Key Takeaways
- A p-value is a statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against observed data.
- A p-value measures the probability of obtaining the observed results, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
- The lower the p-value, the greater the statistical significance of the observed difference.
What does p value stand for Statistics?
The utility of p -values and statistical significance
- Quantifying relative uncertainty of data. First and foremost, p -values are a convenient expression of the uncertainty in the data with respect to a given claim.
- p -values as convenient summary statistics. ...
- Easy comparison of different statistical tests. ...
What is a p value and what does it mean?
The p-value is a number, calculated from a statistical test, that describes how likely you are to have found a particular set of observations if the null hypothesis were true. P-values are used in hypothesis testing to help decide whether to reject the null hypothesis. The smaller the p-value, the more likely you are to reject the null hypothesis.
What p value is considered statistically significant?
The p value, or probability value, tells you the statistical significance of a finding. In most studies, a p value of 0.05 or less is considered statistically significant, but this threshold can also be set higher or lower. How do you test for statistical significance?
How do you calculate a p value?
- Left-tailed F-test: p-value = cdf F,d1,d2 (F score)
- Right-tailed F-test: p-value = 1 - cdf F,d1,d2 (F score)
- Two-tailed F-test: p-value = 2 * min {cdf F,d1,d2 (F score ), 1 - cdf F,d1,d2 (F score )} (By min {a,b} we denote the smaller of the numbers a ...
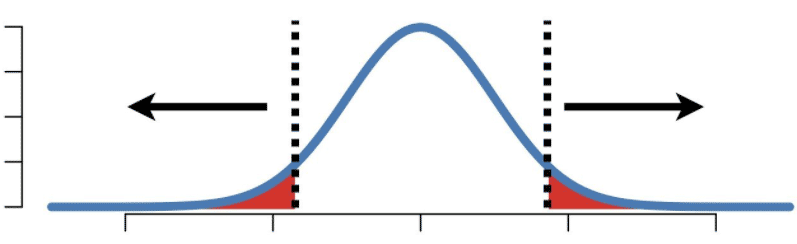
What is the p-value of a test?
In statistics, the p-value is the probability of obtaining results at least as extreme as the observed results of a statistical hypothesis test, assuming that the null hypothesis is correct.
What is the significance of a lower p-value?
The lower the p-value, the greater the statistical significance of the observed difference. P-value can be used as an alternative to or in addition to pre-selected confidence levels for hypothesis testing.
What is the purpose of p-value hypothesis test?
Instead, it provides a measure of how much evidence there is to reject the null hypothesis.
What is the p-value approach to hypothesis testing?
The p-value approach to hypothesis testing uses the calculated probability to determine whether there is evidence to reject the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis, also known as the conjecture, is the initial claim about a population (or data generating process). The alternative hypothesis states whether the population parameter differs from the value of the population parameter stated in the conjecture.
How to determine if portfolio is equivalent to S&P 500?
To determine this, the investor conducts a two-tailed test. The null hypothesis states that the portfolio's returns are equivalent to the S&P 500's returns over a specified period, while the alternative hypothesis states that the portfolio's returns and the S&P 500's returns are not equivalent—if the investor conducted a one-tailed test, the alternative hypothesis would state that the portfolio's returns are either less than or greater than the S&P 500's returns.
Why is significance level important?
In practice, the significance level is stated in advance to determine how small the p-value must be in order to reject the null hypothesis. Because different researchers use different levels of significance when examining a question, a reader may sometimes have difficulty comparing results from two different tests.
What is the difference between p-value and probability?
P-value is similar to the probability of occurrence of the desired result; however, there is a minute difference between the two, as per statistical calculation, although in general, they are used interchangeably. The probability of occurrence of such a result may be directly calculated. However, p-value calculation also includes a probability of other results’ occurrence. However, statisticians refer to this value for more appropriate results. In most cases, it lies within a range of 0 – 0.05 (5%) has a negative result, which means the alternate result would be considered, and a value higher than 0.05 signifies that the desired result will be accepted. However, this will not be hard and fast for all cases and will depend upon the conditions and product.
Why is p-value important?
Finding out a p-value makes it easier to determine between 2 different options.
What is the probability of a null hypothesis?
In case of a null hypothesis made on a scenario, there is always a probability of the occurrence of a required result. There is also an alternate result which is existent and which holds equivalent probability; however, it would be inferred only if the assumed/required result fails to be proved. P-value calculation determines whether the assumed result will hold true or the alternate result. A higher value determines the acceptance of the assumed result, while a lower signifies rejection of this assumed result and acceptance of the alternate result.
What does it mean when the probability is low?
On the contrary, a low value signifies that the required or assumed result has very low chances of its occurrence. This also denotes that the alternate result is more probable to occur.
What does a value of 0.05 mean?
In most cases, it lies within a range of 0 – 0.05 (5%) has a negative result, which means the alternate result would be considered, and a value higher than 0.05 signifies that the desired result will be accepted.
What does a higher value mean in math?
A higher value will signify that the assumed expected result is true, which means 60% of females accept the appliance. Consequently, a lower would imply acceptance of the alternate results, which means 60% of males accept the appliance. Hence, it determines the acceptance or rejection of an assumed result. You are free to use this image on your ...
Is p-value good for forecasting?
Calculation of returns using a p-value is a good way of forecasting results. In reality, the futuristic returns cannot be seen today. However, if all constraints are properly measured and then this calculation is done, then results can be forecasted.
What is the main interpretation of the p-value?
The main interpretation of the p-value is whether there’s enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis. If the p-value is reasonably low (less than the level of significance ), we can state that there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise, we should not reject the null hypothesis.
How to calculate p-value?
In order to use the p-value in hypothesis testing, follow the steps below: 1 Determine your level of significance (α). The level of significance generally should be chosen during the first steps of the design of a hypothesis test. The most common levels of significance include 0.10, 0.05, and 0.01. 2 Calculate the p-value. There are numerous software applications that offer the calculation. For instance, Microsoft Excel allows the calculation of the p-value using the Data Analysis ToolPak. 3 Compare the obtained p-value with the level of significance (α) and draw the relevant conclusions. The general rule here is if the figure is less than the level of significance, then there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis of an experiment.
What is the p-value used for?
The p-value is a primary value used to quantify the statistical significance of the results of a hypothesis test. Hypothesis Testing Hypothesis Testing is a method of statistical inference. It is used to test if a statement regarding a population parameter is correct. Hypothesis testing.
What is statistical significance?
The degree of statistical significance generally varies depending on the level of significance. For example, a p-value that is more than 0.05 is considered statistically significant while a figure that is less than 0.01 is viewed as highly statistically significant.
Is p-value a misinterpreted concept?
Moreover, statistics concepts can help investors monitor. , the p-value can be truly considered as one of the most commonly misinterpreted concepts. The biggest misconception about the concept is that it is a probability that the null hypothesis is true (or it is a probability that the alternative hypothesis is false).
Does p-value determine the probability of a null hypothesis?
In reality, the p-value does not determine the probability of the null hypothesis to be true but merely indicates the probability of encountering the results of a study at least as extreme as the actually observed results if the null hypothesis is true. In other words, it indicates the probability of having enough evidence to reject ...
What is the significance of P value?
P-value is a number that lies between 0 and 1. The level of significance (α) is a predefined threshold that should be set by the researcher. It is generally fixed as 0.05. The formula for the calculation for P-value is
What is the P value in a hypothesis?
The P-value is known as the level of marginal significance within the hypothesis testing that represents the probability of occurrence of the given event . The P-value is used as an alternative to the rejection point to provide the least significance at which the null hypothesis would be rejected. If the P-value is small, then there is stronger evidence in favour of the alternative hypothesis.
What does P mean in math?
P-value means probability value, which tells you the probability of achieving the result under a certain hypothesis. Since it is a probability, its value ranges between 0 and 1, and it cannot exceed 1.
Why is the P value used as an alternative to the rejection point?
The P-value is used as an alternative to the rejection point to provide the least significance at which the null hypothesis would be rejected. If the P-value is small, then there is stronger evidence in favour of the alternative hypothesis.
Is the rejection of the null hypothesis statistically significant?
Hence, the rejection of the null hypothesis is highly possible, as the p-value becomes smaller.

What Is A Null Hypothesis?
- All statistical tests have a null hypothesis. For most tests, the null hypothesis is that there is no relationship between your variables of interest or that there is no difference among groups. For example, in a two-tailed t-test, the null hypothesis is that the difference between two groups is z…
How Do You Calculate The P-Value?
- P-values are usually automatically calculated by your statistical program (R, SPSS, etc.). You can also find tables for estimating the p-value of your test statistic online. These tables show, based on the test statistic and degrees of freedom (number of observations minus number of independent variables) of your test, how frequently you would expect to see that test statistic un…
P-Values and Statistical Significance
- P-values are most often used by researchers to say whether a certain pattern they have measured is statistically significant. Statistical significance is another way of saying that the p-value of a statistical test is small enough to reject the null hypothesis of the test. How small is small enough? The most common threshold is p <0.05; that is, when you would expect to find a test st…
Reporting P-Values
- P-values of statistical tests are usually reported in theresults section of a research paper, along with the key information needed for readers to put the p-values in context – for example, correlation coefficient in a linear regression, or the average difference between treatment groups in a t-test.
Caution When Using P-Values
- P-values are often interpreted as your risk of rejecting the null hypothesis of your test when the null hypothesis is actually true. In reality, the risk of rejecting the null hypothesis is often higher than the p-value, especially when looking at a single study or when using small sample sizes. This is because the smaller your frame of reference, the greater the chance that you stumble across …
What Is P-Value?
- In statistics, the p-value is the probability of obtaining results at least as extreme as the observed results of a statistical hypothesis test, assuming that the null hypothesisis correct. The p-value serves as an alternative to rejection points to provide the smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis would be rejected. A smaller...
How Is P-Value calculated?
- P-values are usually found using p-value tables or spreadsheets/statistical software. These calculations are based on the assumed or known probability distributionof the specific statistic tested. P-values are calculated from the deviation between the observed value and a chosen reference value, given the probability distribution of the statistic, with a greater difference betwe…
The P-Value Approach to Hypothesis Testing
- The p-value approach to hypothesis testing uses the calculated probability to determine whether there is evidence to reject the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis, also known as the “conjecture,” is the initial claim about a population (or data-generating process). The alternative hypothesis states whether the population parameter differs from the value of the population parameter stat…
Example of P-Value
- An investor claims that their investment portfolio’s performance is equivalent to that of the Standard & Poor’s (S&P) 500 Index. To determine this, the investor conducts a two-tailed test. The null hypothesis states that the portfolio’s returns are equivalent to the S&P 500’s returns over a specified period, while the alternative hypothesis states that the portfolio’s returns and the S&P …
Explanation
Formula
Example
Interpretation
Usage and Relevance
Conclusion
- P-value is similar to the probability of occurrence of the desired result; however, there is a minute difference between the two, as per statistical calculation, although in general, they are used interchangeably. The probability of occurrence of such a result may be directly calculated. However, p-value calculation also includes a probability of o...
Recommended Articles
How to Use P-Value in Hypothesis Testing?
Misinterpretations of The P-Value
- In statistics, the p-value can be truly considered as one of the most commonly misinterpreted concepts. The biggest misconception about the concept is that it is a probability that the null hypothesis is true (or it is a probability that the alternative hypothesis is false). In reality, the p-value does not determine the probability of the null hyp...
Additional Resources