
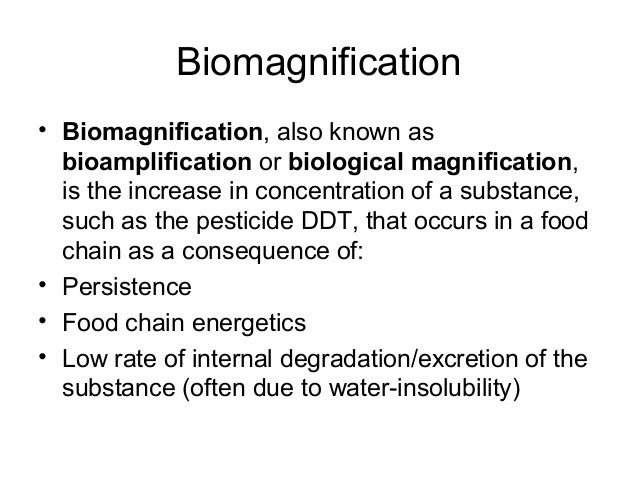
Biological magnification, or biomagnification, is the increasing buildup of toxic substances within organisms that happens at each stage of the food chain.
What does biological magnification describe?
“Biomagnification or biological magnification is the process of accumulation of certain chemicals in living organisms to a concentration higher than that occurring in the inorganic, non-living environment.” What is Biomagnification?
What are some examples of magnification?
Examples of magnification. Some optical instruments provide visual aid by magnifying small or distant subjects.. A magnifying glass, which uses a positive (convex) lens to make things look bigger by allowing the user to hold them closer to their eye.; A telescope, which uses its large objective lens or primary mirror to create an image of a distant object and then allows the user to examine ...
What is the definition of magnification in science?
The modern definition of magnification is the ratio between two measurements, which implies that two objects are needed for a correct evaluation of the value. The first object is obviously the sample. The second is a picture of it.
What is the definition of total magnification?
total magnification The magnification of a microscopic specimen, determined by multiplying the ocular lens magnification by the objective lens magnification. For the term total magnification may also exist other definitions and meanings, the meaning and definition indicated above are indicativenot be used for medical and legal or special purposes.

What is magnification short answer?
Magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of image to the height of object.
What is biological magnification and example?
Biomagnification is defined as the accumulation of a particular substance in the body of the organisms at different trophic levels of a food chain. One example of biomagnification is the accumulation of insecticide DDT which gets accumulated in zooplanktons. Small fishes consume these zooplanktons.
What is biological magnification and give its causes?
Biomagnification refers to increase in concentration of toxicant at successive trophic levels. This happens because a toxic substance accumulated by an organism cannot be metabolised or excreted, and is thus passed on to the next higher trophic level. This phenomenon is well-known for mercury and DDT.
What is biological magnification What are its effect?
Biological magnification, or biomagnification, occurs when pollutants taken up by organisms at the base of the food chain reach high concentrations in the bodies of animals at the top of the food chain. Effects of biomagnification vary widely depending on the pollutant, organism and ecosystem in question.
What are some examples of bioaccumulation?
Examples of bioaccumulation and biomagnification include: Car emission chemicals building up in birds and other animals. Mercury building up in fish. Pesticides building up in small animals.
What is magnification in biology microscope?
Magnification is the ability to make small objects seem larger, such as making a microscopic organism visible. Resolution is the ability to distinguish two objects from each other. Light microscopy has limits to both its resolution and its magnification.
How do you calculate biomagnification?
The simplest measure is the Biomagnification Factor (BMF), which is described as the ratio of the chemical concentrations in the organism (CB) and the diet of the organism (CD), i.e., BMF = CB/CD, where the chemical are usually expressed in units of mass of chemical per kg of the organism (in wet weight or in a lipid ...
What is biological magnification of food chain?
Biomagnification is the build up of toxins in a food chain. The DDT concentration is in parts per million. As the trophic level increases in a food chain, the amount of toxic build up increases. The x's represent the amount of toxic build up accumulating as the trophic level increases.
What is Biological Magnification?
Put simply; the term biological magnification is used to describe the process by which substances used in farming or produced in industrial waste make their way into and up the food chain.
What are some examples of biomagnification?
Another notable example of biomagnification is in predator fish. Species like Shark, Swordfish, Orange Roughy, Tuna, King Mackerel, or Tilefish contain proportionally larger levels of toxic mercury than smaller fish and shellfish.
What is the process of bioamplification?
Also fittingly called bioamplification or biomagnification, this process explains why harmful substances like have metals, or chemicals found in fertilizers or pesticides, present in even the largest, carnivorous predators. In this article, we will discuss the process of biomagnification and how it works.
Why is biomagnification so dangerous?
Although biomagnification is a natural phenomenon that happens in all organisms, the instances where it is worrisome are largely due to anthropogenic factors. Materials that humans introduce into the environment can cause unexpected and hazardous side effects and typically fall into one of the following subcategories.
What is bioaccumulation in biology?
However, bioaccumulation examines the increased presence of a particular substance inside a single organism. While the two processes may be interconnected, for the purpose of this article it’s important to differentiate the terminology to understand the real-life examples and practice.
Is bioamplification a new phenomenon?
Final Thoughts. Bioamplification isn’t a new phenomenon, but the humans have introduced pollutants to the environment that makes it a threat to the ecosystem and our food sources. Understanding how and why it occurs is the first step to combating the problem and preventing the destruction over time.
Does biomagnification affect living things?
Although biomagnification doesn’t always have a direct effect on living organisms , long-term exposure to harmful chemicals may result in unpleasant and irreversible side effects that could threaten a species.
What is the difference between resolution and magnification?
A distinction is made between Magnification and Resolution: Magnification is how large the image is compared to real life, whereas Resolution is the amount of information that can be seen in the image - defined as the smallest distance below which two discrete objects will be seen as one.
What is the maximum magnification of a light microscope?
The maximum magnification of light microscopes is usually ×1500, and their maximum resolution is 200nm, due to the wavelength of light. An advantage of the light microscope is that it can be used to view a variety of samples, including whole living organisms or sections of larger plants and animals. It is also relatively inexpensive.
What is the magnification of a scanning electron microscope?
It has a maximum magnification of about ×100000.
What is a graticule in a microscope?
To work out the size of an object viewed with a microscope, a Graticule is used. It is a small transparent ruler that becomes superimposed over the image. As the same sample may look to be different sizes under different magnifications, the Graticule must be calibrated.
How does a light microscope work?
Light Microscopes, or Optical Microscopes, as they are more correctly termed, use light and several lenses in order to magnify a sample. Light from the Condenser Lens, and then through the Specimen where certain wavelengths are filtered to produce an image. The light then passes through the Objective Lens, which focuses it and can be changed in order to alter the magnification. Finally, the light passes through the Eyepiece Lens, which can also be changed to alter the magnification, and into the eye.
Why use an electron microscope?
It is advantageous to use an Electron Microscope in many situations because they offer a much higher resolution that Light Microscopes, so they can be used to image very small objects in detail, and also because of the 3D images that SEMs offer.
What is cryofixation in biology?
Cryofixation: Freezing the sample very rapidly to preserve its state
What is magnification in science?
Magnification refers to an action of magnifying something. Furthermore, it refers to enlarging the apparent size and not the physical size. This enlargement is certainly quantifiable. Furthermore, how an object magnifies in relation to its actual size, is an important discussion under magnification. In this topic, we will discuss this concept and ...
What is the definition of magnifying?
Definition of Magnification. It refers to the action of visually enlarging an object with the help of lenses. Also, the object does not physically become larger but only appear larger. Besides, this concept ascends from two forms. First is by microscope (that make small objects appear large) and second is by telescope ...
How many times can a magnifying glass magnify an object?
Besides, they are easy to use and can magnify objects up to 6 times which means the object will appear six times larger. Also, magnifying glass and glasses (spectacles) are the most common example of a simple lens. In addition, their quality is not quite good and they produce low-quality images.
What are the two types of magnification lenses?
There are two types of magnification lenses Simple and Compound lenses.
Is it easy to understand magnification?
Understanding the magnification physically is quite easy and every one of us can recognize it. Moreover, we understand it as how big or small an image of the object will appear.
Can a simple lens magnify a compound lens?
Also, the compound lens can magnify objects and projects a clearer image while simple lens only magnifies the image. Moreover, the magnification of both lenses can be easily understood with the help of an example.
What is Magnification in Microscope?
Magnification in a microscope refers to the amount or degree of visual enlargement of an observed object. Magnification is measured by multiples, such as 2X, 4X, and 10X, indicating that the object is enlarged to twice as big, four times as big, or 10 times as big, respectively.
How Is Total Magnification Calculated in Microscope?
The total magnification of a microscope is understood as the magnification of the objective lens multiplied by that of the optical lens.
What are some examples of biological magnification?
Another prominent biological magnification example is the presence of mercury in various predatory fishes. Fishes like swordfish, shark, tuna, orange roughy, king mackerel, etc. contain a higher level of toxic mercury than smaller fishes.
What is Biomagnification?
Biomagnification means gathering various unimportant and, at times, harmful substances by organisms at different levels of a food chain. It occurs when industrial, agricultural, and human wastes are dumped into the oceans via rivers, sewers, streams, etc. Most of this waste is toxic and dangerous and deposited on the sea bed. The bottom feeders of a food chain consume these and gradually, it is carried to the top of that particular food chain.
What is biomagnification in the food chain?
Biomagnification means gathering various unimportant and at times harmful substances by organisms at different levels of a food chain. It occurs when industrial, agricultural, and human wastes are dumped into the oceans via rivers, sewers, streams, etc. Most of this waste is toxic and dangerous and deposited on the sea bed. The bottom feeders of a food chain consume these and gradually it is carried to the top of that particular food chain.
What does it mean to be biomagnified?
Biomagnification. Biology. Biomagnification. Every living organism on this planet requires chemicals to function correctly. However, Biomagnification definition suggests that when the accretion of some non-essential chemicals increases within living organisms, it can become harmful to them.
What are the elements that make up biomagnification?
Organic substances like manures and bio-solids contain essential nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Plants primarily use these. However, the industrial use of these substances causes biomagnification.
Does biological magnification affect health?
A significant effect of biological magnification is noted on human health. For instance, in recent years, a large number of individuals who have consumed seafood regularly have been diagnosed with cancer. The reason behind such a phenomenon is the presence of mercury.
What is biomagnification in biology?
These toxins can be biomagnified, meaning the pollutant is concentrated ten times with each step up in the food chain from plankton to humans.
What is the process of increasing the concentration of a compound in the tissues of organisms?
Definition of biomagnification . : the process by which a compound (such as a pollutant or pesticide) increases its concentration in the tissues of organisms as it travels up the food chain In a process known as biomagnification, fish accumulate mercury more rapidly than they excrete it, and every fish up the aquatic food chain contains more ...
What Is Biological magnification?
Biological Magnification vs. Bioaccumulation
- It’s important to note that there is a significant difference between biomagnification and bioaccumulation. Although some may use the words interchangeably, they actually describe different scenarios in an organism. Biological magnification specifically refers to increasing concentration of materials in each higher link in the food chain. However, bioaccumulation exam…
Examples of Biological Magnification
- There are numerous, well-documented examples of biomagnification where researchers find high concentrations of chemicals in apex predators. Many of these studies also demonstrate the potential negative consequences of this build up over time. Here are a few examples.
What Causes Biological magnification?
- Although biomagnification is a natural phenomenon that happens in all organisms, the instances where it is worrisome are largely due to anthropogenic factors. Materials that humans introduce into the environment can cause unexpected and hazardous side effects and typically fall into one of the following subcategories.
Potential Negative Effects of Biological Magnification
- DDT and mercury aren’t the only hazardous substances that have the potential to biomagnify. Substances like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB’s) that can impair reproductive systems, heavy metals, polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons which are a known carcinogenic, cyanide, and seleniumhave been extensively studied and proven to have similar outcomes. There are dozens …