
What are commonly called fats and oils?
Fats and oils are mixtures of different esters derived from a variety of long-chain carboxylic acids called fatty acids with the alcohol propane-1,2,3-triol (commonly known as glycerol). What are the different between fats and oils? Fats and oils are totally different from each other.
What are some differences between fats and oils?
- Lipids are fats and oils. Both animals and plants use them for energy storage.
- The distinction between fats and oils is that fats are solid at room temperature, and oils are liquid.
- The fat stored in hibernating animals helps them survive. Oil is stored in seeds, which aids in their survival.
- Water doesn't mix with fat or oil.
What are three functions of fats and oils?
- Fats and oils are lipids. They are important energy stores in animals and plants.
- Fats are solid at room temperature whereas oils are liquids.
- Hibernating animals survive by using up their stores of body fat. Some plant seeds survive because they contain a store of oil.
- Fats and oils do not mix with water.
What foods have fats and oils in them?
Fats and oils enter our diet through a variety of sources; dairy products, and meat, fish, poultry and seafood are all sources of fats, and some vegetable and plant foods are sources of oils. Fats and oils also enter our diet through many of the products we add to our foods to aid cooking or to simply make them more ‘palatable’.

What is the meaning for fats and oils?
What is the definition of fat and oil? Fats and oils are made up of molecules known as triglycerides, which are esters consisting of three fatty acid units connected to glycerol. The rise in the amount of shorter chain fatty acids and/or unsaturated fatty acids reduces the melting point for fat or oil.
What is a fat simple definition?
noun. Definition of fat (Entry 3 of 3) 1 : animal tissue consisting chiefly of cells distended with greasy or oily matter. 2a : oily or greasy matter making up the bulk of adipose tissue and often abundant in seeds.
What is the meaning of fats in science?
In chemistry and biology, fats are a type of lipid consisting of triesters of glycerol and fatty acids or triglycerides. Because they are organic compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen atoms, they are generally soluble in organic solvents and largely insoluble in water. Fats are solid at room temperature.
What are the 3 main types of fats?
They are:monounsaturated fats.polyunsaturated fats.saturated fats.trans fats.
What are fats for Class 6?
Fats are obtained either from plants or from animals. Groundnut oil, soybean oil and mustard oil are examples of fats derived from plants. Fats like butter and ghee are obtained from animals. Fats act as fuel in our body but they provide more energy than carbohydrates.
What is a fat in slang terms?
The word fat can mean someone is rich (fat cat) or something is plentiful (a fat stack of dollar bills). Phat comes from Black slang and has been commonly used within the hip-hop community. For example, it was used in the 1996 song “No Diggity” by Blackstreet and the 2000 song “Stan” by Eminem.
What does fat mean in a nice way?
plumpSometimes, people replace the word fat with words intended to be more polite or euphemistic, such as heavy, heavyset, plump, and chubby.
What makes a fat a fat chemistry?
A triglyceride is called a fat if it is a solid at 25°C; it is called an oil if it is a liquid at that temperature. These differences in melting points reflect differences in the degree of unsaturation and number of carbon atoms in the constituent fatty acids.
What is the definition of fat and oil?
Fats and oils are made up of molecules known as triglycerides, which are esters consisting of three fatty acid units connected to glycerol. The ris...
What is the function of fat?
Dietary fats are important to improve your body’s energy and cell growth. They even help to protect your organs and help keep your body moist. Fat...
What are fats and oils functions?
The body uses fat as a power source, and fat is the primary component of energy storage in the body. Fat also has many other essential roles in the...
What types of fat are good?
Monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats are known as ‘healthy fats’ because they are good for your skin, your cholesterol, and your general s...
What are the main sources of fats?
Fat is one of the three essential macronutrients that the body needs, along with carbohydrates and proteins. A balanced diet should contain healthy...
What is the difference between fat and oil?
One difference between fats and oils is that at room temperature fats are solid whereas oils are liquid. Fats and oils are both made of one part called glycerol attached to three other parts called fatty acids. Glycerol is a thick liquid with many industrial uses. The fatty acids can vary and this makes the different kinds of fats and oils.
What are Oils?
Unsaturated fats belong to this category. Consuming food containing unsaturated fat helps improve cholesterol levels. There are two types of unsaturated fats. Monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats.
What is the best fat for cholesterol?
Monounsaturated fat is found in nuts, vegetable oils and avocado. Consuming food that is rich in monounsaturated fats helps in controlling cholesterol levels by keeping high good HDL cholesterol and lowering bad LDL cholesterol. Polyunsaturated fat is found in oils such as sunflower, corn and soybean.
Why are monounsaturated fats considered healthy fats?
Monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats are known as ‘healthy fats’ because they are good for your skin, your cholesterol, and your general safety. These fats can help: reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Lower low levels of LDL cholesterol thus growing healthy HDL.
What are some examples of fatty acids?
Some better examples of these fatty acids are avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds and fatty fish.
Why is trans fat important?
This fat is harder at room temperature. The importance of trans fat is that it makes flakier pie crusts and crispier crankers. It is found in cookies, chips, processed food etc. Avoid eating or consume fewer foods containing trans fats as it increase your cholesterol levels.
What is the primary component of energy storage?
The body uses fat as a power source, and fat is the primary component of energy storage in the body. Fat also has many other essential roles in the body, and a reasonable amount in the diet is required for good health. Food fats come in a number of forms, including saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
What are the requirements for fat?
Different food products have different requirements as far as the functionality of the fat they contain is concerned. These requirements can often be condensed down to four basic headings: 1 melting point and melting profile 2 crystallization characteristics 3 storage stability (oxidative and hydrolytic stability) 4 nutritional requirements.
How many carbon atoms are in a fat?
The fatty acids found in most commonly consumed oils and fats are composed of long carbon and hydrogen chains, typically containing from 8 to 20 carbon atoms, mainly with even numbers of carbon atoms, although animal fats also contain significant levels of odd-chain fatty acids.
Why are animal fats removed from pastry?
However, these were phased out partly for ethical and religious reasons and partly because these kinds of animal fats were considered to be ‘unhealthy’ due to high levels of saturated fat and , therefore, high risks of cardiovascular diseases. This is quite ironic when one considers that they were replaced by partially hydrogenated fats with high levels of trans fatty acids which were subsequently found to have an even worse effect on cardiovascular disease risks. As with all hydrogenated fats, these two animal fats have now been almost completely removed from bakery products and have largely been replaced by either palm oil (Atkinson, 2011) or blends of palm oil and its fractions or with oils such as rapeseed oil. To an extent, considering the history of these changes, this is also quite ironic because palm oil contains about 50% saturates which is higher than the levels of saturates typically found in lard and beef tallow!
What fats are needed for baking?
From a product functionality point of view, different groups of food products will have different requirements. Bakery products (e.g. pastry and biscuits) require a fat with a moderate amount (25-40%) of solid fat to be present during dough preparation to give a light texture without undue oil exudation in the final product. Chocolate needs to be based on cocoa butter from both a legislative and functionality point of view and any fats used to replace cocoa butter need also to conform to legislation and to melt and crystallise in the same way as cocoa butter. In general, ice cream needs to be based on a fat which is at least 50% solid at 0°C and which melts below mouth temperature. Frying oils need to have as good an oxidative stability as possible to allow both an extended ‘fry life’ and also good shelf stability in the end product.
How many carbon atoms are in a monounsaturated fatty acid?
The most common monounsaturated fatty acid is oleic acid, containing 18 carbon atoms. In oleic acid, the double bond is between carbon atoms 9 and 10 (counting from the COOH group) Polyunsaturated fatty acids have more than one double bond in the carbon chain.
Which type of fatty acid has a double bond?
In linolenic acid, the first double bond is at the third carbon atom and so linolenic acid is called an omega-3 polyunsaturate. The fourth type of fatty acid, trans fatty acids, are also unsaturated but, in this case, some or all of the double bonds are in the trans configuration.
What is the process of oil modification?
There are three main types of oil modification process used in foods. Hydrogenation is a reaction between hydrogen and the carbon-carbon double bonds in an unsaturated fatty acid. It changes the cis -unsaturated fatty acid either to saturated or to trans -unsaturated.
What is fat and oil?
fats and oils, group of organic substances that form an important part of the diet and also are useful in many industries. The fats are usually solid, the oils generally liquid at ordinary room temperatures. Some tropical products, liquids in their sites of origin, become solids in cooler climates; in commerce these often retain ...
What is the formula for fats and oils?
Chemically fats and oils are either simple or mixed glyceryl esters ester, any one of a group of organic compounds with general formula RCO2 R′ (where R and R′ are alkyl groups or aryl groups) that are formed by the reaction between an alcohol and an acid. .....
What are the three radicals found in fat?
All known natural fats and oils contain three different acid radicals that are unbranched and usually contain an even number of carbon atoms. The saturated fatty acids most often found in fat and oil molecules are stearic and palmitic acids, and the main unsaturated fatty acids are oleic, linoleic, and linolenic acids.
What are the different types of fats used in food?
Animal fats used in foods include butter, lard, chicken fat, and suet. Olive, corn, peanut, soybean, and palm oils are among the many vegetable oils used in foods. Partially hydrogenated vegetable oils, also known as trans fats, were formerly widely used in packaged foods, but that use is now banned or highly restricted in the United States and other countries. Cod-liver oil and some other fish oils are used therapeutically as sources of vitamins A and D. Nutritionally fats and oils are valued as a source of energy. Because they contain less oxygen than other nutrients, they oxidize more readily and release more energy. Fats are digested in the human body chiefly by the enzyme lipase (in the pancreatic juice) aided by the bile. There are several theories to explain the method of absorption of fats; favored by many is the view that they are absorbed by the epithelial cells of the lining of the small intestine in the form of the fatty acids and glycerol into which they are split by digestion and that a recombination to re-form the fat occurs within the cells. Most of the fat then enters the lymphatic system through the villi in the lining of the small intestine, although some is probably absorbed directly by the blood vessels of the villi. Medical research indicates the possibility that saturated fats in the diet contribute to the incidence of arteriosclerosis arteriosclerosis
What chemical property makes fats solid and oils liquid?
The lower grades are suitable for making soap and for other industrial purposes. The chemical property that makes fats solid and oils liquid is the amount of saturation in the ester (see saturated fats saturated fat, any solid fat that is an ester of glycerol and a saturated fatty acid.
How are fats and oils physicochemical and chemical properties determined?
The physicochemical and chemical properties of a fat or oil are determined to a considerable degree by the ratio of its component saturated and unsaturated acids. Fats and oils are insoluble in water and readily soluble in organic solvents; they are usually slightly soluble in alcohol.
Why is cod liver oil used?
Because they contain less oxygen than other nutrients, they oxidize more readily and release more energy.
What is the type of nutrient that is composed of the ester of fatty acids and their mixtures?
Fat is a type of nutrient composed of the ester of fatty acids and their mixtures which occur in living beings and are taken up through different food sources.
What is the composition of olive oil?
Olive oil has been increasingly used in cooking, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals as well as soaps. The composition of olive oil is triglycerides, free fatty acids, mono and diglycerides, and some hydrocarbons.
What are the two groups of unsaturated fatty acids?
Oils or unsaturated fatty acids can be further divided into two distinct groups; monounsaturated fatty acids with a single double or triple bonds in the structure and polyunsaturated fatty acids with more than one double or triple bond in the structure .
Why are oil molecules not found in cells?
Oils are not commonly found in the structure of cell and living systems as they have stronger forces between the molecules.
What is olive oil used for?
Olive oil has been increasingly used in cooking, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals as well as soaps.
What is the color of butter?
The color of natural butter depends on the source, and the animal’s feed, and genetics. In general, the color can range from deep yellow to nearly white.
What is butter made of?
Butter is a dairy product obtained from milk which has a fat content of about 80%.
What is polyunsaturated fat?
polyunsaturated fat a fat containing polyunsaturated fatty acids; see also fat.
What is a greasy, soft-solid material, found in animal tissues and many plants, composed of a?
3. A greasy, soft-solid material, found in animal tissues and many plants, composed of a mixture of glycerol esters; together with oils, fats comprise the homolipids.
What is brown fat?
brown fat a thermogenic type of adipose tissue containing a dark pigment, and arising during embryonic life in certain specific areas in many mammals, including humans (see illustration); it is prominent in the newborn. Called also brown adipose tissue.
What does "greasy" mean?
2. Full of fat or oil; greasy.
Is margarine a saturated fat?
Through the process of hydrogenation, hydrogen can be incorporated into certain unsaturated fatty acids so that they are converted into solid fats for cooking purposes. Margarine is an example of the hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids into a solid substance.
What are the two main parts of fat?
There are two main parts of fats - glycerol backbone and fatty acid. Fat (and therefore oil) is made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The molecular structure of the fatty acid determines whether it is fat or oil.
Why is fat saturated?
Why saturated? Since there are single bonds and no double bonds, there are enough hydrogen atoms in it. In other words, this fat is saturated with hydrogen atoms. Hence it is called saturated fat. The presence of too many hydrogen atoms results in too strong intermolecular attraction in the fats. Hence the molecular structure of fats remains robust and stable. This makes the fats remain solid at room temperature.
What is the process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated fats?
In most unsaturated fatty acids, the functional groups of the carbons are on the same side. These are called Cis Fats. There is a process called Hydrogenation that can add hydrogen atoms to the unsaturated fats to break the double bond and make it single.
What is the end of a fatty acid?
Omega - 3, 6 & 9. The end of the fatty acid having CH3 compound is known as the methyl end. If there is a double bond after three carbons counting from the end, the fat is known as Omega-3. If there is a double bond after 6 or 9 carbons - counting from the end - then the fat will be known as Omega 6 and 9 respectively.
Why is saturated fat called saturated fat?
Hence it is called saturated fat. The presence of too many hydrogen atoms results in too strong intermolecular attraction in the fats. Hence the molecular structure of fats remains robust and stable. This makes the fats remain solid at room temperature.
Why is hydrogen fat saturated?
Since it has a single bond, there are enough places for many hydrogen atoms to sit. Since it is saturated with hydrogen, it is called saturated fat
What is the backbone of fat?
The backbone of fat is known as glycerol . The glycerol is a compound made up of three carbons bonded with hydrogen atoms and hydroxide. Here is a picture of the structure of glycerol -. I m a g e w i l l b e U p l o a d e d S o o n.
What does "fat" mean?
Full of fat or oil; greasy. 3. Abounding in desirable elements : a paycheck fat with bonus money. 4. Fertile or productive; rich: "It was a fine, green, fat landscape" (Robert Louis Stevenson). 5. Having an abundance or amplitude; well-stocked: a fat larder. 6.
What is fat in science?
fat. ( fæt) n. 1. (Elements & Compounds) any of a class of naturally occurring soft greasy solids that are esters of glycerol and certain fatty acids. They are present in some plants and in the adipose tissue of animals, forming a reserve energy source, and are used in making soap and paint and in the food industry.
What is the fat in a whale called?
Fat is also an excellent insulator. Sea mammals, such as whales, have thick layers of fat, called blubber, to keep them comfortable in chilly waters. A whale's blubber may be two feet thick—now that's fat! The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition.
What does "fat chance" mean?
1. fat chance, a very slight chance; small probability. 2. the fat is in the fire, something has been done or started that cannot be reversed and will probably have dramatic or serious consequences. [before 1000; Middle English; Old English fǣtt]
What does "fat promotion" mean?
a. Yielding profit or plenty; lucrative or rewarding: a fat promotion.
What does "obese" mean in medical terms?
Another word with medical connotations, obese means grossly overweight: "a woman of robust frame ... though stout, not obese" (Charlotte Brontë). While corpulent also refers to conspicuous body weight, it is not always as judgmental a term as obese: the corpulent figure of the seated Buddha.
What are some synonyms for "fat"?
Synonyms: fat, overweight, obese, corpulent, portly, stout, pudgy, rotund, plump1, chubby. These adjectives mean having an abundance and often an excess of flesh. Fat implies more weight than one desires or than is considered desirable by social norms: was getting fat and decided to exercise. Overweight conveys the sense ...
What is the importance of oils and fats?
Incorporating oils and fats into a healthy eating pattern provides important nutrients such as: Vitamin E: With antioxidant properties that protect cells from free radicals, vitamin E is important for visual, reproductive, blood, brain and skin health. Vegetable oils are the major source of vitamin E in the diet, ...
What are the benefits of eating oils and fats?
Dietary fats are found in both plant and animal foods. They supply calories for energy and help with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Why are dairy fats different from other fats?
That is because dairy fats are highly complex and are made up of more than 400 different types of fatty acids. Additionally, fat is not consumed in isolation.
Why are fats important for the brain?
They supply calories for energy and help with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Fats from food sources protect organs, regulate body temperature and help produce hormones. Dietary fats are also important in optimal brain development of infants and young children.
Which fatty acids are essential for the body?
Essential fatty acids: Polyunsaturated fats contain some linoleic (omega-6) acid and α-linolenic (omega-3) acid, essential fatty acids that humans must ingest because the body needs but cannot synthesize them on its own. The Western diet typically provides adequate omega-6 fatty acids but needs more omega-3 fatty acids.
Is milk a fatty acid?
All dietary fats are composed of a mix of the three types of fatty acids in varied proportions. For example, most of the fatty acids in whole milk are saturated, but it also contains monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, in addition to the many beneficial nutrients that support health—including calcium, vitamin D, potassium and more.
Does saturated fat help with heart disease?
They can help lower LDL cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Yet not all fats are created equal, and certain foods containing saturated fats may not be as directly linked to cardiovascular disease risk as previously thought.
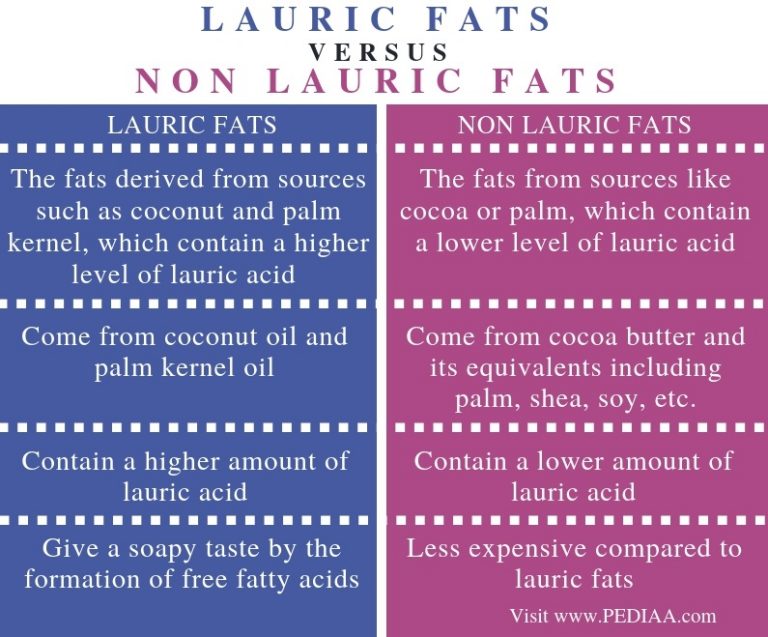
Fats Definition
Oils Definition
- Oil is a type of triglycerides composed of unsaturated fatty acids that are defined by their physical state and hydrophobicity. 1. Oil is a type of lipid with a high carbon and hydrogen content. Chemically, it is a triglyceride with unsaturated fatty acids. 2. Oil remains in the liquid state at room temperature and is lipophilic and hydrophobic. 3....
Examples of Fats
- Butter
1. Butter is a dairy product obtained from milk which has a fat content of about 80%. 2. It exists in a semisolid state at room temperature and is used in the form of spread, melted condiment, or an ingredient in baking. 3. A tablespoon of butter roughly contains 8 gm of fats, where 7.5gm is sat…
Examples of Oils
- Olive Oil
1. Olive oil is a type of liquid fat that is extracted from olives in different regions of the world. 2. Olive oil has been increasingly used in cooking, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals as well as soaps. 3. The composition of olive oil is triglycerides, free fatty acids, mono and diglycerides, and some h…
References and Sources
- Jain JL, Jain S and Jain N (2005). Fundamentals of Biochemistry. S. Chand and Company.
- Nelson DL and Cox MM. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. Fourth Edition.
- Berg JM et al. (2012) Biochemistry. Seventh Edition. W. H Freeman and Company.
- Dimitrios Boskou, Georgios Blekas, Maria Tsimidou. Olive Oil Composition. Olive Oil (Second Edition). AOCS Press. 2006. Pages 41-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-893997-88-2.5000…
- Jain JL, Jain S and Jain N (2005). Fundamentals of Biochemistry. S. Chand and Company.
- Nelson DL and Cox MM. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. Fourth Edition.
- Berg JM et al. (2012) Biochemistry. Seventh Edition. W. H Freeman and Company.
- Dimitrios Boskou, Georgios Blekas, Maria Tsimidou. Olive Oil Composition. Olive Oil (Second Edition). AOCS Press. 2006. Pages 41-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-893997-88-2.50008-0.