
aerobic (ɛəˈrəʊbɪk) adj 1. (Biology) (of an organism or process) depending on oxygen 2. (Biology) of or relating to aerobes
What is aerobic vs. anaerobic in biology?
Anaerobic in Biology?
- Working for ATP. The cells in any living organism require energy to do their jobs, whether that's protecting the body from harmful bacteria, breaking down food inside the stomach or ...
- Cellular Respiration Basics. All cells must undergo cellular respiration in order to function. ...
- Oxygen Use and Glycosis. ...
- Aerobic vs Anaerobic Respiration. ...
What is the difference between aerobic and anerobic?
- Zone 1: Recovery – Less than 85% of LTHR
- Zone 2: Aerobic – 85-89%
- Zone 3: Tempo – 90-94%
- Zone 4: Sub-Threshold – 95-99%
- Zone 5A: Super-Threshold – 100-102%
- Zone 5B: Aerobic Capacity – 103-106%
- Zone 5C: Anaerobic Capacity – More than 106%
What organisms are anaerobic and aerobic?
The anaerobic bacteria commonly recovered are Prevotella, Porphyromonas, Fusobacterium and Peptostreptococcus spp., and the aerobic bacteria are beta-hemolytic and microaerophilic streptococci. Is E coli aerobic or anaerobic? E. coli is a metabolically versatile bacterium that is able to grow under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic process?
- The anaerobic treatment of wastewater generates much less sludge than the aerobic treatment does.
- The sludge produced in anaerobic wastewater treatment can be used for soil enrichment.
- There are lower costs required to handle sludge compared to those incurred in aerobic treatment.
What is aerobic short answer?
Aerobic respiration is the respiration where glucose is broken in the presence of oxygen to release energy (ATP) with carbon dioxide and water being produced as by-product.
What is aerobic and anaerobic in biology?
Living organisms use energy released by respiration for their life processes. There are two types of respiration – aerobic (which needs oxygen) and anaerobic (which doesn't need oxygen). Biology (Single Science)
What is an example of aerobic in biology?
Aerobic organisms are organisms that need oxygen to make energy. Although some aerobic organisms, such as animals, breathe in oxygen through lungs or gills, other organisms, like plants, fungi, and bacteria, are also aerobic. All aerobic organisms use cellular respiration to make energy.
What does aerobic mean in biology quizlet?
relating to, involving, or requiring free oxygen. Exercise Physiology.
What is anaerobic in biology?
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment.
What is aerobic and and aerobic respiration?
Aerobic means “with air”. Therefore, aerobic respiration is the process of cellular respiration that uses oxygen to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most plants and animals, including humans, birds and other mammals.
What is aerobes and anaerobes?
aerobe, an organism able to live and reproduce only in the presence of free oxygen (e.g., certain bacteria and certain yeasts). Organisms that grow in the absence of free oxygen are termed anaerobes; those that grow only in the absence of oxygen are obligate, or strict, anaerobes.
What does aerobic mean in cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts.
What is aerobic and anaerobic quizlet?
Aerobic respiration. Respiration which uses oxygen and produces relatively large amounts of energy. Anaerobic respiration. Respiration without oxygen and produces relatively small amounts of energy.
What does aerobic and anaerobic mean quizlet?
Anaerobic. means without oxygen. exercise consists of brief intense bursts of physical activity, such as weightlifting and sprints, where oxygen demand surpasses oxygen supply. While aerobic exercise relies on oxygen, anaerobic exercise is fueled by energy stored in your muscles through a process called glycolysis.
What is aerobic cellular respiration quizlet?
aerobic cellular respiration. a metabolic process that efficiently converts the energy found within food molecules into ATP. summary reaction of ACR. oxygen + sugar - carbon dioxide + water + energy.
Why do we need aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is why we need both food and oxygen, as both are required to produce the ATP that allows our cells to function.
How are aerobic and anaerobic respiration similar?
Similarities. Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration are methods of generating energy. They also both start in the same way, with the process of glycolysis. “Glycolysis” literally means “sugar splitting,” and involves breaking a sugar molecule down into two smaller molecules. In the process of glycolysis, two ATP molecules are consumed ...
What is the sugar molecule that is broken down in aerobic respiration?
In cells that have oxygen and aerobic respiration can proceed, a sugar molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. In cells that do not have oxygen, the sugar molecule is broken down into other forms, such as lactate.
Where does glycolysis occur?
Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first stage of aerobic respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves the splitting of 1 six-carbon sugar molecule into 2 three-carbon pyruvate molecules. This process creates two ATP molecules.
Which is more efficient, aerobic or anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is much more efficient, and produces ATP much more quickly, than anaerobic respiration. This is because oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor for the chemical reactions involved in generating ATP. An overview of the stages of aerobic respiration.
What is the product of respiration?
The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate ( ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to power chemical reactions. It is often referred to as the “currency” of the cell.
Do cells use anaerobic respiration?
Cells that are deprived of oxygen but do not normally use anaerobic respiration, like our own muscle cells, may leave the end products of glycolysis sitting around, obtaining only two ATP per sugar molecule they split. This is an inefficient method of obtaining energy by respiration.
What does aerobics mean?
pertaining to or caused by the presence of oxygen. of or utilizing the principles of aerobics: aerobic exercises; aerobic dances.
What is aerobic exercise?
Aerobic exercise, such as running, swimming, and doing calisthenics for an extended time, is designed to improve the body's use of oxygen. The New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy, Third Edition Copyright © 2005 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
Which process requires oxygen?
Occurring in the presence of oxygen or requiring oxygen to live. In aerobic respiration, which is the process used by the cells of most organisms, the production of energy from glucose metabolism requires the presence of oxygen. Compare anaerobic.
Does aerobic fermentation require oxygen?
Gradually, as decay progresses, the aerobic organisms increase in number. An aerobic species usually require little oxygen, but aerobic species a free supply. It is one of the aerobic ferments, and is present in what is known as the "mother" of vinegar and is secreted by it.
Is aerobic exercise good for weight loss?
But the science reveals that aerobic training is the best form of exercise for weight loss. Over-training is the result of systemic inflammation and under-recovery—not aerobic exercise. My hypnotic trip is the highly oxygenated state of aerobic exercise.
Is aerobic microbe revivable?
So Morono and colleagues wondered whether any aerobic, or oxygen-liking, microbes found there might be revivable.
What does "aerobic" mean?
aerobic synonyms, aerobic pronunciation, aerobic translation, English dictionary definition of aerobic. adj. 1. Biology a. Living or occurring only in the presence of free oxygen: aerobic bacteria. b.
Why is aerobicstability important in corn silage?
Aerobicstability is an important factor to ensure corn silage quality and provide a good preserved nutrient with low amount of mold spores and toxicogenic compounds [4]. Temperature and microbial changes of corn silage during aerobic exposure.
Is running anaerobic or aerobic?
anaerobic, anaerobiotic- living or active in the absence of free oxygen; "anaerobic bacteria". 2. aerobic- based on or using the principles of aerobics; enhancing respiratory and circulatory efficiency; "aerobic dance"; "running is very aerobic". anaerobic- not aerobic; "isometric exercises are anaerobic".
Does aerobic fitness affect heart disease?
Poor aerobic fitness can up diabetes , heart disease risk in kids. ISLAMABAD -- Lack of exercise, particularly poor aerobicfitness, in children increases their risk for developing Type-2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, said a new study. Poor aerobic fitness can up diabetes, heart disease risk in kids.
Why do aerobes need oxygen?
The reason aerobes need oxygen is to make energy.
Where does air travel in the body?
In humans, air enters through the nose and mouth and travels through tubes called bronchi into the lungs. At the end of the bronchi are small spheres called alveoli, which is where oxygen from the lungs moves into the blood and carbon dioxide moves out of the blood into the lungs to be exhaled.
How do plants get oxygen?
Plants, which make their own oxygen through a process called photosynthesis, take in oxygen through their stomata. Fungi use root-like structures called hyphae to get oxygen from the soil. Bacteria are single-celled and absorb oxygen directly from their environment. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
How do animals get oxygen?
Animals are multicellular, made of many cells. Most animals are aerobic, which means they need oxygen to survive. Even fish and sharks that live underwater use gills to filter oxygen into their blood. Other animals that live on land take in oxygen through their lungs. In humans, air enters through the nose and mouth and travels through tubes called bronchi into the lungs. At the end of the bronchi are small spheres called alveoli, which is where oxygen from the lungs moves into the blood and carbon dioxide moves out of the blood into the lungs to be exhaled. The fresh oxygen in the blood travels throughout the body, where it is used by cells to make energy.
Is fungus an aerobe?
Aerobic Fungi. As with plants, fungi might not be the first thing to come to mind when we think of aerobes. And actually, not all fungi are aerobes. For example, some yeasts, which are types of fungi, are anaerobic, which means they don't use oxygen. These are the same yeast we use to make alcoholic beverages, like beer and wine.
Is a bacteria anaerobic or aerobic?
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that are everywhere in the world, even though we can't see them with the naked eye. Although some bacteria are anaerobic, many are aerobic. Oxygen diffuses into bacteria's cells directly from the environment. Bacteria also go through cellular respiration, using oxygen to make ATP.
What is aerobic respiration?
All cells can get a little energy through a process called glycolysis, during which sugars are broken down. Aerobic respiration is a much more efficient way to produce energy.
How does aerobic respiration produce energy?
Aerobic respiration is a much more efficient way to produce energy. Aerobic organisms use oxygen in the cellular processes called the Kreb’s cycle and electron transport chain to produce 36 ATP, the molecules that transport energy within the cell.
What are facultative anaerobes?
Facultative anaerobes are organisms that can survive both with and without oxygen. They are aerobic when they have access to oxygen, but when they are in environments without oxygen, they switch to anaerobic respiration or fermentation. Yeast is a good example of a facultative anaerobe. In the presence of oxygen they produce carbon dioxide, ...
What is the process of breaking down food into energy called?
They use either fermentation or a process called anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is limited to glycolysis, which produces 2 ATP to fuel the cell.
Why do organisms need oxygen?
Most organisms need oxygen to survive. They use it to metabolize sugars, proteins and lipids, but they also suffer oxidative damage, or breakdown of DNA and other cell components, if they don’t get rid of it fast enough.
What are the two types of organisms that are anaerobic?
Aerobic organisms include almost all plants and animals and many protozoa, fungi and bacteria . Anaerobic organisms are mostly microscopic, like bacteria and protozoa, but some more complex organisms that exist in harsh environments are anaerobic.
Is yeast anaerobe?
Yeast is a good example of a facultative anaerobe. In the presence of oxygen they produce carbon dioxide, which makes bread rise, but when they are deprived of oxygen, they resort to the fermentation, which produces alcohol in wines and beer.
How does aerobic respiration work?
Both processes begin with the splitting of a six-carbon sugar molecule into 2 three-carbon pyruvate molecules in a process called glycolysis. This process consumes two ATP molecules and creates four ATP, for a net gain of two ATP per sugar molecule that is split.
Where do chemical reactions occur in aerobic respiration?
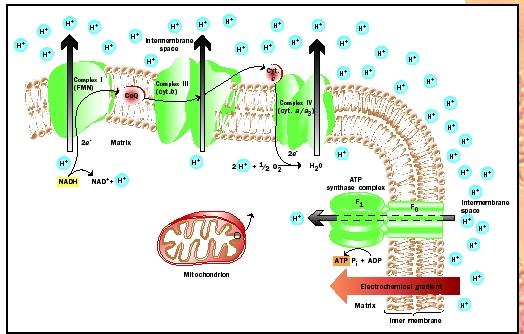
During aerobic respiration, the electron transport chain, and most of the chemical reactions of respiration, occur in the mitochondria.
What are the two types of organisms that cannot survive without oxygen?
Organisms can be classified based on the types of cellular respiration they carry out. Obligate aerobes – organisms that cannot survive without oxygen. For example, humans are obligate aerobes. Obligate anaerobes – organisms that cannot survive in the presence of oxygen.
What are the different types of anaerobic respiration?
The types of anaerobic respiration are as varied as its electron acceptors. Important types of anaerobic respiration include: 1 Lactic acid fermentation – In this type of anaerobic respiration, glucose is split into two molecules of lactic acid to produce two ATP. It occurs in certain types of bacteria and some animal tissues, such as muscle cells 2 Alcoholic fermentation – In this type of anaerobic respiration, glucose is split into ethanol or ethyl alcohol. This process also produces two ATP per sugar molecule. This occurs in yeast and even in some types of fish, such as goldfish. 3 Other types of fermentation – Other types of fermentation are performed by some bacteria and archaea. These include propionic acid fermentation, butyric acid fermentation, solvent fermentation, mixed acid fermentation, butanediol fermentation, Stickland fermentation, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis.
What substances do anaerobic cells use?
Instead of oxygen, anaerobic cells use substances such as sulfate, nitrate, sulfur, and fumarate to drive their cellular respiration. Many cells can perform either aerobic or anaerobic respiration, depending on whether oxygen is available.
What is the process of converting energy from fuel into a form that a cell can use?
Respiration is the process through which the energy stored in fuel is converted into a form that a cell can use. Typically, energy stored in the molecular bonds of a sugar or fat molecule is used to make ATP, by taking electrons from the fuel molecule and using them to power an electron transport chain.
Why is respiration important for survival?
Respiration is crucial to a cell’s survival because if it cannot liberate energy from fuels, it will not have sufficient energy to drive its normal functions. This is why air-breathing organisms die so quickly without a constant supply of oxygen: our cells cannot generate enough energy to stay alive without it.
.PNG)