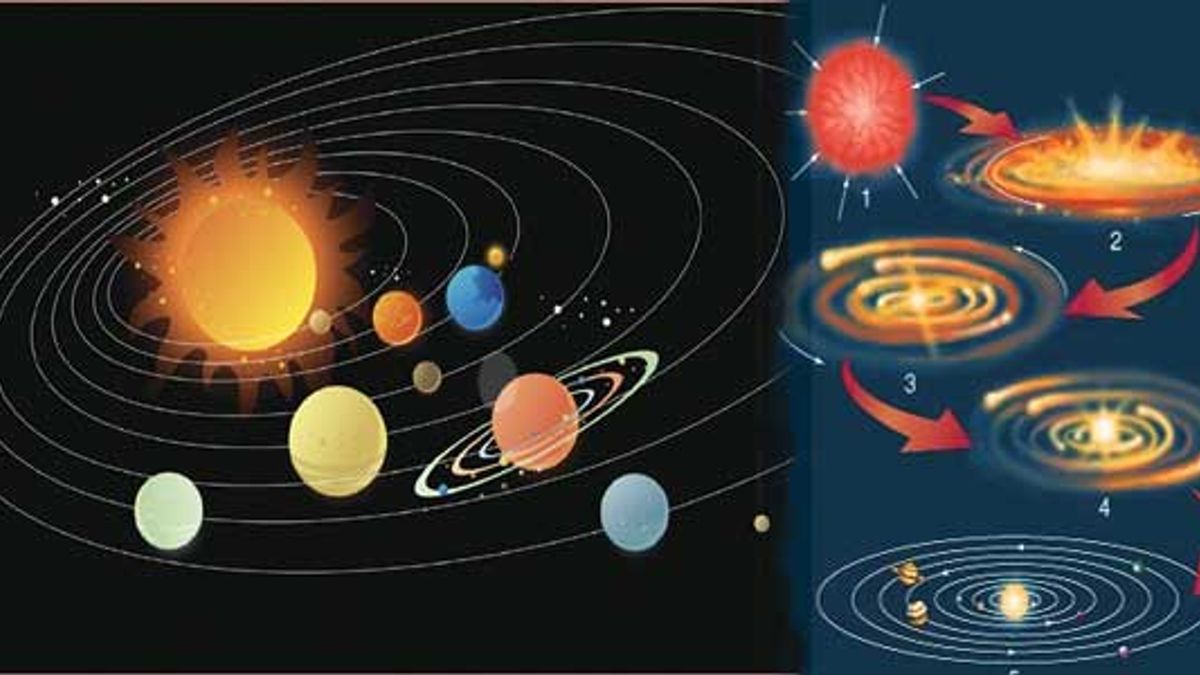
What does solar nebula mean?
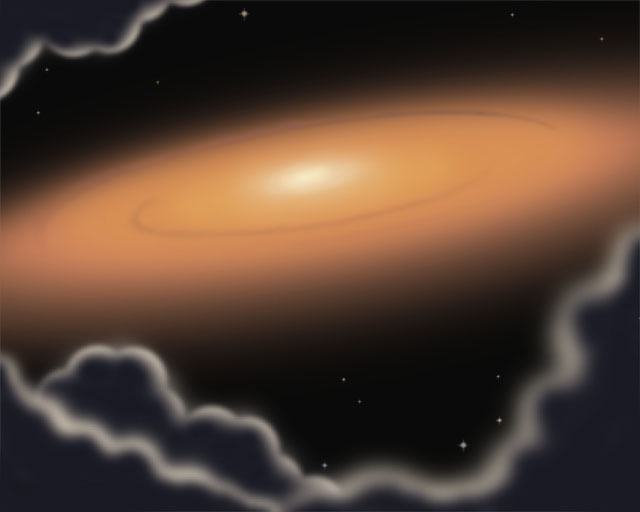
The solar nebula is the cloud of gas from which our solar system was born when it collapsed under its own gravity. By using the compositions of the Sun, other stars, and interstellar gas clouds, we know that the solar nebula contained 98% hydrogen and helium and only 2% of all other elements combined.
How does the solar nebula theory explain?
How does the solar nebula theory explain? The solar nebula hypothesis states that the outer planets were able to collect hydrogen within their gravity, while closer to the sun, most of the hydrogen was blown away by solar winds, leaving less hydrogen and exposing the rocky core.
How does a Nebula form a solar system?
a collision with another cloud and the rotation of nebula forces clouds to collapse into a rotating disk thus producing our solar system. The conservation laws: angular momentum and energy. angular momentum: can always be conserved so as the size of the object decreases, the velocity increases (figure skater when arms go in as she spins) energy: can transfer between forms, but it is always conserved, so the solar nebular heats up as it collapses thus the gravitational potential energy is ...
What was the solar nebula like?
The solar nebula was a twisting, flattened disk of gas and dust from which the solar system originated ~ 4.6 Ga ago, where Nebulae are made of residue and gases - hydrogen and helium. The residue and gases in a cloud are extremely fanned out, however, gravity can gradually pull together the bunches of residue and gas. What will You Learn Here?

What is the solar nebula for kids?
The Sun and all the planets in our solar system originally were a huge cloud of space dust, ice particles and gases. Although scientists aren't sure what caused it, they know the cloud collapsed about 4.5 billion years ago. When this happened, the dust and gas started to gather together in some spots.
What is the nebular theory short answer?
The nebular hypothesis is the idea that a spinning cloud of dust made of mostly light elements, called a nebula, flattened into a protoplanetary disk, and became a solar system consisting of a star with orbiting planets [12].
What is an example of a solar nebula?
The solar nebula is a cloud of interstellar gas and dust that condensed to form the entire solar system, including the sun and planets. This interstellar cloud of gas and dust rotated and flattened into a disk, with the sun forming in the center and the planets in orbits around the sun.
What is a solar nebula and how is it formed?
Our solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago from a dense cloud of interstellar gas and dust. The cloud collapsed, possibly due to the shockwave of a nearby exploding star, called a supernova. When this dust cloud collapsed, it formed a solar nebula – a spinning, swirling disk of material.
What happens in the solar nebula?
The Sun and the planets formed together, 4.6 billion years ago, from a cloud of gas and dust called the solar nebula. A shock wave from a nearby supernova explosion probably initiated the collapse of the solar nebula. The Sun formed in the center, and the planets formed in a thin disk orbiting around it.
What is the solar nebula mostly made of?
Meteorites, Comets, and Planets The solar nebula was the rotating, flattened disk of gas and dust from which the solar system originated ∼4.6 Ga (Figure 1).
What is nebular form?
Nebula Formation: In essence, a nebula is formed when portions of the interstellar medium undergo gravitational collapse. Mutual gravitational attraction causes matter to clump together, forming regions of greater and greater density.
Who made the nebular theory?
The generally accepted model for the formation of the solar system is called the nebular hypothesis. It takes all the different kinds of information and merges them into one hypothesis that seems to match all the observations. The theory was proposed by French mathematician Pierre Simon Laplace more than 200 years ago.
Where is the solar nebula?
Our solar system began forming within a concentration of interstellar dust and hydrogen gas called a molecular cloud. The cloud contracted under its own gravity and our proto-Sun formed in the hot dense center. The remainder of the cloud formed a swirling disk called of the solar nebula.
What are 3 facts about the nebula?
Fun Facts About Nebulas -The Orion Nebula is the closest one to the Earth. - Nebulae are also known as "Stellar Nurseries" because stars are born in them. - The nebulae outside the Milky Way are referred to as extra-galactic nebulae. - Diffuse Nebulae are very well outspread and don't have any limits, or so we believe.
Is nebula a planet?
A planetary nebula is a region of cosmic gas and dust formed from the cast-off outer layers of a dying star. Despite their name, planetary nebulae have nothing to do with planets.
How big is a solar nebula?
The nebular hypothesis says that the Solar System formed from the gravitational collapse of a fragment of a giant molecular cloud. The cloud was about 20 parsecs (65 light years) across, while the fragments were roughly 1 parsec (three and a quarter light-years) across.
How nebula was formed?
They either form through clouds of cold interstellar gas and dust or through the aftermath of a supernova. For example, in the Carina Nebula, hot, young stars erode and sculpt the clouds into this fantasy landscape by sending out thick stellar winds and scorching ultraviolet radiation.
Can the Sun become a nebula?
Ultimately, most scientists believe that the Sun will become a planetary nebula. As is progresses though the red giant stage, the outer envelope of the Sun will be blown off into space.
Can Earth Survive in a nebula?
Can a habitable world exist that would orbit in and out of a nebula? The answer would be yes. As the planet orbits its star that orbits the center of the galaxy, the planet and its star could enter a nebula and pass through that nebula for thousands or millions of years and then emerge on the other side of the nebula.
Can a planet survive in a nebula?
Likely not. With nebulae having densities ranging from 100 to 10,000 particles per cubic centimeter, it won't be massive enough to simply disintegrate the planet. This is despite the fact that they're blazing at a few kilometers per second, and the planet will be molten.
What would happen if a nebula hit Earth?
0:323:24What If Earth Was Inside of a Nebula? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's 24 light-years across and has a mass equivalent to two thousand suns if the earth was formedMoreIt's 24 light-years across and has a mass equivalent to two thousand suns if the earth was formed inside it all you'd see in the night sky.
Which nebula is Earth in?
The nearest nebula to earth is the Helix Nebula. It is 700 light years away from Earth. Most of them are less dense than any vacuum created on earth and a nebular cloud of the size of Earth would have a total mass of only a few kgs.
How big is a nebula?
A nebula is a cloud of dust and gas, usually tens to hundreds of light years across. A galaxy is much larger — usually thousands to hundreds of thousands of light years across. Nebulae are one of the many things that galaxies are made of, along with stars, black holes, cosmic dust, dark matter and much more.
Does the solar nebula still exist?
The story of our solar system's origin is pretty well known. It goes like this: the Sun began as a protostar in its “solar nebula” over 4.5 billion years ago. Over the course of several million years, the planets emerged from this nebula and it dissipated away.
What are 5 examples of solar energy?
The five main uses of solar energy are solar electricity, solar water heating, solar heating, solar ventilation and solar lighting. There are more uses for solar energy, but homes and businesses typically use solar energy for these purposes.
What are the three nebula?
Clouds out in space interact with light in different ways as well. This leads to the classification of three different types of nebulae: emission, reflection, and dark.
What is an example of solar?
Solar energy is commonly used for solar water heaters and house heating. The heat from solar ponds enables the production of chemicals, food, textiles, warm greenhouses, swimming pools, and livestock buildings. Cooking and providing a power source for electronic devices can also be achieved by using solar energy.
What is an example of a solar system?
Our solar system consists of our star, the Sun, and everything bound to it by gravity – the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune; dwarf planets such as Pluto; dozens of moons; and millions of asteroids, comets, and meteoroids.
Q1: Are There Any New Planets in the Solar System?
Ans: Astronomers have found 139 new trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) - minor planets situated in the most distant ranges of the close planetary syste...
Q2: Is Sun the Livelihood of the Solar System?
Ans: The Sun is the biggest object inside our solar system, containing 99.8% of the system's mass. The Sun is situated at the focal point of our so...
Q3: Is There a Planet Beyond the Solar System?
Ans: A worldwide group of scientists has gathered the principal conceivable radio signal from a planet past the solar system, radiating from an exo...
Q4: State Two Demerits of Nebula Hypothesis.
Ans: It doesn't fulfill the standard of conservation of angular momentum in the solar system. This hypothesis was dismissed when it was discovered...
What are the elements in the Sun's nebula?
Early evidence for mixing in the solar nebula was provided with the discovery of the Inti particle (Stardust track #25), consisting of spinel and Al,Ti-pyroxene with anorthite, melilite, perovskite, refractory metal and osbornite (TiN) (Simon et al., 2008; Matzel et al., 2010; Brownlee et al., 2012; Joswiak et al., 2012; Nakashima et al., 2012 ). This particle is a CAI of the type common in CCs and thought to form early in nebular history at high temperatures and low oxygen fugacities in the vicinity of the early Sun. The mineralogical and textural characteristics of CAI in chondrites are described in more detail in this volume ( Velbel et al., in this volume ). The occurrence of this and other refractory inclusions in Wild2 ( Joswiak et al., 2017) strengthened arguments for nebula-wide mixing in the formation of comets ( Nuth et al., 2000 ), either by ballistic ejection of material from the plane of the disk ( Shu et al., 1996) or in or near the midplane during turbulent transport (e.g., Ciesla, 2007 ).
How are hydrated minerals formed?
A considerable amount of petrographic ( Bunch and Chang, 1980) and isotopic ( Clayton and Mayeda, 1983) data indicate that the hydrated minerals were formed by internal processes inside parent bodies and not preaccretionary nebula processes. Hydrated silicate formation was probably not prevalent by nebular gas–grain reactions, because the timescale of the reaction was longer than the time span of the gaseous nebula at the low temperatures where hydration reactions are thermodynamically possible ( Fegley and Prinn, 1989 ). Alternatively, the work of Ganguly and Bose (1995) suggests that nebular hydration reactions could have occurred before the nebula dissipated. The preponderance of evidence from aqueous alteration products in primitive meteorites implies that many of the asteroids contained ice and they were heated to the melting point of ice, yielding internal liquid water, at least as surface films.
How would the solar system be cooled?
It is interesting that the entire inner Solar System would be dramatically cooled by dispersing the nebula and turning on the superluminous T Tauri phase! This is of course directly attributable to the dissipation of the thick insulating blanket of gases and dust that hindered radiative cooling while the nebula was in place. From about 4 to 10 AU the thermal effects of removing the nebula would not have been great, and beyond about 10 AU solar radiation would cause a significant increase in the temperature, perhaps to the serious detriment of any solid methane or solid argon that may have originally condensed. Their vulnerability to evaporation depends on the size of the solid bodies: particles can evaporate very readily, while planets with deep potential wells would persist.
Why did the Sun's nebula end?
The events surrounding the ignition of the Sun may have been violent, because a slight overshoot in the collapse process may have caused a “hydrogen flash” analogous to the helium flash we encountered in our survey of stellar evolution. Whether or not such a heat pulse occurred, the Sun entered the T Tauri phase with two or three times its present luminosity and subsided over about 107 years into a stable early MS star. The effective temperature of the T Tauri Sun was probably close to the present value.
What does the solar nebula indicate?
Theoretical models for the solar nebula indicate a decreasing temperature with increasing distance from the Sun. If the thermal gradient were steep enough, the composition of condensates from the nebula, if at equilibrium, would vary as a function of distance and temperature (Lewis, 1972, 1974).
What are exoplanets made of?
Exoplanets entirely made of carbon have been theorized ( Lodders, 2004; Kuchner and Seager, 2005; Bond et al., 2010; Madhusudan et al., 2011, 2012a; Öberg et al., 2011; Johnson et al., 2012; Mashian and Loeb, 2016) and tentatively observed in the local universe, especially around stars with high C/O and C/H ratios ( Madhusudan et al., 2011; Madhusudan, 2012b ). In the early universe and most probably in the circumstellar envelopes of CEMP stars, carbon dust might have accreted under the influence of gravitational hydrodynamics to grow into meter- and kilometer-scale planetesimals and further to carbonaceous exoplanets ( Mashian and Loeb, 2016 ). The detection of carbon exoplanets at high-redshifts, whenever it happens, would be of immense scientific significance.
What are the cosmological studies of meteorites?
Cosmochemical studies of meteorites, comets, and other primitive bodies have illuminated the chemical conditions in the solar nebula, allowing people to gain important insight into the processes that occurred during the formation of the planets.
What will You Learn Here?
On this page, you will learn about the nebula solar system and the nebular theory of formation of our solar system.
Was Nebula Hypothesis a Failure?
For quite a few years, most astronomers supported the presumed collision theory, wherein planets were considered to have formed because of a close approach to the Sun by another star.
How long does it take for a planet to form?
however, the sun-like star usually takes around 10⁶ years to form, with the protoplanetary disk evolving into a planetary system over the next 10-100 million years.
What is the cloud of gas and dust that forms the Sun?
Solar Nebula is a large disc-shaped cloud of gas and dust from which planets, the sun, and other bodies of a solar system are formed.
How many TNOs have been found?
Ans: Astronomers have found 139 new trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) - minor planets situated in the most distant ranges of the close planetary system. Researchers have recognized a fascinating planet in another planetary system where the climate estimate is consistently critical - a 100% possibility of the most unbelievable downpour comprehensible, with drops of scaldingly warm fluid iron.
Why are the masses of the original planets greater than the prior version of the theory?
The masses of the original planets were thought to be greater than in the prior version of the theory, and the obvious distinction in momentum was ascribed to the magnetic forces associating the Sun and the planets.
How far away is the radio signal from the solar system?
Ans: A worldwide group of scientists has gathered the principal conceivable radio signal from a planet past the solar system, radiating from an exoplanet framework around 51 light-years away.
How do stars form in a nebula?
In this image of the Carina Nebula, you can spot tiny yellow and white dots inside pink dust clouds. Those tiny dots are newly-formed stars! Credit NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Colorado
Where are nebulae?
Nebulae exist in the space between the stars—al so known as interstellar space. The closest known nebula to Earth is called the Helix Nebula. It is the remnant of a dying star—possibly one like the Sun. It is approximately 700 light-years away from Earth. That means even if you could travel at the speed of light, it would still take you 700 years to get there!
What telescopes can take pictures of nebulae?
Astronomers use very powerful telescopes to take pictures of faraway nebulae. Space telescopes such as NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and Hubble Space Telescope have captured many images of faraway nebulae.
What are nebulas made of?
Nebulae are made of dust and gases—mostly hydrogen and helium. The dust and gases in a nebula are very spread out, but gravity can slowly begin to pull together clumps of dust and gas. As these clumps get bigger and bigger, their gravity gets stronger and stronger.
What are the towers of cosmic dust and gas?
These towers of cosmic dust and gas make up part of the Eagle Nebula. These so-called Pillars of Creation are part of an active star-forming region within the nebula. Credits: NASA, ESA and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
What causes a star to heat up?
Eventually, the clump of dust and gas gets so big that it collapses from its own gravity. The collapse causes the material at the center of the cloud to heat up-and this hot core is the beginning of a star.
Where is the Helix Nebula located?
NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope captured this image of the Helix Nebula, which is located in the constellation Aquarius -about 700 light-years away from Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona.
What is the cloud that forms the solar system?
To sum everything up, an interstellar cloud of gas and dust rotated and flattened into a disk, with the sun forming in the center and the planets in orbits around the sun. Meaning, the solar system, sun and planets included, formed from the same solar nebula, a cloud of interstellar gas and dust that condensed to form the entire solar system, ...
What is the catastrophic hypothesis?
The catastrophic hypothesis is a hypothesis that states that our solar system formed thanks to a sudden and improbable event such as the collision of two stars. The evolutionary hypothesis is ...
What is the evolutionary hypothesis of the solar nebula?
What came out of the evolutionary hypothesis was the solar nebula theory, the theory that posits that the planets and sun in the solar system formed from the solar nebula. The solar nebula is a cloud of interstellar gas and dust that condensed to form the entire solar system, including the sun and planets.
What were the two competing theories as to what force was responsible for the creation of the solar system?
Back in the 20th century, the two competing theories as to what force was responsible for the creation of the solar system were the catastrophic hypothesis and the evolutionary hypothesis.
What is the theory that the Sun and the Sun form from the Sun?
Enough evidence was gathered in the 20th century to make the evolutionary hypothesis into a theory. The solar nebula theory is the theory that posits that the planets and sun in the solar system formed from the solar nebula.
What is the evolutionary hypothesis?
The evolutionary hypothesis is a hypothesis that states that gradual and natural changes caused the formation of our solar system. Although many astronomers and physicists tend to lean towards the catastrophic explanation for the extinction of the dinosaurs, they don't seem to do so for the explanation of the solar system. Odd bunch they are.
What are the two camps that study dinosaurs?
Paleontologists who study the extinction of the dinosaurs seem to be split into two camps. There are the intrinsic gradualists and the extrinsic catastrophists. Since this lesson isn't really about the debate of what killed giant lizards, I'll put everything this way: the gradualists believe that the extinction of the dinosaurs was mainly caused by ...
What is a nebula?
Nebula, (Latin: “mist” or “cloud”) plural nebulae or nebulas, any of the various tenuous clouds of gas and dust that occur in interstellar space. The term was formerly applied to any object outside the solar system that had a diffuse appearance rather than a pointlike image, as in the case of a star. This definition, adopted at a time ...
What is diffuse ionized gas?
Diffuse ionized gas, so pervasiveamong the nebular clouds, is a major component of the Galaxy. It is observed by faint emissions of positive hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfurions (H+, N+, and S+) detectable in all directions. These emissions collectively require far more power than the much more spectacular H II regions, planetary nebulae, or supernovaremnants that occupy a tiny fraction of the volume.
What percentage of the mass of a nebula is in the form of dust?
In a spiral galaxy the interstellar medium makes up 3 to 5 percent of the galaxy’s mass, but within a spiral arm its mass fraction increases to about 20 percent. About 1 percent of the mass of the interstellar medium is in the form of “dust”—small solid particles ...
What is a supernova remnant?
Supernova remnants are the clouds of gas expanding at speeds of hundreds or even thousands of kilometres per second from comparatively recent explosions of massive stars. If a supernova remnant is younger than a few thousand years, it may be assumed that the gas in the nebula was mostly ejected by the exploded star.
What percentage of the mass of a galaxy is in the interstellar medium?
In a spiral galaxythe interstellar medium makes up 3 to 5 percent of the galaxy’s mass, but within a spiral armits mass fraction increases to about 20 percent. About 1 percent of the mass of the interstellar medium is in the form of “dust”—small solid particles that are efficient in absorbing and scattering radiation. Much of the rest of the mass within a galaxy is concentrated in visible stars, but there is also some form of dark matterthat accounts for a substantial fraction of the mass in the outer regions.
What type of star is the most massive?
The star must be of stellar type O or B, the most massive and hottest of normal stars in the Galaxy, in order to produce enough of the radiation required to ionize the hydrogen. Diffuse ionized gas, so pervasive among the nebular clouds, is a major component of the Galaxy.
What is the gas of reflection nebulae?
Reflection nebulaereflect the light of a nearby star from their constituent dust grains. The gas of reflection nebulae is cold, and such objects would be seen as dark nebulae if it were not for the nearby light source.
Are we missing a good definition for solar nebula? Don't keep it to yourself..
The ASL fingerspelling provided here is most commonly used for proper names of people and places; it is also used in some languages for concepts for which no sign is available at that moment.
Definitions & Translations
Get instant definitions for any word that hits you anywhere on the web!
What is a nebula?
So, what exactly is a nebula? A nebula is a huge cloud of combined gas and dust in space. It can contain hydrogen, helium, and/or plasma. They are sometimes considered nurseries, because oftentimes they are the location where stars are created and born.
Why do emission nebulae emit their own light?
On the other hand, emission nebulae can give off their own light because they have ionized gas. These nebulae are extremely hot and have high-energy stars that give off UV photons. When you look at a picture of a nebula, you will notice a variety of vibrant colors. You will often see hues of blue, purple, red, and white.
What happens when a new star is born?
The newly-born stars release energy and radiation. The moving particles move and push the gas and dust surrounding it in the nebula. The cloud and gas moving cause the nebula to shift and change its shape overall. The energy released from the new stars lights up the nebula, creating the vibrant color and light.
What color is the nebula?
Astronomers know that the orange color is hydrogen, the red color in the nebula is sulfur, and the green color is oxygen. When you think about a nebula, you can think of it it two ways: a nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas in space, and a nebula is the place where stars are formed and born.
Why are nebulas called nurseries?
They are sometimes considered nurseries, because oftentimes they are the location where stars are created and born. Nebulae, which is the plural form (more than one) of nebula, form when gas, like hydrogen and helium, as well as molecules, particles, ions, and electrons are pulled together by gravity. Some of the gas and dust particles group ...
How far away is the Orion Nebula?
The Orion Nebula is one of the most famous nebula, which happens to be about 1500 light-years away from us. You can find this nebula by finding the Orion constellation. Astronomers note that many stars are being born out of this nebula, especially in the location noted by Orion’s sword. This nebula has many colors.
Do stars form out of collapsing material?
In areas that become more dense, stars can form out of the collapsing material. There are a few different kinds of nebula formations. Many nebulae have no clear beginning or end, and no clear boundaries. These are diffuse nebulae.
