Do the deep abdominal muscles need strengthening?
“Core fitness is strengthening the muscles that support and stabilize the spine.” True core-building moves focus on that deep muscle of the abdominals, not the top rectus abdominus muscles, which don’t do much more than give you six-pack abs and help you bend forward.
What exercises strengthen abdominal muscles?
- Core exercises build abs and other core muscles
- Abdominal crunch
- Bridge
- Single-leg abdominal press
- Single-leg abdominal press variations
- Double-leg abdominal press
- Double-leg abdominal press variations
- Segmental rotation
- Quadruped
- Modified plank
What are the 4 layers of abdominal muscles?
transverse abdominis. the muscle layer on the side of the abdomen, below the internal obliques, responsible for compressing the ribs to bend the spine sideways. rectus abdominis. Rectus abdominis: the double line of muscle the runs up the front of the abdomen, responsible for flexing the lower spine. internal obliques.
What are the best exercises for lower abdomen?
- Bear. Get into an extended arm plank, propped up on your hands with hands directly beneath your shoulders, feet hip-width apart.
- One-Legged Mountain Climber. Start in a plank position with your right knee pulled into your chest. ...
- Army Crawl. ...
- C-Curve. ...
- Hip Tips. ...
- X-Factor. ...
- Six Pack Scissor. ...

What is the deepest muscle of the anterior abdomen?
transversus abdoministransversus abdominis – the deepest muscle layer. Its main roles are to stabilise the trunk and maintain internal abdominal pressure.
What is the deepest of the four abdominal muscles?
Transversus abdominis: The transversus abdominis is at the bottom of the stack. This pair of muscles is the deepest of the flat muscles. They stabilize the trunk and help maintain internal abdominal pressure.
Which is the deepest anterolateral muscle of the abdominal wall?
Transversus AbdominisTransversus Abdominis This is thinnest and deepest of the 3 anterolateral abdominal wall muscles. It originates from the lower 6 costal cartilages, lumbar vertebrae, iliac crests, and iliopsoas fascia. The fibers are oriented transversely and contribute to the rectus sheath medially.
What is the order of the abdominal muscles from the deepest to the most superficial?
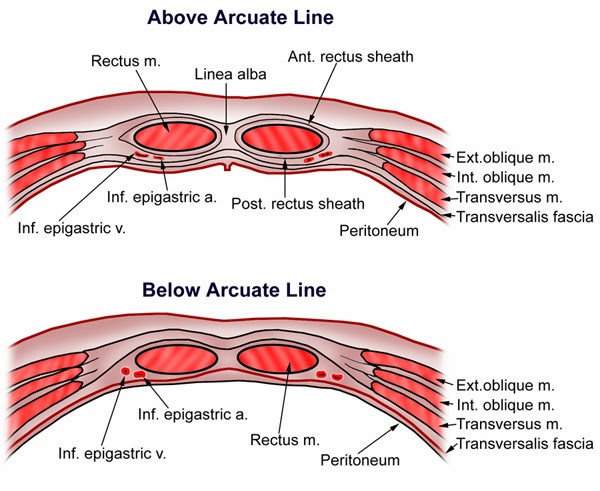
On the flanks of the body, medial to the rectus abdominis, the abdominal wall is composed of three layers. The external oblique muscles form the superficial layer, while the internal oblique muscles form the middle layer, and the transverses abdominus forms the deepest layer.
Is the rectus abdominis superficial or deep?
superficialHowever, trunk muscles are classified into 2 groups; superficial muscles that are part of the global muscle system and include the rectus abdominis (RA) and the external oblique (EO), and deep muscles that are part of the local muscle system and include the transverses abdominis (TrA), the multifidus and the internal ...
Is rectus abdominis deep to internal oblique?
From superficial to deep they consist of the external abdominal oblique's, the internal abdominal oblique's, rectus abdominis and the transversus abdominis. Working together these muscles form a wall that protects the internal organs and also helps to maintain an erect posture.
Is deep fascia present in anterior abdominal wall?
Chief layers of the abdominal wall include: Skin, Superficial fascia (the subcutaneous tissue which forms the thin, single layer above the umbilicus. Below the umbilicus, it is divided into two layers (1) the fatty superficial layer called Camper's fascia and (2) the deep layer called Scarpa's fascia.
Which are muscles of the anterior abdominal wall quizlet?
External Oblique Muscle.Internal Oblique Muscle.Transversalis Muscle.Rectus Abdominus.
Which of the following is the anterior abdominal wall muscle?
MusculatureOverview of the muscles of abdominal wallMuscleVascular supplyAnterior muscles (vertical muscles)Rectus abdominisSuperior and inferior epigastric arteriesPyramidalisInferior epigastric arteriesAnterolateral muscles (flat muscles)External obliqueLower intercostal, subcostal, and deep circumflex iliac arteries2 more rows•Jan 25, 2022
Which abdominal muscle is most superficial quizlet?
Terms in this set (5)Rectus abdominis (tendinous inscriptions) A superficial medial muscle layer on wall of abdomen (six pack) ... External oblique. The largest & most superficial of three muscle layers on abdominal wall. ... Internal Oblique. This muscle lies immediately under the external oblique. ... Transversus abdominis. ... Diaphram.
What are the 7 layers of abdomen?
LayersSkin.Subcutaneous tissue.Fascia. Camper's fascia - fatty superficial layer. Scarpa's fascia - deep fibrous layer. Superficial Abdominal fascia.Muscle. External oblique abdominal muscle. Internal oblique abdominal muscle. Rectus abdominis. Transverse abdominal muscle. ... Transversalis fascia.Extraperitoneal fat.Peritoneum.
What are the layers of abdominal muscles?
There are nine layers to the abdominal wall: skin, subcutaneous tissue, superficial fascia, external oblique muscle, internal oblique muscle, transversus abdominis muscle, transversalis fascia, preperitoneal adipose and areolar tissue, and peritoneum. Nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatics are present throughout.
Which of the following is the deepest of the abdominal muscles quizlet?
The transverse abdominal is the deepest muscle of the abdominal wall. The internal oblique is superficial to the transverse abdominal muscle (the external oblique is superficial to the internal oblique).
Which is a deep muscle of the back that runs vertically from the cranium to the sacrum?
Erector spinae musclesDefinitionThree groups of deep muscles located on either side of the vertebral columnFunctionBilateral contraction - extension of spine Unilateral contraction - lateral flexion of spine (ipsilateral)MnemonicI Like Standing (stands for Iliocostalis, Longissimus & Spinalis)
Which three muscles are responsible for compressing the abdomen?
To either side of the rectus abdominis are the other three layers of abdominal muscles. The deepest of those layers is the transversus abdominis, which has fibres that run perpendicular to the rectus abdominus; the transversus abdominis acts to compress and support the abdomen and provides static core stabilization.
What is the transversus abdominis?
The transverse abdominis is located in the abdomen immediately inside of the internal oblique muscle. It is one of the innermost muscles of the abdomen and it arises from the inguinal ligament, iliac crest, the inner surfaces of the lower six ribs and from the thoracolumbar fascia.
What are the deep muscles?
Deep muscles. Medically reviewed by the Healthline Medical Network — Written by the Healthline Editorial Team on January 19, 2018. The abdominal muscles provide postural support, protect internal organs, and perform other important functions. The lower abdominal muscles help protect the pelvic cavity. The rectus abdominis is the large muscle in the ...
Which muscle is responsible for a wide range of motions in the body?
Next to it on both sides of the body is the internal oblique. This wide muscle rotates the spine, increases pressure on the abdomen, and aids in breathing. It stretches from the front of the abdomen to the back of the torso. Another important group of muscles related to posture is the erector spinae. These elongated muscles run vertically ...
What muscles help protect the pelvic cavity?
The lower abdominal muscles help protect the pelvic cavity. The rectus abdominis is the large muscle in the middle portion of the abdomen. It facilitates the tilt of the pelvis and the curvature of the lower spine. Next to it on both sides of the body is the internal oblique.
What muscles are in the thigh?
These muscles include the piriformis, obturator internus, and gemellus inferior.
What muscles attach to the tibia?
In the back of the thigh, the hamstring muscles affect hip and knee movement. They begin under the gluteus maximus behind the hip bone and attach to the tibia at the knee. They are the biceps femoris (long head and short head), semimembranosus, and semitendinosus. Last medically reviewed on January 19, 2018.
Where do the adductor muscles attach?
They begin at the pelvis and attach to the femur. They are the adductor longus, adductor magnus, adductor minimus, and adductor brevis. When these muscles are strained during physical activity, the injury is commonly referred to as a “groin pull,” which is a frequent football injury.
Which muscles are involved in hip movement?
Other muscles that affect hip movement are the psoas major and iliacus. They are located near the adductors. They flex and rotate the hip and thigh.
What is the deepest abdominal muscle?
It is the deepest abdominal muscles and originates from the iliac crest, in guinal ligament, thoracolumbar fascia and inner surface of lower six costal cartilage and their ribs 7 to 12, inserts on xyphoid process and linea alba and pubis. The contraction of the transverses abdominis compresses the abdomen and tones the abdominal organs, example santolasana.
How many groups of muscles are there in the anterior abdominal region?
The anterior abdominal muscles can be divided in to four groups:
What is the purpose of the abdominal press?
The main tasks of this muscle is the movement of the trunk, stabilization of the vertebral column and the tension of the abdominal wall. The abdominal press increases the intra-abdominal pressure which occurs during defecation or vomiting. It also support the exhalation by pulling down the thorax through their contraction. Contracting the rectus abdominis brings the trunk forward or ventral flexion, elevation of the pelvis, lowering the thorax. The yoga asana navasana can strengthen the rectus abdominis.
Where is the obliques located?
It is located under the external obliques and originates from the lower borders of the lateral 1/3 of inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia and linea alba, inserts on linea alba and ribs 9 through 12. The contraction of the internal obliques brings the opposite side of the shoulder forward, example parivrita trikonasana.
What muscles are used to relax back bends?
The tightness of the abdominal muscles limits the depth of backbends. The stretching of this muscles can help you to relax and ease the muscles stress and tension.
What muscles are used to stabilize the trunk?
The abdominal muscles play a big role to stabilize, rotate our trunk and protect the abdominal organs. It has the airbag effect to protect our lumbar spine and prevent the hyperextension of the lumbar spine when we do the backbend in the yoga postures.
Where is the latissimus dorsi located?
It originates from the front of ribs 5 through 12 and lower section of latissimus dorsi, inserts on lower ribs, linea alba, inguinal ligament and anterior half of the iliac crest. When the external obliques are contracted, the same side of the shoulder will be drawn forward. It is responsible to the twist of the body by combining the contraction of the external obliques with the contraction of the other side internal obliques.
Which muscle group is located on either side of the abdomen?
Lateral flat muscle group situated on either side of the abdomen, which includes three muscles: external oblique, internal oblique and transversus abdominis .
Where is the anterolateral abdominal wall?
The anterolateral abdominal wall spans the anterior and lateral sides of the abdomen. It can be divided into several topographical areas, which are used to describe the location of abdominal organs and the pain associated with them:
What are the two sections of the abdominal wall?
The abdominal wall can be divided into two sections: anterolateral and posterior abdominal walls. This complex structure consists of numerous layers, from superficial to deep: skin, superficial fascia, muscles and their respective fasciae, and peritoneum . Key facts about the abdominal wall. Layers of the abdominal wall.
What is the abdominal wall?
The abdominal wall surrounds the abdominal cavity, providing it with flexible coverage and protecting the internal organs from damage. It is bounded superiorly by the xiphoid process and costal margins, posteriorly by the vertebral column and inferiorly by the pelvic bones and inguinal ligament.
How are the abdominal regions divided?
Nine abdominopelvic regions, which are divided horizontally by the superior subcostal plane, which passes right under the costal margins of the 10th ribs, and the inferior intertubercular plane, which connects the tubercules of the iliac crest. Vertically they are divided by the two midclavicular planes which pass through the midpoint of each clavicle and halfway between the pubic symphysis and the anterior superior iliac spine. The four planes create nine abdominal regions as you see in the picture: hypochondriac (right, left) and epigastric regions superiorly, flanks (right, left) and umbilical region in the middle, groin (right, left) and hypogastric region inferiorly.
How many abdominal regions are there?
The four planes create nine abdominal regions as you see in the picture: hypochondriac (right, left) and epigastric regions superiorly, flanks (right, left) and umbilical region in the middle, groin (right, left) and hypogastric region inferiorly. The regions and quadrants of the abdomen (diagram)
Which fascia is firmly attached to the linea alba and pubic symphysis?
Deep Scarpa's fascia, which is a thinner and denser membranous layer overlying the muscle layer of the abdominal wall. It is firmly attached to the linea alba and pubic symphysis and fuses with the fascia lata (deep fascia of the thigh) right below the inguinal ligament.
Which abdominal muscles are deepest?
Transversus abdominis: The transversus abdominis is at the bottom of the stack. This pair of muscles is the deepest of the flat muscles. They stabilize the trunk and help maintain internal abdominal pressure.
What muscle is located in the lower abdomen?
Pyramidalis: This vertical muscle is small and shaped like a triangle. It’s located very low, in your pelvis. It helps maintain internal pressure in your abdomen.
What are the main muscles of the abdominal region?
There are five main muscles: pyramidalis, rectus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques, and transversus abdominis. Ab strains and hernias are common, but several strategies can keep your abs safe and healthy.
What are the external obliques?
External obliques: The external obliques are a pair of muscles, one on each side of the rectus abdominis. They are the largest of the flat muscles and at the bottom of the stack. They run from the sides of your body toward the middle. The external obliques allow the trunk to twist side to side.
Where are the internal obliques located?
Internal obliques: The internal obliques are a pair of muscles on top of the external obliques, just inside your hip bones. Like the external obliques, they are on the sides of the rectus abdominis, running from the sides of your trunk toward the middle. They work with the external oblique muscles to allow the trunk to twist and turn.
How many muscles are there in the abdomen?
There are five main muscles in your abdomen. Two are vertical (up and down) muscles located toward the middle of your body. Three are flat muscles stacked on top of each other, situated toward the sides of the trunk.
Where are the abdominal muscles located?
They’re located toward the front of your body, between your ribs and your pelvis.
Where does the transverse abdominal tendon originate?
The transverse abdominal arises as fleshy fibers, from the lateral third of the inguinal ligament, from the anterior three-fourths of the inner lip of the iliac crest, from the inner surfaces of the cartilages of the lower six ribs , interdigitating with the diaphragm, and from the thoracolumbar fascia. It ends anteriorly in a broad aponeurosis (the Spigelian fascia), the lower fibers of which curve inferomedially (medially and downward), and are inserted, together with those of the internal oblique muscle, into the crest of the pubis and pectineal line, forming the inguinal conjoint tendon also called the aponeurotic falx. In layman's terms, the muscle ends in the middle line of a person's abdomen. : 248–250
Why do we use the transverse abdominal?
The transverse abdominal helps to compress the ribs and viscera, providing thoracic and pelvic stability. This is explained further here. The transverse abdominal also helps a pregnant woman to deliver her child.
Where is the aponeurosis inserted?
Throughout the rest of its extent the aponeurosis passes horizontally to the middle line, and is inserted into the linea alba; its upper three-fourths lie behind the rectus muscle and blend with the posterior lamella of the aponeurosis of the internal oblique; its lower fourth is in front of the rectus abdominis .
Which surface of the sternum and costal cartilages shows transversus thoracis?
Posterior surface of sternum and costal cartilages, showing Transversus thoracis.
Does TVA work on the abdominal muscles?
Training the rectus abdominis muscles alone will not and can not give one a "flat" belly; this effect is achieved only through training the TVA. Thus to the extent that traditional abdominal exercises (e.g. crunches) or more advanced abdominal exercises tend to "flatten" the belly, this is owed to the tangential training of the TVA inherent in such exercises. Recently the transverse abdominal has become the subject of debate between biokineticists, kinesiologists, strength trainers, and physical therapists. The two positions on the muscle are (1) that the muscle is effective and capable of bracing the human core during extremely heavy lifts and (2) that it is not. Specifically, one recent systematic review has found that the baseline dysfunction of TVA cannot predict the clinical outcomes of low back pain. Similarly, another systematic review has revealed that the changes in TVA function or morphology after different nonsurgical treatments are unrelated to the improvement of pain intensity or low back pain related-disability. These findings have challenged the traditional emphasis of using TVA-targeted intervention to treat low back pain.
/images/library/2101/tqClxjNaEpu6oFGzhfA_Musculus_rectus_abdominis_02.png)