many persons are required to be authorised to conduct litigation in relation to all proceedings in the Senior Courts?
When did the Civil Procedure Rules come into force?
Who published the Access to Justice Report?
See 4 more
About this website

What does CPR stand for in court?
CPR. Civil Procedure s Rules. Procedure, Court, Government.
What are the Civil Procedure Rules UK?
The civil procedure rules make up a procedural code whose overriding aim is to enable the courts to deal with cases justly.
What is the overriding objective?
The Overriding Objective seeks to ensure that parties to litigation are dealt with fairly, cases proceed swiftly in the most cost-efficient way possible and that the system can be easily understood by those that use it.
Why was the Uniform Civil Procedure Rules 1999 QLD introduced?
5 Philosophy—overriding obligations of parties and court (1)The purpose of these rules is to facilitate the just and expeditious resolution of the real issues in civil proceedings at a minimum of expense.
What are the four types of civil law?
Four of the most important types of civil law deal with 1) contracts, 2) property, 3) family relations, and 4) civil wrongs causing physical injury or injury to property (tort). C. Contract law involves a contract, or a set of enforceable voluntary promises. D.
What is an example of a civil action?
General civil cases, usually involving suing someone for money in disputes over things like contracts, damage to property, or someone getting hurt. Family law cases such as divorce, child support, child custody, and adoptions.
How must the court further the overriding objective in the CPR?
Court's duty to manage cases (1) The court must further the overriding objective by actively managing cases. (l) giving directions to ensure that the trial of a case proceeds quickly and efficiently.
How do you write a pre action protocol letter?
The letter should contain the date and details of the decision, act or omission being challenged, a clear summary of the facts and the legal basis for the claim. It should also contain the details of any information that the claimant is seeking and an explanation of why this is considered relevant.
What is an overriding principle?
adjective [usually ADJECTIVE noun] In a particular situation, the overriding factor is the one that is the most important.
What is a Rule 444 letter?
The letter is known as a “Rule 444 letter”, after the UCPR rule that governs it. That rule stipulates that a letter must be sent and dictates what it must contain. The Rule 444 letter process alerts the opposing party to any complaints and allows them to respond to or remedy those complaints.
How do you address a magistrate in Qld?
As and from 17 November 2004, Magistrates are to be addressed as “Your Honour” and not as “Your Worship.” This Practice Direction applies to all Courts in Queensland in which magistrates preside.
What is the purpose of the Civil Proceedings Act 2011 QLD?
The main purpose of the Act is to streamline, modernise and simplify the law in relation to civil proceedings in the Supreme, District and Magistrates Courts and to assist in the integration, consistency and effectiveness of the court registries.
Who makes the decision in civil cases UK?
The two main courts dealing with civil cases in England and Wales are the County Court and the High Court. The County Court deals with minor civil matters, while the High Court deals with large or complex civil disputes.
What is a civil claim UK?
It covers cases about broken contracts (often called 'breach of contract'), money owed, compensation, and personal injury - including road traffic accidents and accidents at work.
What are the Jackson reforms?
A package of interlocking reforms, impacting on a number of areas of civil litigation, including but not limited to: costs, funding, case management, disclosure and Part 36. The changes largely came into force on 1 April 2013.
Which Lords report formed the basis of the Civil Procedure Rules?
Lord Woolf listed two of the requirements of case management as "... fixing timetables for the parties to take particular steps in the case; and limiting disclosure and expert evidence".
The New Civil Procedure Rules Explained | The Student Lawyer
On 1 April 2013, significant changes were implemented to the civil law of England and Wales in the form of legislation regarding the Civil Procedure Rules […]
The Civil Procedure Rules 1998 - Legislation.gov.uk
Status: This is the original version (as it was originally made). This item of legislation is currently only available in its original format.
The Civil Procedure Rules 1998 - Legislation.gov.uk
These Rules provide a new code of civil procedure for the civil courts. They replace the Rules of the Supreme Court 1965 and the County Court Rules 1981. As well as the main body of the new rules (Parts 1—48), they also provide for certain specialist proceedings (Part 49) and transitional provisions (Part 51); the details of these are contained in practice directions.
Rules & Practice Directions - Civil Procedure Rules
Parts 21-30; Web Version ; Part 21 - Children and Protected Parties : Practice Direction 21 : Part 22 - Statements of Truth : Practice Direction 22 : Part 23 - General Rules about Applications for Court Orders
Civil - Civil Procedure Rules - Justice
Civil Procedure (Amendment No.2) Rules 2022 & 149th PD Update. The Statutory Instrument (SI) is published via the legislation website and the online rules will be updated in due course.. The Civil Procedure (Amendment No. 2) Rules 2022 (enter into force variously, on 1st December in respect of Welsh Housing and on 1 st October in respect of all other amendments)
Civil Procedure Rules - LawTeacher.net
The Civil Procedure Rules were used by all courts after 1999 and replaced the Supreme Court Rules and County Court Rules.
What is the CPR in court?
The Civil Procedure Rules ( CPR) are the rules of civil procedure used by the Court of Appeal, High Court of Justice, and County Courts in civil cases in England and Wales. They apply to all cases commenced after 26 April 1999, and largely replace the Rules of the Supreme Court and the County Court Rules. The CPR were designed to improve access ...
What is the purpose of CPR?
The CPR were designed to improve access to justice by making legal proceedings cheaper, quicker, and easier to understand for non-lawyers. As a consequence of this, many archaic legal terms were replaced with "plain English" equivalents, such as "claimant" for "plaintiff" and "witness summons" for "subpoena". ...
What is the purpose of pre action protocols in CPR?
To support the ethos of narrowing the issues prior to the use of proceedings and encapsulate best practice, the CPR introduced “pre-action protocols”. They are given force by Practice Direction – Protocols
What is the Civil Procedure Act?
The Civil Procedure Act 1997 (c. 12) was enacted on 27 February 1997. It conferred the power to make civil procedure rules. It also established the Civil Justice Council, a body composed of members of the judiciary, members of the legal professions and civil servants, and charged with reviewing the civil justice system.
How many persons are required to be authorised to conduct litigation in relation to all proceedings in the Senior Courts?
Three persons who have been authorised by a relevant approved regulator to conduct litigation in relation to all proceedings in the Senior Courts, including at least one with particular experience of practice in county courts
When did the Civil Procedure Rules come into force?
The Civil Procedure Rules 1998 (SI 1998/3132) were made on 10 December 1998 and came into force on 26 April 1999. The draft rules of practice formed their core.
Who published the Access to Justice Report?
History. In 1994, the Lord Chancellor instructed the then Master of the Rolls, Lord Woolf, to report on options to consolidate the existing rules of civil procedure. On 26 July 1996, Lord Woolf published his Access to Justice Report 1996 in which he "...identified a number of principles the civil justice system should meet to ensure access ...
What is CPR in court?
The CPR comprise rules, regulations and guidelines in relation to civil court procedure and have been updated numerous times over the years. They must be complied with by all parties to civil proceedings (though there are separate Criminal Procedure Rules related to criminal proceedings).
What are the other parts of CPR?
Other Parts of the CPR regulate more specific procedures including disclosure and inspection of documents (Part 31), rules on evidence (Part 32), rules on expert evidence (Part 35) together with Experts’ Protocol, offers to settle (Part 36), and rules about costs (Part 44).
What does the defendant have to state in the defence?
The defendant must state in the defence which allegations it does or does not admit, and which allegations it denies. The defence must also be verified by a statement of truth. The defendant can file a counterclaim against the Claimant (Part 20).
What is civil litigation?
Civil litigation is governed by the Civil Procedure Rules (CPR) which came into effect in 1998. The CPR represent a single code of rules setting out how a case is to be conducted in the civil courts in England and Wales. The CPR comprise rules, regulations and guidelines in relation to civil court procedure and have been updated numerous times ...
How many parts are there in CPR?
The CPR are divided into 74 Parts, each with several Rules. There are also Practice Directions which relate to each Part. Practice Directions are divided into paragraphs and their purpose is to assist in clarification and better understanding of the main rules. The most important Parts of the CPR are:
What is the overriding objective of the court to deal with cases justly?
Dealing with cases justly means preserving equality of the parties to the dispute; saving expenses; dealing with cases proportionately bearing in mind the complexity and nature of the case; and ensuring that cases are dealt with fairly and expeditiously.
How long is CPR certification good for?
These certifications are generally valid in any state for two years.
How long is a first responder certification valid?
These certifications are generally valid in any state for two years. The modules you take will depend on your certification. For example, if you are a first responder or a daycare provider, your training may be contextualized to fit your field.
How many people survive cardiac arrest?
In fact, an estimated 45% of people who go into cardiac arrest will survive because a bystander gave them CPR. 1. Being trained and certified to perform CPR is one thing, but doing so without fear or hesitation is another.
How many people go into cardiac arrest every year?
Every year, at least 350,000 people go into cardiac arrest outside of a hospital setting. Of those, around 90% do not survive. Knowing how to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and having the confidence to administer it saves lives. In fact, an estimated 45% of people who go into cardiac arrest will survive because a bystander gave them CPR. 1
What is the duty of a rescuer?
Rescuers who are part of an organized ambulance agency, fire department, law enforcement organization, or rescue squad have what is known as a duty to act and are usually bound to provide help.
What to do if someone is unconscious and nonresponsive?
Ask for consent. If the person is unconscious or non-responsive, their consent is implied. Call 911 and begin resuscitation.
Is it brave to do CPR?
Taking command of an emergency situation by offering to administer CPR is brave. If you have ever felt nervous or reluctant about having to use CPR, you're not alone.
How to stay out of court for CPR?
In order to stay out of court, your best bet is to keep your CPR certification current, know the law in your state, refuse any reward for an act of rescue, and follow your training to the best of your ability in an emergency situation.
Who can not provide CPR?
There is usually an exception for those in the profession, such as ambulance staff, EMT’s, doctors and nurses, firefighters, law enforcement officers, and others who have what the law defines as a “duty to act.”.
What are the Good Samaritan laws?
Simply put, Good Samaritan laws are there to protect people who selflessly jump in to help—without the expectation of a reward or accolades. They generally do not apply to paid medical or emergency rescue staff, as these people are getting paid for their services—not, from a legal standpoint at least, acting only out of the goodness of their hearts.#N#In some states, Good Samaritan protections may be revoked if you rescue someone and receive monetary reward for it—even if you received the reward after you provided the help and with no expectation of reward. The laws on this vary by state, but if you want to raise your chances of staying out of court or winning if you get dragged in, it’s best to refuse any and all monetary or other types of rewards for a rescue.
What is the loophole in CPR?
The loophole is that if the patient is impaired, they cannot legally give consent. And in cases where CPR is needed and every minute counts—chances are the victim will be unconscious or otherwise impaired during this time—rescuers are expected to assume consent rather than waiting for it to be given.
Is CPR better than nothing?
Some states are more committed than others to encouraging bystander response to emergencies, which has been shown to boost survival rates for victims of cardiac arrest—even if the rescuer is not well trained and the CPR technique is not perfect, it is still better than nothing.
Is Good Samaritan law airtight?
However, no Good Samaritan law is airtight—and it’s a good idea to know what they say. Here’s an overview—with the caveat that we’re not lawyers and this article is not intended to be taken as legal advice, as well as the fact that Good Samaritan law can change at any time.
Do you need to be certified to do CPR?
You may or may not need to have CPR certification. In some states, the only people covered by Good Samaritan protections are medically trained—including people with CPR certification. In other cases, Good Samaritan laws—or specific parts of them—are meant to apply only to people without medical training. In other states, everyone is covered by ...
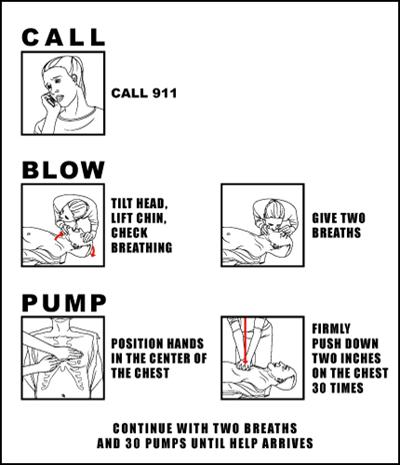
What is CPR, and when should I use it?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure that can help save a person’s life if their breathing or heart stops.
What do you not know about CPR?
Three Things You May Not Know About CPR. People who have cardiac arrests may benefit from CPR, yet many people who witness cardiac arrest do not perform CPR. Learn about CPR so you can be prepared. Cardiac arrest is not the same as a heart attack. Someone whose heart has stopped beating is in cardiac arrest and needs CPR.
How does CPR help people?
1. CPR Saves Lives. Currently, about 9 in 10 people who have cardiac arrest outside the hospital die. 2 But CPR can help improve those odds. If it is performed in the first few minutes of cardiac arrest, CPR can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. 2.
How does CPR work during cardiac arrest?
Death can happen in minutes without treatment. 1 CPR uses chest compressions to mimic how the heart pumps. These compressions help keep blood flowing throughout the body. Cardiac arrest is not the same as a heart attack.
What to do if you have a cardiac arrest?
If you see cardiac arrest happen (see sidebar), call 9-1-1 right away and then do CPR until medical professionals arrive. Keep reading to learn how to perform CPR.
How many cardiac arrests happen at home?
Cardiac Arrests Often Happen at Home. About 350,000 cardiac arrests happen outside of hospitals each year—and about 7 in 10 of those happen at home. 3 Unfortunately, about half of the people who experience cardiac arrests at home don’t get the help they need from bystanders before an ambulance arrives. 4.
What is the hand only method of CPR?
This method of CPR is called “hands-only” and does not involve breathing into the person’s mouth. Continue giving CPR until medical professionals arrive or until a person with formal CPR training can take over. Learn more about the hands-only method. external icon. of CPR from AHA.
Who is responsible for the provision of CPR forms?
Her Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service (HMCTS) is responsible for the provision of the CPR forms - if you have any comments or observations about the availability of court forms, please email [email protected]
Who approved the pre action protocol for personal injury claims below the small claims limit in road traffic accidents?
The Master of the Rolls as Head of Civil Justice has approved amendments to the Pre-Action Protocol for Personal Injury Claims Below the Small Claims Limit in Road Traffic Accidents (“the Protocol”).
What is the amendment to the Civil Procedure Act?
The Civil Procedure (Amendment No.5) (Coronavirus) Rules 2020 have been laid before Parliament.This follows the Lord Chancellor giving written notice to the Civil Procedure Rule Committee under s. 3A Civil Procedure Act 1997 that he thought it expedient that the Committee include provision in the rules that would extend the stay on possession proceedings.
Why Is CPR Important?
Keeping the blood flow active – even partially – extends the opportunity for a successful resuscitation once trained medical staff arrive on site.
What is CPR for collapse?
For the general public or bystanders who witness an adult suddenly collapse: compression-only CPR, or Hands-Only CPR. Hands-Only CPR is CPR without mouth-to-mouth breaths. It is recommended for use by people who see a teen or adult suddenly collapse in an out-of-hospital setting (such as at home, at work, or in a park).
What is the procedure called when the heart stops beating?
CPR – or Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation – is an emergency lifesaving procedure performed when the heart stops beating. Immediate CPR can double or triple chances of survival after cardiac arrest.
How deep should a CPR be?
In adult victims of cardiac arrest, it is reasonable for rescuers to perform chest compressions at a rate of 100 to 120/min and to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) for an average adult, while avoiding excessive chest compression depths (greater than 2.4 inches [6 cm]).
How many times more likely are men to receive CPR?
Men were 1.23 times more likely to receive bystander CPR in public, and their chance of survival was 23 percent higher compared to women.
What is cardiac arrest?
Occurs when the heart malfunctions and stops beating unexpectedly. Cardiac arrest is an “ELECTRICAL” problem.
Can children do CPR?
Even Children Can Perform Successful CPR. A recent study tested sixth graders and their capacity to use Hands-Only CPR to save lives. The study found that the majority of children could perform CPR in the correct location and at the appropriate compression rate, making this a viable group to train to help save lives.
Philadelphia Personal Injury Attorneys
We represent the families of infants who suffer with cerebral palsy as a result of negligence during delivery, retired workers and their families suffering from mesothelioma and other diseases caused by their exposure to asbestos, brain injury victims of every age, and investors or consumers who have been harmed through securities fraud, breaches of fiduciary duty, or consumer fraud.
Awards and Recognitions Nationally Recognized Trial Attorneys
Issued by: Trial Masters, LLC Selection Methodology can be found at: https://www.trialmasters.com/apply-membership/ Issued by: U.S. News & World Report L.P.
What is the CPR in court?
The Civil Procedure Rules ( CPR) are the rules of civil procedure used by the Court of Appeal, High Court of Justice, and County Courts in civil cases in England and Wales. They apply to all cases commenced after 26 April 1999, and largely replace the Rules of the Supreme Court and the County Court Rules. The CPR were designed to improve access ...
What is the purpose of CPR?
The CPR were designed to improve access to justice by making legal proceedings cheaper, quicker, and easier to understand for non-lawyers. As a consequence of this, many archaic legal terms were replaced with "plain English" equivalents, such as "claimant" for "plaintiff" and "witness summons" for "subpoena". ...
What is the purpose of pre action protocols in CPR?
To support the ethos of narrowing the issues prior to the use of proceedings and encapsulate best practice, the CPR introduced “pre-action protocols”. They are given force by Practice Direction – Protocols
What is the Civil Procedure Act?
The Civil Procedure Act 1997 (c. 12) was enacted on 27 February 1997. It conferred the power to make civil procedure rules. It also established the Civil Justice Council, a body composed of members of the judiciary, members of the legal professions and civil servants, and charged with reviewing the civil justice system.
How many persons are required to be authorised to conduct litigation in relation to all proceedings in the Senior Courts?
Three persons who have been authorised by a relevant approved regulator to conduct litigation in relation to all proceedings in the Senior Courts, including at least one with particular experience of practice in county courts
When did the Civil Procedure Rules come into force?
The Civil Procedure Rules 1998 (SI 1998/3132) were made on 10 December 1998 and came into force on 26 April 1999. The draft rules of practice formed their core.
Who published the Access to Justice Report?
History. In 1994, the Lord Chancellor instructed the then Master of the Rolls, Lord Woolf, to report on options to consolidate the existing rules of civil procedure. On 26 July 1996, Lord Woolf published his Access to Justice Report 1996 in which he "...identified a number of principles the civil justice system should meet to ensure access ...
Overview
The Civil Procedure Rules (CPR) were introduced in 1997 as per the Civil Procedure Act 1997 by the Civil Procedure Rule Committee and are the rules of civil procedure used by the Court of Appeal, High Court of Justice, and County Courts in civil cases in England and Wales. They apply to all cases commenced after 26 April 1999, and largely replace the Rules of the Supreme Court and the County Court Rules. The Civil Procedure Rules 1998 is the statutory instrument listing the rules.
History
In 1994, the Lord Chancellor instructed the then Master of the Rolls, Lord Woolf, to report on options to consolidate the existing rules of civil procedure. On 26 July 1996, Lord Woolf published his Access to Justice Report 1996 in which he "...identified a number of principles the civil justice system should meet to ensure access to justice. The system should –
(a) be just in the results it delivers; (b) be fair in the way it treats litigants; (c) offer appropriate pr…
The overriding objective
Implemented as a result of reforms suggested by Lord Woolf and his committee, one of the revelations of the rules is the “overriding objective” embodied in Part 1 of the Rules, which states:
1.1 (1) These Rules are a new procedural code with the overriding objective of enabling the court to deal with cases justly and at proportionate cost. (2) Dealing with a case justly includes, so far as is practicable – (a) ensuring that the parties are on an equal footing; (b) saving expense; (c) d…
Tracks
Claims with a value of not more than £10,000 (the amount increased on 1 April 2013) are usually allocated to the Small Claims Track unless: the amount claimed for pain, suffering, and loss of amenity is more than £1,000.00.; or the cost of the repairs or other work to residential premises claimed against the landlord by a tenant is estimated to be more than £1,000 - whether or not they are also seeking another remedy - or the financial value of any claim in addition to those repairs …
Pre-action Protocols
To support the ethos of narrowing the issues prior to the use of proceedings and encapsulate best practice, the CPR introduced “pre-action protocols”. They are given force by Practice Direction – Protocols
Pre-action protocols outline the steps that parties should take in particular types of dispute to seek information from, and to provide information to, each other prior to making a legal claim.
Creation of the Rules
Section 2 of the Civil Procedure Act 1997 requires that the CPR are made by a committee called the Civil Procedure Rule Committee. Members of the committee consist of:
Ex officio
• the Master of the Rolls/Head of Civil Justice
• the Deputy Head of Civil Justice (if there is one)
See also
• Civil Jurisdiction and Judgments Act 1982
• Lord Woolf
• Practice Direction
• The Civil Procedure Rules 1998
Bibliography
• Dwyer, D, The Civil Procedure Rules Ten Years On, Oxford University Press (2009).