Enthalpy
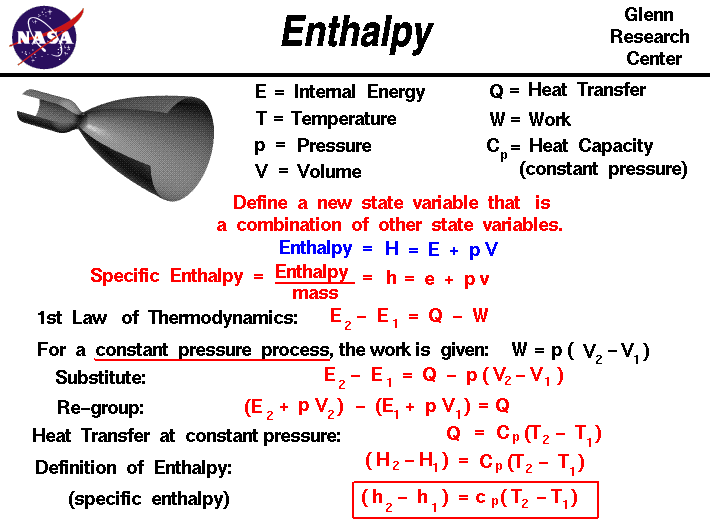
Enthalpy is a measure of energy in a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.
How to calculate enthalpy change?
Solution
- The reaction can be reversed. This will change the sign of ΔH f.
- The reaction can be multiplied by a constant. The value of ΔH f must be multiplied by the same constant.
- Any combination of the first two rules may be used.
How do you calculate enthalpy of change?
To calculate the enthalpy of solution (heat of solution) using experimental data:
- Amount of energy released or absorbed is calculated. q = m × C g × ΔT. q = amount of energy released or absorbed.
- calculate moles of solute. n = m ÷ M.
- Amount of energy (heat) released or absorbed per mole of solute is calculated. ΔH soln = q ÷ n.
What is the formula for enthalpy change?
- ρ (" rho ") is density (mass per unit volume),
- h is the specific enthalpy (enthalpy per unit mass),
- (ρh) represents the enthalpy density (enthalpy per unit volume),
What is standard enthalpy change?
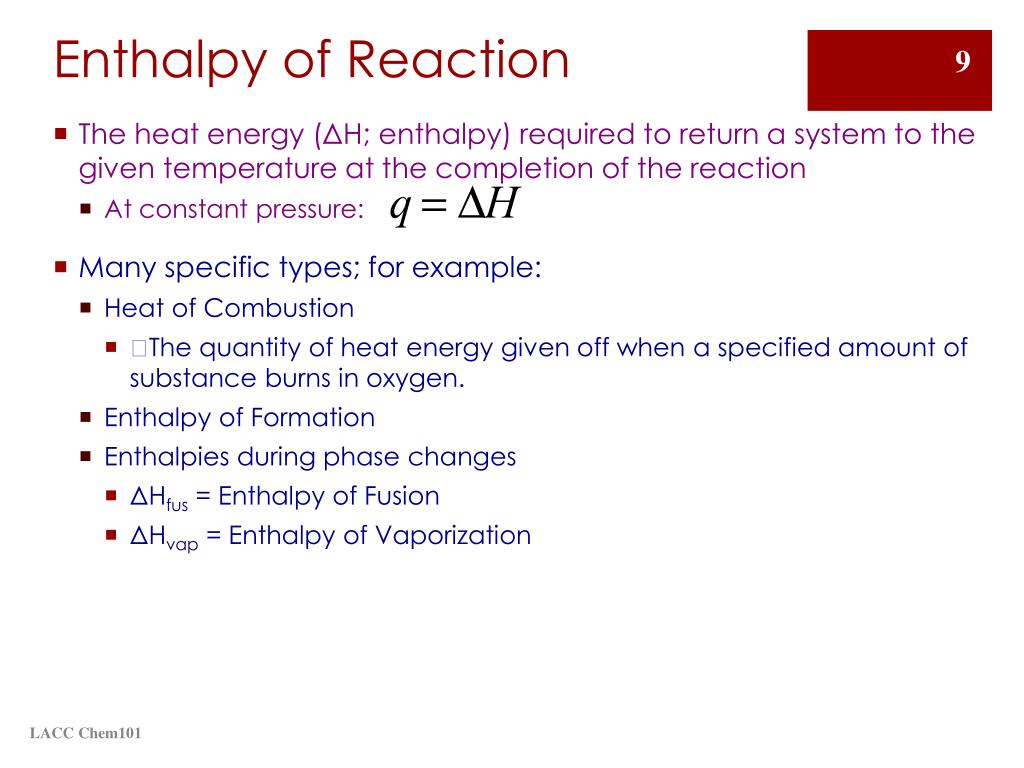
The standard enthalpy of reaction is the enthalpy change that occurs in a system when a chemical reaction transforms one mole of matter under standard conditions.
What is the definition of enthalpy change of reaction quizlet?
Enthalpy change is defined as the. amount of energy released/taken in during a chemical reaction (cannot be measured) An exothermic reaction is one that. releases energy into its surroundings.
What is enthalpy change in physical chemistry?
Enthalpy (H) is the heat content of a system at constant pressure. Chemists routinely measure changes in enthalpy of chemical systems as reactants are converted into products. The heat that is absorbed or released by a reaction at constant pressure is the same as the enthalpy change, and is given the symbol ΔH.
What is an example of enthalpy change?
One example is if you start with six moles of carbon combined with three of hydrogen, they combust to combine with oxygen as an intermediary step and then form benzene as an end-product. Hess' law states that the change in enthalpy of the reaction is the sum of the changes in enthalpy of both parts.
Which definition describes enthalpy quizlet?
Enthalpy, H, is a measure of the heat energy in a chemical system, and it cannot be measured.
What is enthalpy and entropy?
Enthalpy is the measure of total heat present in the thermodynamic system where the pressure is constant. It is represented as. Δ H = Δ E + P Δ V. where E is the internal energy. Entropy is the measure of disorder in a thermodynamic system.
What is the definition and symbol for enthalpy change?
Enthalpy change is the name given to the amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a reaction carried out at constant pressure. It is given the symbol ΔH, read as "delta H".
How do you determine enthalpy change?
Use the formula ∆H = m x s x ∆T to solve. Once you have m, the mass of your reactants, s, the specific heat of your product, and ∆T, the temperature change from your reaction, you are prepared to find the enthalpy of reaction. Simply plug your values into the formula ∆H = m x s x ∆T and multiply to solve.
Does enthalpy change with temperature?
In general, enthalpy of any substance increases with temperature, which means both the products and the reactants' enthalpies increase.
What are the types of enthalpy changes?
The following are some of the most common types of enthalpies:Enthalpy of Formation.Enthalpy of Combustion.Enthalpy of Solution.Enthalpy of Neutralisation.Enthalpy of Hydration.Enthalpy of Fusion.Enthalpy of Vaporisation.Enthalpy of Sublimation.More items...•
What statement is true about enthalpy?
Which statement about enthalpy is true? The enthalpy of formation for a pure element in its standard state is always positive. The enthalpy of formation for a pure element in its standard state is always negative. Enthalpy is a state function because its change depends only on initial and final conditions.
What describes the enthalpy change associated with endothermic?
Which describes the enthalpy change associated with an endothermic reaction? It is positive because the enthalpy of the products is greater than the enthalpy of the reactants.
What is entropy quizlet?
Entropy. It is the measure of disorder (randomness) in a system. The thermochemical variable 'S' stands for the amount of randomness in a system. Phases of matter involving entropy.
What is the enthalpy change?
An enthalpy change is approximately equal to the difference between the energy used to break bonds in a chemical reaction and the energy gained by the formation of new chemical bonds in the reaction. It describes the energy change of a system at constant pressure. Enthalpy change is denoted by ΔH. At constant pressure, ΔH equals ...
How is entropy related to heat?
In an exothermic reaction, the entropy of the surroundings increases. As heat is evolved, the energy imparted to the system increases disorder. In an endothermic reaction, the external entropy decreases.
What happens to the external entropy of an endothermic reaction?
In an endothermic reaction, the external entropy decreases. As heat is absorbed by a process or reaction, the kinetic energy of molecules in the surroundings decreases, which tends to reduce reduce disorder. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. "Enthalpy Change Definition in Science.".
Definitions of enthalpy changes
Standard enthalpy change of reaction ( ΔHrθ ) is the energy change in a chemical reaction when the molar quantities of reactants stated in the chemical equation react at 298K and 1 bar.
Keywords in the definition of enthalpy changes
If you look at all the definitions above, they generally involve writing these keywords or phrases:
Learn about Chemical Energetics
Now that you have learnt the definitions of the different types of enthalpy change, it’s time to apply them to questions. I If you would like to learn the topic on enthalpy change and chemical energetics in detail, do check out our course on Chemical Energetics here.
What is the enthalpy of a substance?
The specific enthalpy is equal to the specific internal energy of the system plus the product of pressure and specific volume. h = u + pv. In general, enthalpy is a property of a substance, like pressure, temperature, and volume, but it cannot be measured directly.
How is enthalpy determined in chemistry?
The enthalpy is widely used also in chemistry. Chemical reactions are determined by the laws of thermodynamics. In thermodynamics, the internal energy of a system is the energy contained within the system, excluding the kinetic energy of motion of the system as a whole and the potential energy of the system as a whole due to external force fields. The enthalpy of a chemical reaction is defined as the enthalpy change observed in a constituent of a thermodynamic system when one mole of substance reacts completely.
What is the SI unit of enthalpy?
The SI unit of enthalpy is the joule (J). It is the energy contained within the system, excluding the kinetic energy of motion of the system as a whole and the potential energy of the system as a whole due to external force fields. It is the thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the total heat content of a system.
What is the enthalpy of a fuel rod?
Temperature field inside a fuel rod. As was written, the enthalpy is one of thermodynamic potentials and represents a measure of energy in a thermodynamic system. Enthalpy is an extensive quantity, it depends on the size of the system, or on the amount of substance it contains. H = U + pV.
Why is change in enthalpy calculated?
Change in enthalpy is calculated rather than enthalpy, in part because total enthalpy of a system cannot be measured since it is impossible to know the zero point. However, it is possible to measure the difference in enthalpy between one state and another.
What is enthalpy in science?
She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Enthalpy is a thermodynamic property of a system. It is the sum of the internal energy added to the product of the pressure and volume of the system. It reflects the capacity to do non-mechanical work and the capacity to release heat .
Can total enthalpy be measured?
In the same way, total enthalpy cannot be measured, but the change in enthalpy (three ladder rungs) can.
What is the enthalpy change of a reaction?
The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change which occurs when equation quantities of materials react under standard conditions, and with everything in its standard state.
What is standard enthalpy change?
Standard enthalpy changes. Standard enthalpy changes refer to reactions done under standard conditions, and with everything present in their standard states. Standard states are sometimes referred to as "reference states". Standard conditions. Standard conditions are: 298 K (25°C) a pressure of 1 bar (100 kPa).
How many kJ of heat is formed when 2 moles of hydrogen gas react with 1 mole of oxygen gas
In this case, 572 kJ of heat is evolved when 2 moles of hydrogen gas react with 1 mole of oxygen gas to form 2 moles of liquid water. Notice that everything is in its standard state. In particular, the water has to be formed as a liquid. And there is a hidden problem!
What is the enthalpy change of an element in its standard state?
The standard enthalpy change of formation of an element in its standard state is zero. That's an important fact. The reason is obvious . . . For example, if you "make" one mole of hydrogen gas starting from one mole of hydrogen gas you aren't changing it in any way, so you wouldn't expect any enthalpy change.
What is the symbol for a standard enthalpy change of reaction?
Here is a simple reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to make water: First, notice that the symbol for a standard enthalpy change of reaction is ΔH°r. For enthalpy changes of reaction, the "r" (for reaction) is often missed off - it is just assumed.
What is the name of the amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a reaction carried out at constant pressure?
Enthalpy change is the name given to the amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a reaction carried out at constant pressure. It is given the symbol ΔH, read as "delta H". Note: The term "enthalpy change" only applies to reactions done at constant pressure.
When a standard enthalpy change is quoted, what are standard conditions assumed?
Whenever a standard enthalpy change is quoted, standard conditions are assumed. If the reaction has to be done under different conditions, a different enthalpy change would be recorded. That has to be calculated back to what it would be under standard conditions.
What is the enthalpy of a chemical reaction?
The heat absorbed or emitted under constant pressure from a device is referred to as enthalpy, and the reaction enthalpy is the change in enthalpy arising from a chemical reaction.
What is enthalpy in thermodynamics?
What is Enthalpy? Enthalpy is the measurement of energy in a thermodynamic system. The quantity of enthalpy equals to the total content of heat of a system, equivalent to the system’s internal energy plus the product of volume and pressure. For more content on thermodynamics click here. Technically, enthalpy describes the internal energy ...
What is the term for the amount of energy required to generate a system?
For more content on thermodynamics click here. Technically, enthalpy describes the internal energy that is required to generate a system and the amount of energy that is required to make room for it by establishing its pressure and volume and displacing its environment. Enthalpy diagram.
Why is enthalpy important?
Enthalpy is important because it informs us how much heat is in a system (energy). Heat is important, since from it, we can derive valuable work. An enthalpy shift shows us how much enthalpy was lost or obtained in terms of a chemical reaction, enthalpy meaning the system’s heat energy.
What is enthalpy based on?
Enthalpy is also described as a state function completely based on state functions P, T and U. It is normally shown by the change in enthalpy (ΔH) of a process between the beginning and final states.
When a process begins at constant pressure, the evolved heat (either absorbed or released) equals the answer
When a process begins at constant pressure, the evolved heat (either absorbed or released) equals the change in enthalpy. Enthalpy change is the sum of internal energy denoted by U and product of volume and Pressure, denoted by PV, expressed in the following manner.
What is cumulative energy?
The cumulative energy that is stored in the device is internal energy. It is the amount held by the mechanism of potential and kinetic energy. Enthalpy is specified as the amount of the system’s internal energy plus the combination of the system’s gas pressure and its length.
What is the enthalpy change of a reaction?
The enthalpy change of a reaction is the amount of heat absorbed or released as the reaction takes place, if it happens at a constant pressure. You complete the calculation in different ways depending on the specific situation and what information you have available. For many calculations, Hess’s law is the key piece of information you need to use, ...
What is the enthalpy of fusion?
When a substance changes from solid to liquid, liquid to gas or solid to gas, there are specific enthalpies involved in these changes. The enthalpy (or latent heat) of melting describes the transition from solid to liquid (the reverse is minus this value and called the enthalpy of fusion), the enthalpy of vaporization describes ...
What is the enthalpy of sodium chloride?
The addition of a sodium ion to a chloride ion to form sodium chloride is an example of a reaction you can calculate this way. Ionic sodium has an enthalpy of −239.7 kJ/mol, and chloride ion has enthalpy −167.4 kJ/mol. Sodium chloride (table salt) has an enthalpy of −411 kJ/mol. Inserting these values gives:
What is the end product of a reaction if you start with six moles of carbon combined with three of hydrogen
One example is if you start with six moles of carbon combined with three of hydrogen, they combust to combine with oxygen as an intermediary step and then form benzene as an end-product. Hess’ law states that the change in enthalpy of the reaction is the sum of the changes in enthalpy of both parts.
Does it matter if a reaction transforms on a substance into another substance?
This means that if reaction transforms on substance into another, it doesn’t matter if the reaction occurs in one step (reactants become products immediately) or whether it goes through many steps (reactants become intermediaries and then become products), the resulting enthalpy change is the same in both cases.
Is enthalpy endothermic or exothermic?
If (q) is positive, the reaction is endothermic (i.e., absorbs heat from its surroundings), and if it is negative, the reaction is exothermic (i.e., releases heat into its surroundings). Enthalpy has units of kJ/mol or J/mol, or in general, energy/mass. The equations above are really related to the physics of heat flow and energy: thermodynamics.
What is the enthalpy of a reaction?
Chemical properties: Enthalpy of reaction, defined as the enthalpy change observed in a constituent of a thermodynamic system when one mole of substance reacts completely.
What is the enthalpy of a system?
The enthalpy, H(S[p], p, {Ni}), expresses the thermodynamics of a system in the energy representation. As a function of state, its arguments include both one intensive and several extensive state variables. The state variables S[p], p, and {Ni} are said to be the natural state variables in this representation. They are suitable for describing processes in which they are determined by factors in the surroundings. For example, when a virtual parcel of atmospheric air moves to a different altitude, the pressure surrounding it changes, and the process is often so rapid that there is too little time for heat transfer. This is the basis of the so-called adiabatic approximation that is used in meteorology.
What is the difference between entropy and energy?
The term enthalpy was coined relatively late in the history of thermodynamics, in the early 20th century. Energy was introduced in a modern sense by Thomas Young in 1802 , while entropy was coined by Rudolf Clausius in 1865. Energy uses the root of the Greek word ἔργον ( ergon ), meaning "work", to express the idea of capacity to perform work. Entropy uses the Greek word τροπή ( tropē) meaning transformation. Enthalpy uses the root of the Greek word θάλπος ( thalpos) "warmth, heat"
What is the temperature of enthalpy?
Standard state does not strictly specify a temperature, but expressions for enthalpy generally reference the standard heat of formation at 25 °C (298 K). For endothermic (heat-absorbing) processes, the change ΔH is a positive value; for exothermic (heat-releasing) processes it is negative.
Is the enthalpy of a gas dependent on its temperature?
The enthalpy of an ideal gas is independent of its pressure, and depends only on its temperature, which correlates to its internal energy. Real gases at common temperatures and pressures often closely approximate this behavior, which simplifies practical thermodynamic design and analysis.
Is enthalpy an intensive property?
Enthalpy is an extensive property ; it is proportional to the size of the system (for homogeneous systems). As intensive properties, the specific enthalpy h = H. /. m is referenced to a unit of mass m of the system, and the molar enthalpy Hm is H.
Who used the term "heat content"?
Introduction of the concept of "heat content" H is associated with Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron and Rudolf Clausius ( Clausius–Clapeyron relation, 1850). The term enthalpy first appeared in print in 1909.
