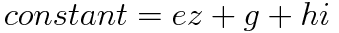
What is the critical fractile ratio?
Intuitively, this ratio, referred to as the critical fractile, balances the cost of being understocked (a lost sale worth (p − c) {\displaystyle (p-c)}) and the total costs of being either overstocked or understocked (where the cost of being overstocked is the inventory cost, or c {\displaystyle c} so total cost is simply p {\displaystyle p}).
What is the critical fractile of newsvendor model?
The crux of the newsvendor model is the critical fractile. In our newsvendor model example, we worked out the cost of underage or Cu of $0.80 and a cost of overage or Co of $0.20 above.
What is the fractile of a distribution?
If your distribution is known, then the fractile is just the cut-off point where the distribution reaches a certain probability. In visual terms, a fractile is the point on a probability density curve (PDF) so that the area under the curve between that point and the origin (i.e. zero) is equal to a specified fraction.
What is the profit function in critical fractile?
Profit function and the critical fractile formula. The standard newsvendor profit function is where is a random variable with probability distribution representing demand, each unit is sold for price and purchased for price , is the number of units stocked, and is the expectation operator.

What is the critical ratio in newsvendor model?
The critical ratio that is the optimal probability of not stocking out is the ratio of the unit underage cost to the sum of the unit underage and overage costs.
What is the purpose of the newsvendor model?
The newsvendor model is a mathematical approach in operations management to determine optimal inventory levels. The name is based on a newsboy trying to decide how many copies of newspaper will contemplate the demand of the day.
What is the newsvendor decision model?
The newsvendor (or newsboy or single-period or salvageable) model is a mathematical model in operations management and applied economics used to determine optimal inventory levels. It is (typically) characterized by fixed prices and uncertain demand for a perishable product.
What is Newspaperboy problem?
Also referred to as “newsboy problem”, it is named by analogy with the situation faced by a newspaper vendor who must decide how many copies of the day's paper to stock in the face of uncertain demand and knowing that unsold copies will be worthless at the end of the day.
What does newsvendor mean?
Definition of news vendor : a seller of newspapers.
How is newsvendor model different from EOQ model?
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model determines the least cost level of inventory to carry, as well as costs. News Vendor models are used for products only available for a single period.
What is the safety stock formula?
What is the safety stock formula? The safety stock formula is therefore: [maximum daily use x maximum lead time] – [average daily use x average lead time] = safety stock.
What is optimal service level?
An optimal service level is defined as a service level (delivered by certain number of servers) for which total cost of the system is minimum.
What is the optimal order quantity?
What is optimal order quantity? Optimal order quantity is the most cost-effective amount of inventory that a business should have at any given time. Put simply, this calculation represents your ideal order size to meet demand without tying up too much working capital in excess stock.
What is critical Fractile in supply chain?
The critical fractile defines the cost of having too much as the “cost of overage” or Co. Overage here indicates stocking more units than the demand of the relevant period. In our example, the newsvendor buys a newspaper for $0.20. So if he has newspapers remaining unsold, he loses $0.20 for every unsold newspaper.
How is underage cost calculated?
The overage cost per unit (Co) equals the item cost less any salvage value. The underage cost (Cu) per unit is the lost gross margin (price – cost), which is sometimes expanded to include estimates of lost goodwill from unsatisfied demand. Second, calculate the “critical ratio:” Cu/(Cu+Co).
What are common challenges with the newsvendor model?
Common Challenges With the Newsvendor Model No one ever wants to turn a customer away because of a stock-out. You might lose their business for good! Industries that rely on deep customer relationships (often with high switching costs) may have a substantial goodwill cost associated with underage events.
What is single period inventory model?
The single-period model is designed for products that share the following characteristics: They are sold at their regular price only during a single time period. Demand for these products is highly variable but follows a known probability distribution.
How do you find the optimal order quantity using the news vendor model?
4 Finding the Optimal Order Quantity cu = selling price - procurement/manufacturing cost. 2. Calculate the overage cost per unit, co. co = procurement/manufacturing cost - salvage value, where salvage value = discount price - any holding or transportation costs per unit.
How do you calculate underage costs?
The overage cost per unit (Co) equals the item cost less any salvage value. The underage cost (Cu) per unit is the lost gross margin (price – cost), which is sometimes expanded to include estimates of lost goodwill from unsatisfied demand. Second, calculate the “critical ratio:” Cu/(Cu+Co).
How is order up to level calculated?
Order up to level formulaOrder up to level quantity = Target level – (Safety Stock + Basic stock +(Lead Time in days* Unit Sales Per Day )).Order up to level quantity = Target level – (Lead Time in days* Unit Sales Per Day ).
Abstract
Explains a method for deciding upon inventory levels when demand is uncertain.
Citation
Bell, David E. "Critical-Fractile Method for Inventory Planning." Harvard Business School Background Note 191-132, January 1991. (Revised November 1994.)
What are the safety factors of geotechnical parameters?
The safety factors γ F, i = γ Sd γ f, i (as the factors γ E, i) account for the possibility of unfavourable deviation of the action values from the representative values and inaccuracies in the analyses related to the modelling of the effects of actions or to the modelling of the actions themselves. The safety factors γ M, i = γ Rd γ m, i account for the uncertainty in the resistance model and geometric deviations if these are not modelled explicitly, and the possible unfavourable deviation of the material or product properties from the representative values.
Can partial factors be applied to design values?
In these situations, the partial factors may be applied directly to the effects of actions derived from representative values of the actions ( EN 1997, 2004 ).
Newsvendor Model Applications
The setting used to formulate the newsvendor model may have been a humble news vendors’ challenge but this problem is faced by many businesses. Most MBA students will encounter the newsvendor problem given it’s possible application in a wide range of industries. Some of the situations where the newsvendor model can be applied include:
News Vendor Problem Example
Let’s say that the newsvendor sells about 50 papers a day. Unfortunately, demand is uncertain. On some days he sells as many as 80 papers and other days he sells as few as 10 papers. Let’s also assume that the newsvendor buys a paper for $0.20 and sells it for $1.
The Intuition Behind the Critical Fractile
The problem facing the newsvendor is two dimensional: On one side, if he orders too many newspapers, he will be left with unsold newspapers which reduces his profits. On the other hand, if he orders too few newspapers, he is losing out on the profit he could have had if he had newspapers to sell.
The Critical Fractile
So the critical fractile tries to balance Co and Cu. the critical fractile does this using the critical fractile formula below.
Applying The Critical Fractile to Different Distributions
Once the critical fractile is arrived at, inventory is ordered up to that point on the demand distribution. This is the level of inventory that meets the demand for the critical fractile percentage of times. This level of inventory is the point at which we maximize demand.
Critical fractal vs. Critical Fractile
The word fractile is defined in statistics as the value of a distribution for which some fraction of the sample lies below and therefore is the better word to pick up the concept of critical fractile. We have seen faculty use the word fractal.
Testing the News Vendor Model with a Simulation
Often students do not really believe that the newsvendor model works. They find it difficult to believe the newsvendor model because it uses the critical fractile formula which is so simple. We help address this doubt by simulating the newsvendor model using @Risk or Crystal Ball.
History
The mathematical problem appears to date from 1888 where Edgeworth used the central limit theorem to determine the optimal cash reserves to satisfy random withdrawals from depositors. According to Chen, Cheng, Choi and Wang (2016), the term "newsboy" was first mentioned in an example of the Morse and Kimball (1951)'s book.
Profit function and the critical fractile formula
where D {\displaystyle D} is a random variable with probability distribution F {\displaystyle F} representing demand, each unit is sold for price p {\displaystyle p} and purchased for price c {\displaystyle c} , q {\displaystyle q} is the number of units stocked, and E {\displaystyle E} is the expectation operator.
Derivation of optimal inventory level
To derive the critical fractile formula, start with E [ min { q , D } ] {\displaystyle \operatorname {E} \left [ {\min\ {q,D\}}\right]} and condition on the event D ≤ q {\displaystyle D\leq q} :
Data-driven models
There are several data-driven models for the newsvendor problem. Among them, a deep learning model provides quite stable results in any kind of non-noisy or volatile data. More details can be found in a blog explained the model.
Stepping Through Newsvendor Basics
Let’s say the vendor buys papers in bulk for $0.50 each and sells them for $2.50. Every paper sold generates $2.00 in profit, and at the end of the day unsold papers are discarded for a $0.50 loss. Naturally, we expect the vendor to prefer having some extra papers, because turning away a customer is more painful than tossing out a paper.
Getting More Advanced
In the real world, newsvendor problems are more nuanced and we need to account for more factors. The first step is to use more sophisticated overage and underage costs.
Situations Where the Newsvendor Model Shines
One core concept of the newsvendor is that you should favor outcomes that are less painful.
Common Challenges With the Newsvendor Model
No one ever wants to turn a customer away because of a stock-out. You might lose their business for good! Industries that rely on deep customer relationships (often with high switching costs) may have a substantial goodwill cost associated with underage events.
Final Thoughts
I hope this has been a useful introductory primer to the newsvendor model. It is a powerful tool at the core of many supply chain and operations strategies. My last takeaway for you is to remember that numbers don’t make decisions, people do. Any time you use a model like this, focus on clear and concise rationale for what you include.
What happens if the capacity of a factory or a machine over the planning horizon is set too low?
Selecting the right capacity for a facility or machine – If the capacity of a factory or a machine over the planning horizon is set too low, stockouts will occur. If capacity is set too high, the capital costs will be too high.
Is Q* a global optimum?
Testing the second derivative proves that Q* is a global optimum.