What is the prognosis for autonomic dysfunction?
Patients with autonomic dysfunction (AUD) often have peripheral and/or cardiac denervation leading to impairment of the baroreflex, which is known to play a major role in determining hemodynamic outcome during orthostatic stress and low cardiac output states.
What are the symptoms of autonomic dysfunction?
What are the symptoms of autonomic dysfunction?
- Cardiovascular system. The most common symptoms that are caused by a dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system are lightheadedness and dizziness or fainting episodes.
- Gastro-intestinal symptoms. ...
- Urinary symptoms. ...
- Sexual dysfunction. ...
- Impaired sweating. ...
- Pupillary abnormalities. ...
How to live with autonomic dysfunction?
To help manage your dysautonomia symptoms:
- Do not smoke or drink alcoholic beverages.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Drink a lot of water. ...
- Add extra salt to your diet. ...
- Get plenty of sleep.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Keep your blood sugar within normal limits if you have diabetes.
- Listen to what your body is telling you it needs. ...
- If you feel dizzy, sit down, lie down, and/or raise your feet.
- Stand up slowly.
What are the symptoms of autonomic neuropathy?
What are the symptoms of autonomic neuropathy?
- Heart rate and blood pressure. Damage to the nerves that control your heart rate and blood pressure may make these nerves respond more slowly to a change in your body’s ...
- Digestive system. Autonomic neuropathy may also cause gastroparesis. ...
- Bladder. ...
- Sex organs. ...
- Sweat glands. ...
- Eyes. ...
- Ability to feel symptoms of hypoglycemia. ...

What is the autonomic nervous system definition?
Listen to pronunciation. (AW-toh-NAH-mik NER-vus SIS-tem) The part of the nervous system that controls muscles of internal organs (such as the heart, blood vessels, lungs, stomach, and intestines) and glands (such as salivary glands and sweat glands).
What is the main function of the autonomic nervous system quizlet?
What is the function of the autonomic nervous system? a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal.
What are the four functions of the autonomic nervous system?
Autonomic functions include control of respiration, cardiac regulation (the cardiac control center), vasomotor activity (the vasomotor center), and certain reflex actions such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting.
Whats the definition of autonomic?
Definition of autonomic 1 : acting or occurring involuntarily autonomic reflexes. 2 : relating to, affecting, or controlled by the autonomic nervous system or its effects or activity autonomic drugs.
Which is an autonomic body function?
The autonomic nervous system controls all "automatic" body functions, such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, mouth-watering (salivating), and the movement of food through the intestines (peristalsis).
Which of the following statements best describes the function of the autonomic nervous system?
The correct answer is (c) Controls and maintains homeostasis. The autonomic nervous system consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which control the unconscious processes that help maintain homeostasis, or stable, internal conditions.
What are 3 autonomic nervous system?
There are three branches to the ANS; the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system, and the enteric nervous system. The nerves in the sympathetic nervous system help to prepare the body for something happening within the environment and expend energy.
What are the 3 main functions of the nervous system?
The nervous system has three overlapping functions based on sensory input, integration, and motor output. At a more integrative level, the primary function of the nervous system is to control and communicate information throughout the body.
What are the main functions of the nervous system?
The nervous system helps all the parts of the body to communicate with each other. It also reacts to changes both outside and inside the body. The nervous system uses both electrical and chemical means to send and receive messages.
What is the main function of the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system directs the body's rapid involuntary response to dangerous or stressful situations. A flash flood of hormones boosts the body's alertness and heart rate, sending extra blood to the muscles.
Which part of the brain is involved in autonomic function?
The hypothalamusThe hypothalamus is the key brain site for central control of the autonomic nervous system, and the paraventricular nucleus is the key hypothalamic site for this control.
What is another word for autonomic?
What is another word for autonomic?independentautonomousself-directingemancipatedself-sufficientself-reliantenfranchisedmanumittedseparateselfstanding28 more rows
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Testing. Summary. The autonomic nervous system is a complex network of cells that controls the body’s internal state. It regulates and supports many different internal processes, often outside of a person’s conscious awareness. This article will explain the autonomic nervous system, or ANS, how it works, and the disorders ...
Which system regulates the heart rate?
For example, the SNS may increase heart rate to prepare a person to escape from danger. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS): Parasympathetic neurons mostly regulate bodily functions when a person is at rest.
What is the ANS in anatomy?
Anatomy. Share on Pinterest. The ANS helps to regulate many of the body’s internal functions, such as heart rate. The nervous system is a collection of cells that send and receive electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. The nervous system consists of two main parts:
How do sympathetic neurons react to a threat?
If the body perceives a threat in the environment, the sympathetic neurons of the ANS react by: increasing heart rate. widening the airways to make breathing easier. releasing stored energy. increasing strength in the muscles. slowing digestion and other bodily processes that are less important for taking action.
Which branch of the ANS regulates the internal organs?
The ANS regulates the internal organs to maintain homeostasis or to prepare the body for action. The sympathetic branch of the ANS is responsible for stimulating the fight or flight response. The parasympathetic branch has the opposite effect and helps regulate the body at rest.
Which system contains the brain and spinal cord?
The central nervous system: This consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system: This contains all the neurons outside of the central nervous system. The ANS is part of the peripheral nervous system. It is a collection of neurons that influence the activity of many different organs, including the stomach, heart, and lungs.
Can autonomic disorders be serious?
Autonomic disorders can be serious. People who experience symptoms of an autonomic disorder should see a doctor for a full diagnosis. Talking to a doctor is particularly important for people with diabetes or other conditions that can increase the likelihood of autonomic disorders.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Overview. The autonomic nervous system ( ANS) maintains blood pressure, regulates the rate of breathing, influences digestion, urination, and modulates sexual arousal. The sympathetic portion of the ANS controls reactions like the stress response and the fight-or-flight reaction. The parasympathetic portion of the ANS controls responses related ...
What is the relationship between the autonomic nervous system and the cardiovascular system?
The interaction between the autonomic nervous system and the cardiovascular system becomes even more important during pregnancy as there are large-scale changes to hemodynamics. Blood volume, basal oxygen consumption, red cell mass, cardiac output, and the heart rate increase in pregnant women.
What are the two major divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
There are two major divisions of the autonomic nervous system. The first is the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system generally controls the “flight-or-fight” response. This includes releasing stress hormones, regulating the metabolism of cells, and generally maintaining homeostasis in an ...
How does the nervous system affect the body?
The autonomic nervous system can influence digestive efficiency, altering the secretion of enzymes from glands and the rate of peristaltic movement.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system in a woman's labor?
There is evidence that the autonomic nervous system not only influences sexual arousal but also plays a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy and inducing labor.
Where do the sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons come from?
The neurons of the sympathetic nervous system emerge from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord, while the parasympathetic neurons are associated with the cranial and sacral regions. The sympathetic nervous system is usually activated in response to emergencies, especially those that threaten survival.
Which part of the ANS controls responses related to eating, growth, and reproduction?
The parasympathetic portion of the ANS controls responses related to eating, growth, and reproduction. The autonomic nervous system can be contrasted to the somatic nervous system, which is controlled voluntarily. Where the autonomic nervous system controls things like heart rate and digestion, the somatic nervous system controls things like muscle ...
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is one of the most incredible parts of the human body. Your nervous system takes in all the information in the world around you and sends a message to your muscles, allowing you to make your way through the world. Your autonomic nervous system also controls all of your vital functions, many of which you aren't consciously aware ...
Which neurotransmitter is responsible for communication in the autonomic nervous system?
Neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and norepinephrine are primarily responsible for communication in your autonomic nervous system. For both parasympathetic and sympathetic parts of the autonomic system, acetylcholine is released at the level of the ganglia. The acetylcholine receptors in ganglia are nicotinic and may be blocked by drugs such as ...
What is the name of the clump of nerves that synapse before the message is transmitted to
One of the interesting things about the autonomic nervous system is that, almost without exception, the nerves synapse in a clump of nerves called a ganglion before the message is transmitted to the target organ, such as a salivary gland. This allows for another level of communication and control.
Where do parasympathetic nerves travel?
Many nerves of the parasympathetic autonomic nervous system begin in the nuclei in your brainstem. From there, they travel through cranial nerves such as the vagus nerve, which slows the heart rate, or the oculomotor nerve, which constricts the pupil of the eye. Parasympathetic are what causes your eyes to tear and your mouth to salivate. Other parasympathetic terminate in the walls of thoracic and abdominal organs like the esophagus, gastrointestinal tract, pharynx, heart, pancreas, gallbladder, kidney, and ureter. The sacral parasympathetic synapse in ganglia in the walls of the colon, bladder, and other pelvic organs.
What happens when the sympathetic nervous system dominates?
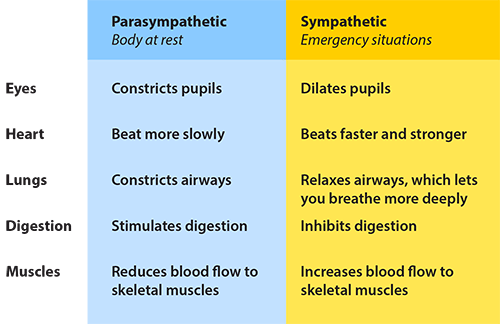
When the sympathetic nervous system dominates, your heart pumps hard and quickly, your peripheral blood vessels are narrow and tight, and your blood pressure will be high . In contrast, the parasympathetic system slows the heart and opens peripheral blood vessels, causing the blood pressure to fall.
Where do sympathetic nerve fibers exit?
Sympathetic fibers of the autonomic nervous system exit the lateral part of your spinal cord where they receive information from parts of the brain such as the brainstem and the hypothalamus. Fibers run from synapses in ganglia just outside the spinal column to their targets, usually along blood vessels.
Which nerves run along the carotid artery to the face and eye?
For example, the sympathetic nerves that dilate your eyes in response to darkness or a threat exit the spinal cord in your neck and synapse in the ganglion called the superior sympathetic ganglion, they then run along the carotid artery to your face and eye.
Why is the autonomic nervous system important?
Your autonomic nervous system is important for several reasons. It keeps your cardiac muscles and smooth muscles regulated (like the ones in your stomach). It also regulates various aspects of your body's glands depending on the type of environment and conditions.
Why do we need the autonomic nervous system?
You need the autonomic nervous system to stay alive, because it alerts your body to danger so you have the opportunity to move out of harm's way. Also, it has the ability to cause your body to rest. It is in this resting phase that your body has the ability to recuperate from stressful conditions or even the stresses of daily life.
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system is the part responsible for your fight or flight reaction, like the reaction you would have if you encountered a large animal while walking in the forest. It actually uses your body's energy to increase blood pressure, increase your heart rate, and decrease the digestive process, so you automatically go on full alert and can make the correct decision whether to leave the situation or remain face to face with the danger.
Which system uses norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter to put your body on full alert
The sympathetic nervous system uses norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter to put your body on full alert. Once the danger is over, however, the body will return to normal and your heart rate, blood pressure, and digestive system will begin working as they should. Parasympathetic Nervous System.
What are the divisions of the ANS?
There are three divisions of the ANS: sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, and enteric nervous system. Each works a bit differently, but they are all vital to ensuring your body remains intact and safe. {"error":true,"iframe":true}. You must c C reate an account to continue watching. Register to view this lesson.
Which part of the nervous system regulates the activity of the heart muscle?
Autonomic nervous system: A part of the nervous system that regulates key involuntary functions of the body, including the activity of the heart muscle; the smooth muscles, including the muscles of the intestinal tract; and the glands.
Which system slows the heart rate?
The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: the sympathetic nervous system, which accelerates the heart rate, constricts blood vessels, and raises blood pressure, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which slows the heart rate, increases intestinal and gland activity, and relaxes sphincter muscles. CONTINUE SCROLLING OR CLICK HERE.
Why is the sympathetic nervous system important?
The purpose of stimulating these bodily responses is to prepare the individual to either escape or fight in dangerous situations. Although the sympathetic nervous system was evolutionarily used in life threatening situations, modern day life and mental health can also trigger this response.
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems work?
The nerves in the parasympathetic nervous system mostly work by regulating the body’s functions when at rest, controlling mostly ‘quieter’ activities.
What are the causes of ANS dysfunction?
There are a number of other disorders which can be the result of ANS dysfunction: 1 Acute autonomic paralysis – associated with spinal cord injury, resulting in acute and uncontrolled hypertension. 2 Multiple system atrophy – a rare condition which causes gradual damage to the nerve cells. Pure autonomic failure – dysfunction of many processes controlled by the ANS. 3 Familial dysautonomia – also known as Riley-Day syndrome. This is an inherited condition where the nerve fibers do not function properly so these individuals have trouble feeling pain, temperature, pressure, and positioning their arms and legs.
What is the ANS system?
It can be further subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The ANS transmits information from and to the internal body organs such as the liver and the lungs.
What is a dysautonomic disorder?
Dautonomic dysfunction, or dysautonomia, is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does not function properly. In developed countries, the most common cause of issues with the ANS result from diabetes (Bishop, 2010).
What system comes into action when a situation is over?
The parasympathetic nervous system can also come into action once a threatening situation is over. For instance, thinking back to the scenario of walking home alone at night, once returned home and the threatening situation is over, the body relaxes.
How does the ANS work?
The ANS works by receiving information from either external stimuli or the body. The hypothalamus, which is right above the brain stem, receives autonomic regulatory input from the limbic system (a group of structures deep in the brain which are associated with functions such as memory, emotion, and fear). The hypothalamus uses this input ...
Which system contains both afferent and efferent fibers that provide sensory input and motor output?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) contain both afferent and efferent fibers that provide sensory input and motor output, respectively, to the central nervous system (CNS).
Which nerve receives information from the aortic arch and the carotid sinus?
Additionally, the vagus nerve conducts sensory information from baroreceptors of the carotid sinus and the aortic arch to the medulla.
Where do parasympathetic nerves exit?
Parasympathetic fibers exit the CNS via cranial nerves (CN) III, VII, IX, and X, as well as through the S2-4 nerve roots. There are four pairs of parasympathetic ganglia, and they are all located in the head. CN III, via the ciliary ganglion, innervates the iris and ciliary muscles of the eye.
Which ganglia receives input from the splanchnic nerve?
These include the celiac, aorticorenal, and superior and inferior mesenteric ganglia. The celiac ganglion receives input from the greater splanchnic nerve, the aorticorenal from the lesser and least splanchnic nerves, and the superior and inferior mesenteric from the least and lumbar splanchnic nerves.
What is the process of activation of the SNS?
Activation of the SNS leads to a state of overall elevated activity and attention: the “fight or flight” response. In this process, blood pressure and heart rate increase, glycogenolysis ensues, gastrointestinal peristalsis ceases, etc.[5] The SNS innervates nearly every living tissue in the body.
Which receptors are activated by the innate immune system?
Cells of the adaptive immune system primarily express beta-2 receptors, while those of the innate immune system express those as well as alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. [15][24] Macrophages activate by alpha-2 stimulation and are suppressed by beta-2 adrenergic receptor activation.
Which receptors express affinity for NE?
The subtype of the receptor, alpha-1, alpha-2, beta-1, beta-2, or beta-3, and the tissues in which they express influences the affinity of NE for the receptor.[15] . For more information, see the StatPearls articles related to adrenergic receptors, at the following references.

How It Works
Functions
Potential Problems
- When the parasympathetic and sympathetic components of the autonomic nervous systems become out of sync, people can experience an autonomic disorder, also called dysautonomia. There are numerous types of autonomic disorders, each with its own unique set of symptoms, including:4 1. Acute autonomic paralysis 2. Afferent baroreflex failure 3. Familial dysautonomia …
Symptoms
- If you or someone you love is experiencing disruptions in the autonomic nervous system, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms. Some people experience one cluster of symptoms at one time, and another set of symptoms at other times. The symptoms can be fleeting and unpredictable or triggered by specific situations or actions, like after ingesting certa…
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis of an autonomic disorder requires a doctor's evaluation, which may include a physical examination, recording blood pressure when the patient is both lying down and standing, testing of the sweat response, and an electrocardiogram. Diagnosing an autonomic disorder is often tricky since both the physical exam and laboratory tests can come back normal. There is current…
A Word from Verywell
- The autonomic nervous system plays an important role in the human body, controlling many of the body's automatic processes. This system also helps prepare the body to cope with stress and threats, as well as returning the body to a resting state afterward. Learning more about this part …
Overview
- The autonomic nervous system (ANS) maintains blood pressure, regulates the rate of breathing, influences digestion, urination, and modulates sexual arousal.The sympathetic portion of the ANS controls reactions like the stress response and the fight-or-flight reaction. The parasympathetic portion of the ANS controls responses related to eating, growth, and reproduction. The autonom…
Autonomic Nervous System Function
- The autonomic nervous system controls many systems, including the cardiovascular system. It can alter the force and rate of heart contractility, as well as the constriction and dilation of blood vessels. Therefore, it also influences blood pressure. The rate of breathing can also be changed by the autonomic nervous system. It affects both skeletal ...
Autonomic Nervous System Divisions
- There are two major divisions of the autonomic nervous system. The first is the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system generally controls the “flight-or-fight” response. This includes releasing stress hormones, regulating the metabolism of cells, and generally maintaining homeostasis in an organism. The second division of the autonomic nervous syste…
Examples of The Autonomic Nervous System Response
- Fight or Flight Responses
The autonomic nervous system is often described using theresponse to imminent physical danger and the recovery of the body after the threat has receded. For instance, when faced with a predator, the body increases heart rate and breathing, reduces digestive secretions and activity, … - General Activity
However, even in the absence of an external threat, the two branches of the autonomic nervous system undergo changes and interact closely with the endocrine system to minutely monitor the internal and external environment. For instance, sympathetic activation can lead to an increase i…
Autonomic Nervous System Disorders
- There are a wide variety of autonomic nervous system disorders within humans. Over 1 million Americans every year will experience dysfunction of the autonomic system, known as dysautonomia.Since the ANS is mainly responsible for the fight-or-flight response and the breed-and-feed response, any disorder will likely affect one of these two systems. For example, a com…