
Definition: The Defense Planning Guidance establishes DoD’s force development planning and resource priorities in order to prevail in the Nation’s current operations and to develop a balanced joint force to meet future contingencies. Defense Planning/Programming Guidance (DPG) Classification The DPG is classified SECRET.
What is the National Defense Planning Guidance phase?
The phase involves reviewing the President’s National Security Strategy (NSS), the SECDEF’s National Defense Strategy (NDS), and the CJCS’s National Military Strategy (NMS) to ensure the resulting Defense Planning Guidance (DPG) aligns with the Administration’s policy goals and takes into account potential threats, force
What is the purpose of the Department of Defense Force planning program?
The DPG establishes DoD's force development planning and resource priorities in order to prevail in the Nation's current operations and to develop a balanced joint force to meet future contingencies.
What is the purpose of the Department of Defense program guidance?
The purpose of the DPG is to provide guidance in the form of goals, priorities, and objectives, including fiscal constraints, for the development of each Military Departments Program Objective Memorandum (POM) and Budget Estimate Submissions (BES).
What is the Department of Defense Policy (DPG)?
The DPG reflects the President’s National Security Strategy (NSS), the SECDEF’s National Defense Strategy (NDS), and the Chairman’s National Military Strategy (NMS). It also reflects the results of the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR), and the annual Chairman’s Program Recommendations (CPR). [1]
What is the DPG in the military?
What is the purpose of the DPG?
What is the Defense Planning Guidance?
What is the DPG?
When did the DPG replace the GDF?
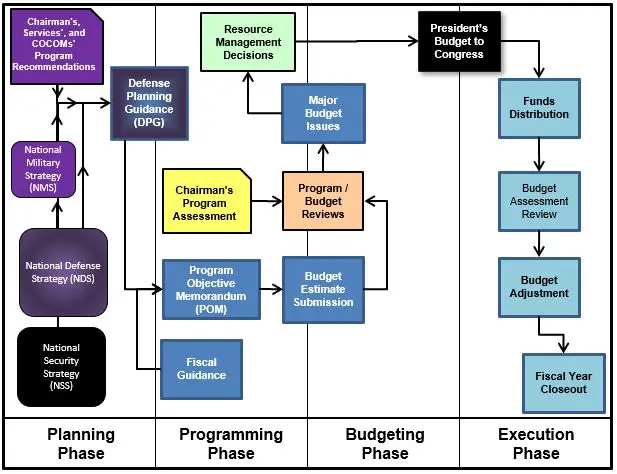
What is the impact of the Defense planning Guidance?
Defense Planning/Programming Guidance (DPG) Purpose The purpose of the DPG is to provide guidance in the form of goals, priorities, and objectives, including fiscal constraints, for the development of each Military Departments Program Objective Memorandum (POM) and Budget Estimate Submissions (BES).
Who creates the Defense planning Guidance?
The Under Secretary of Defense (USD) for Policy leads the planning phase. The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS) also plays a significant role in the process, in accordance with responsibilities as the principal military advisor to the SECDEF under Section 151 of Title 10, United States Code (U.S.C.).
What is the National Security Strategy 2022?
The 2022 National Security Strategy outlines how my Administration will seize this decisive decade to advance America's vital interests, position the United States to outmaneuver our geopolitical competitors, tackle shared challenges, and set our world firmly on a path toward a brighter and more hopeful tomorrow.
What is the purpose of the PPBE process?
Planning, Programming, Budgeting, and Execution (PPBE) is an annual Department of Defense (DOD) process for allocating resources. It serves as the framework for DOD civilian and military leaders to decide which programs and force structure requirements to fund based on strategic objectives.
What is the difference between POM and BES?
The POM and BES update the Future Years Defense Program (FYDP). The BES covers two years (such as FY 12 and FY 13). Changes to the POM are known as Fact of Life Changes (FoLCs), while changes to the BES are known as Change Proposals (CPs).
How long is the POM cycle?
POM Description The Program Objective Memorandum (POM) is a five-year plan that begins three years out from the current year, as shown in the Generate POM Input Every Year process flowchart.
What are the 7 elements of national security?
2.1 Physical security.2.2 Infrastructure security.2.3 Computer security.2.4 Political security.2.5 Economic security.2.6 Ecological security.2.7 Security of energy and natural resources.
What are the four pillars of security strategy?
By incorporating the four pillars of an effective security strategy – partnership, people, process and technology – companies can create a culture of risk awareness that permeates the entire organization.
What are the four pillars in the National Security Strategy?
Protect the homeland, the American people, and the American way of life. Promote American prosperity. Preserve peace through strength. Advance American influence.
What is the focus of the PPBE planning phase?
In the planning phase of the PPBE process, the focus is on defining the national defense strategy and ensuring that we have the military forces necessary to support that strategy, maintain national security, and support foreign policy.
Who is responsible for PPBE?
The PB organization has responsibility to: Oversee the Planning, Programming, Budgeting and Execution (PPBE) process for Department of Defense.
What is the planning phase of PPBE?
Planning: The Planning Phase of the PPBE Process is the definition and examination of alternative strategies, the analysis of changing conditions and trends, threats, technology, and economic assessments in conjunction with efforts to understand both change and the long-term implications of current choices.
Who approves the contingency planning guidance?
The Secretary issues this guidance with the approval of the President after consultation with the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The CPG focuses the guidance given in the National Security Strategy and Defense Planning Guidance, and is the principal source document for the Joint Strategic Capabilities Plan.
Who is in charge with the responsibility of directing planning and supervising the national defense program *?
The secretary of national defense (Filipino: kalihim ng tanggulang pambansa) is the head of the Department of National Defense and is a member of the president's Cabinet.
Who creates war plans?
In the U.S. military, an Operation Plan (OPLAN) is a complete and detailed plan for conducting joint military operations. An OPLAN is developed by the Combatant Commander (CCDR) of a Unified Combatant Command in response to actual or potential situations for which military operations may be required.
Who manages the Defense Travel System?
Defense Manpower Data Center (DMDC) Program Management Office DTS (PMO-DTS) has the program (acquisition, technical, operation and maintenance) oversight of DTS and the Defense Travel Management Office, OUSD (P&R) has functional oversight.
DOD Rules and Guidance Documents - U.S. Department of Defense
The Department of Defense provides the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security.
Untitled Document [ssl.armywarcollege.edu]
Defense Planning Guidance (DPG) Effective April 2010, the DPG replaces the Guidance for the Development of the Force (GDF) and the Joint Programming Guidance (JPG). The DPG establishes DoD's force development planning and resource priorities in order to prevail in the Nation's current operations and to develop a balanced joint force to meet future contingencies.
Approval Draft of the Defense Planning Guidance-Action ... - Archives
2 , SECftE'f/NOFORN . Powell, we have changed the text to read, "in which they can most effectively (including with minimum casualties) and most
Defense Primer: Planning, Programming, Budgeting, and ... - Congress
Defense Primer: Planning, Programming, Budgeting, and Execution (PPBE) Process https://crsreports.congress.gov (NMS) to align the resulting Defense Planning Guidance
Coronavirus: Latest DoD Guidance - U.S. Department of Defense
Coronavirus: Latest DoD Guidance The Defense Department continually provides information and resources on a variety of coronavirus-related subjects for members of the DOD community and the general ...
What was the DPG in 2002?
Many of the ideas contained in the draft DPG were also revived repeatedly over the next decade, serving as a broad framework for building a new neoconservative consensus whose preeminent expression ultimately arrived in the form of President George W. Bush’s 2002 National Security Strategy.
What is the PNAC statement?
Like the draft guidance, the PNAC statement called for U.S. global leadership and preemptive action, arguing, “Of course, the United States must be prudent in how it exercises its power. But we cannot safely avoid the responsibilities of global leadership or the costs that are associated with its exercise.
What is the first objective of the new regional defense strategy?
The guidance argued, “Our first objective is to prevent the reemergence of a new rival. This is a dominant consideration underlying the new regional defense strategy and requires that we endeavor to prevent any hostile power from dominating a region whose resources would, under consolidated control, be sufficient to generate global power. These regions include Western Europe, East Asia, the territory of the former Soviet Union, and Southwest Asia. There are three additional aspects to this objective: First the United States must show the leadership necessary to establish and protect a new order that holds the promise of convincing potential competitors that they need not aspire to a greater role or pursue a more aggressive posture to protect their legitimate interests. Second, in the non-defense areas, we must account sufficiently for the interests of the advanced industrial nations to discourage them from challenging our leadership or seeking to overturn the established political and economic order. Finally, we must maintain the mechanisms for deterring potential competitors from even aspiring to a larger regional or global role.” (For redacted versions of the original draft DPG and supporting documents, see the National Security Archive, February 26, 2008.)
What is the DPG?
The Defense Policy Guidance (DPG) drafted in the early months of 1992 provided a blueprint for maintaining U.S. preeminence, precluding the rise of a great power rival, and shaping the international security order in line with American principles and interests.
Who was responsible for the DPG?
Although rejected by the White House, the draft document had its supporters. Khalilzad told Mann that Cheney was impressed by it, allegedly telling Khalilzad, who was responsible for the actual writing of the DPG, “You’ve discovered a new rationale for our role in the world.” Neoconservatives outside government, like Charles Krauthammer, were also impressed. In a Washington Post column, Krauthammer asked, “What is the alternative? The alternative is Japanese carriers patrolling the Strait of Malacca, and a nuclear Germany dominating Europe” (quoted in Mann).
Did the DPG get declassified?
Declassification of the Draft DPG Despite the well-documented connection between the draft DPG and the Bush administration’s policies, efforts to declassify the DPG and related documents has proved difficult. In February 2008, the National Security Archive (NSA) at George Washington University published a number of redacted documents, including the original draft DPG. However, a February 26, 2008 archive press release about the documents, which it received through a Freedom of Information Act request, said, “Remarkably, these new releases censor a half dozen large sections of text that The New York Times printed on March 8, 1992, as well as a number of phrases that were officially published by the Pentagon in January 1993.” Tom Blanton, director of the archive, said, “On close inspection none of those deleted passages actually meet the standards for classification because embarrassment is not a legal basis for secrecy.”
Who created the DPG?
The Origins of the Draft DPG. Under the auspices of then-Defense Secretary Dick Cheney, Libby and Wolfowitz, two of the few neoconservatives with posts in the realist-dominated administration of George H.W. Bush, were given the task of producing the DPG, a classified document that outlines U.S.
What is WRDA 204?
Section 204 (f) authorizes the Secretary of the Army to be responsible for the operation and maintenance of improvements to a federally authorized harbor or inland harbor carried out by a non-Federal interest when certain conditions are met. Separate guidance is provided in ER 1165-2-209 regarding non-Federal interests undertaking a feasibility study, as authorized by Section 203 of WRDA 1986, as amended by Section 1014 (a) of WRRDA 2014, and in ER 1165-2-210 regarding non-Federal interests constructing a water resources development project, as authorized by Section 204 of WRDA 1986, as amended by Section 1014 (b) of WRRDA 2014.
What is USACE regulation?
This regulation establishes the policy for the management of operation and maintenance activities of U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) personnel performing civil works functions related to flood control, navigation, dredging, hydroelectric power generation, environmental stewardship, and recreation services at water resource, waterway, and other USACE projects.
What is an O&M pamphlet?
This operations and maintenance ( O&M) pamphlet establishes guidance and procedures for the management of activities at U.S. Army Corps of Engineers water resource development projects and supplements Engineer Regulation (ER) 1130-2-500.
What is the purpose of 36 CFR Part 327?
The purpose of this regulation is to provide policy and guidance on management of shorelines of Civil Works projects where 36 CFR Part 327 is applicable.
What is the purpose of the sedimentation manual?
This manual provides current guidance and engineering procedures for river and reservoir sedimentation investigations.
What is Section 215?
credit, repay, or combination) a non-Federal public body for construction of part of an authorized Federal project. It establishes general policies, outlines procedures to be followed in preparing a Section 215 agreement with an eligible non-Federal entity, and provides guidance on the provisions of such an agreement. The actual reaching of an agreement depends, in addition to observance of this guidance, on HQUSACE judgments concerning budget priorities, as set forth in paragraph 4f. All projects specifically authorized by the Congress are subject to this Act and this regulation.
What is the purpose of Executive Order 11988?
The purpose of this regulation is to set forth general policy and guidance for Corps of Engineers implementation of Executive Order 11988, Floodplain Management, as it pertains to the planning, design and construction of Civil Works projects, to activities under the operation and maintenance program , and to the real estate program of the Corps. Policy and guidance for implementation of Executive Order 11988 as it pertains to the Corps' regulatory program are contained in 33 CFR 320-330.
Force Health Protection Guidance
Department of Defense Guidance for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination Attestation, Screening Testing, and Vaccination Verification (Updated)
General Guidance
Supplemented, see June 21, 2021 Force Health Protection Guidance Supplement 17, Revision 1 memo
Pentagon Personnel Guidance
Rescinds CMO May 26, 2020 memo, “Pentagon Reservation Plan for Reslience and Aligning with National Guidelines for Opening Up American Again”
Vaccine Guidance
Memo from Director of Administration and Management: Supplemental Guidance for Mandatory COVID-19 Vaccination Attestation, Screening Testing, and Vaccination Verification of DoD Civilian Employees for the DoD Fourth Estate-Revision 2
What is the DPG in the military?
The Defense Planning/Programming Guidance (DPG) is used to lead the overall Planning Phase of the Planning, Programming & Budget Execution (PPBE) Process and consolidates force development planning priorities into a single overarching document for DOD planners to use. The DPG reflects the President’s National Security Strategy (NSS), the SECDEF’s National Defense Strategy (NDS), and the Chairman’s National Military Strategy (NMS). It also reflects the results of the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR), and the annual Chairman’s Program Recommendations (CPR). [1]
What is the purpose of the DPG?
The purpose of the DPG is to provide guidance in the form of goals, priorities, and objectives, including fiscal constraints, for the development of each Military Departments Program Objective Memorandum (POM) and Budget Estimate Submissions (BES).
What is the Defense Planning Guidance?
Definition: The Defense Planning Guidance establishes DoD’s force development planning and resource priorities in order to prevail in the Nation’s current operations and to develop a balanced joint force to meet future contingencies.
What is the DPG?
The DPG reflects the President’s National Security Strategy (NSS), the SECDEF’s National Defense Strategy (NDS), and the Chairman’s National Military Strategy (NMS). It also reflects the results of the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR), and the annual Chairman’s Program Recommendations (CPR). [1]
When did the DPG replace the GDF?
In 2010 the DPG replaced the Guidance for the Development of the Force (GDF) and the Joint Programming Guidance (JPG).
