
Is the Milky Way the largest galaxy of its kind?
UGC 2885 may be the biggest spiral galaxy ever seen. We live in the Milky Way galaxy, considered to be a pretty beefy example of its kind. It's a spiral galaxy, with over 200 billion stars, stretching about 150,000 (and perhaps up to 200,000) light
What is approximate size of the Milky Way?
- Star count
- Milky Way: Less than 500 billion
- Andromeda: Around 1 trillion
- Winner: Andromeda
- Mass
- Milky Way: 1.5 trillion solar masses.
- Andromeda: 0.8 trillion solar masses.
- Winner: Milky Way. It seemed for a long time that the Milky Way has
What is the largest thing in the Milky Way galaxy?
VY CMa is described as the largest star in the Milky Way although galactic red supergiants above are possibly larger but they have less accurate radius estimates. How heavy is the universe? The total mass of ordinary matter in the universe can be calculated using the critical density and the diameter of the observable universe to be about 1.5 × 1053 kg.
What is bigger the galaxy or the Milky Way?
The galaxy’s bright, starry disk is about 120,000 light years in diameter, making it slightly larger than the Milky Way. What is the name of the largest galaxy? The biggest known galaxy is IC 1101, which is 50 times the Milky Way’s size and about 2,000 times more massive.
What is the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy in which we live?
So how big is it, and how does it measure up with other neighborhood residents? The numbers are pretty astounding. NASA estimates the galaxy at 100,000 light-years across. Since one light year is about 9.5 x 1012km, so the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy is about 9.5 x 1017 km in diameter.
What is the diameter of our galaxy in terms of astronomical unit?
The Milky Way is about 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 km (about 100,000 light years or about 30 kpc) across.
What is the size of the Milky Way galaxy?
52,850 light yearsMilky Way / Radius
How many AU is the Milky Way?
Useful astronomical distance scalesExampleLight TimeApproximate DistanceBetelgeuse470 years30 million AUMost naked-eye starsSeveral thousand years~100 million AUSize of Milky Way100,000 years6 billion AUAndromeda Galaxy2.2 million years140 billion AU8 more rows•Apr 6, 2022
Is the diameter of the Earth 1 astronomical unit?
1 Answer. Earth's diameter = 12756 km = 8.5269 E-04 AU = 1.35 E-09 LY. Best unit for size of space bodies is km or mile. .
What is the value of 1 astronomical unit in Metre?
Astronomical unit1 au or AU or AU in ...... is equal to ...metric (SI) units1.495978707×1011 mimperial & US units9.2956×107 miastronomical units4.8481×10−6 pc 1.5813×10−5 ly7 more rows
What is the diameter of galaxies?
Most of the galaxies are 1,000 to 100,000 parsecs in diameter (approximately 3,000 to 300,000 light years) and are separated by distances on the order of millions of parsecs (or megaparsecs).
What is the diameter and thickness of the disk of the Milky Way?
The diameter of the disk is c. 120,000 light-years; its average thickness is 10,000 light-years, increasing to 30,000 light-years at the nucleus. Certain features of the region near the sun suggested that our galaxy resembles the Andromeda Galaxy.
What is the diameter of the disk of the Milky Way quizlet?
Terms in this set (8) What is the diameter of the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy? The thickness? The diameter is 100,000 light years and the thickness is 1,000 light years.
What is AU measurement?
astronomical unit (AU, or au), a unit of length effectively equal to the average, or mean, distance between Earth and the Sun, defined as 149,597,870.7 km (92,955,807.3 miles).
How many times larger is the diameter of the Milky Way than the diameter of Earth?
Answer: Assuming a diameter for the Milky Way galaxy of about 15 kpc, which is about 4.6×10^(17) km, and a diameter for the Earth of about 12756 km, the ratio of the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy to that of the Earth is about 3.6×10^(13).
How big is Milky Way in light years?
52,850 light yearsMilky Way / Radius
How many light years is the Milky Way?
If you are just measuring the normal matter we can see (in visible, infrared, X-ray and ultraviolet light), then the Milky Way is at least 100,000 light years across.
Is there dark matter in the Milky Way?
But normal matter isn’t all that makes up the Milky Way. Simulations of our galaxy show that it has a “halo” of dark matter, which makes up about 10 times the mass of the visible matter in the Milky Way. Dark matter has never been directly observed, but is inferred due to its gravitational pull.
How far is the Milky Way from the Sun?
The Milky Way is about 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 km (about 100,000 light years or about 30 kpc) across. The Sun does not lie near the center of our Galaxy. It lies about 8 kpc from the center on what is known as the Orion Arm of the Milky Way.
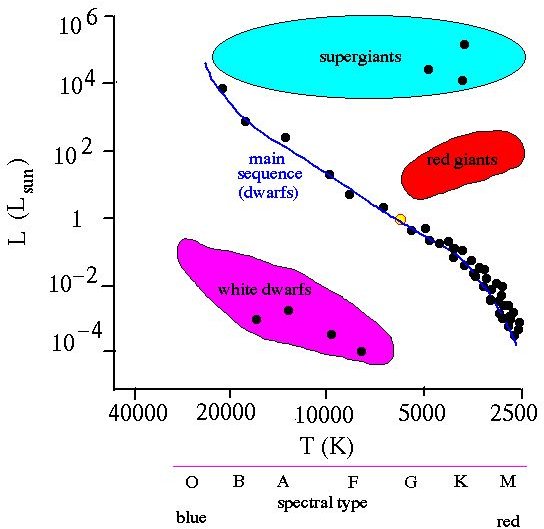
What is the spectrum of a star?
The spectrum is the array of colors or wavelengths that is obtained when light is dispersed.) The further a star is, the more absorption will be observed, since the light has passed through more of the interstellar medium.
How far can parallaxes be measured?
Parallaxes give us distances to stars up to perhaps a few thousand light years. Beyond that distance, parallaxes are so small than they cannot be measured with contemporary instruments. Astronomers use more indirect methods beyond a few thousand light years.
How many light years is a parsec?
Although the light year is a commonly used unit, astronomers prefer a different unit called the parsec (pc). A parsec, equal to 3.26 light years, is defined as the distance at which 1 Astronomical Unit subtends an angle of 1 second of arc (1/3600 of a degree) When we use the parsec for really large distances, we often put a prefix in front ...
What is a globular cluster of stars?
Globular clusters of stars - swarms of old stars tightly bound together by gravity and orbiting at the outskirts of galaxies, contain many variable stars, including RR Lyraes. Shapley was able use these to find the distance to the globular clusters that surround our Galaxy.
When was the period-luminosity relation discovered?
From this, and its apparent magnitude, we can calculate its distance. The period-luminosity relation was discovered by Henrietta Swan Leavitt in 1908 when she was studying Cepheid Variable stars in the Magellanic Clouds.
Does the interstellar medium affect the brightness of a star?
Secondly, the absorption of certain wavelengths of light by the interstellar medium can affect the apparent brightness of the star and therefore must be accounted for. Even with these (and other) complications, Cepheid Variables provide an excellent way to measure the relative distances.
How many stars are in our galaxy?
Our galaxy probably contains 100 to 400 billion stars, and is about 100,000 light-years across. That sounds huge, and it is, at least until we start comparing it to other galaxies. Our neighboring Andromeda galaxy, for example, is some 220,000 light-years wide. Another galaxy, IC 1101, spans as much as 4 million light-years.
How many galaxies are there in the universe?
Based on the deepest images obtained so far, it’s one of about 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe.
How far away is Proxima Centauri?
It’s a small, probably rocky planet orbiting Proxima Centauri – as mentioned before, the next star over. A little more than four light-years away, or 24 trillion miles as the crow flies. If an airline offered a flight there by jet, it would take 5 million years. Not much is known about this world; its close orbit and the periodic flaring of its star lower its chances of being habitable.
How far does light travel in a year?
Light zips along through interstellar space at 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second (more than 66 trips across the entire United States, in one second). Multiply that by all the seconds in one year, and you get 5.8 trillion miles (9.5 trillion kilometers). Just for reference, Earth is about eight light minutes from the Sun. A trip at light speed to the very edge of our solar system – the farthest reaches of the Oort Cloud, a collection of dormant comets way, way out there – would take about 1.87 years. Keep going to Proxima Centauri, our nearest neighboring star, and plan on arriving in 4.25 years at light speed.
How long does it take for the Earth to reach the Sun?
Just for reference, Earth is about eight light minutes from the Sun. A trip at light speed to the very edge of our solar system – the farthest reaches of the Oort Cloud, a collection of dormant comets way, way out there – would take about 1.87 years.
How much does the Milky Way weigh?
The Milky Way weighs in at about 1.5 trillion solar masses (one solar mass is the mass of our Sun), according to the latest measurements. Only a tiny percentage of this is attributed to the approximately 200 billion stars in the Milky Way and includes a 4-million-solar-mass supermassive black hole at the center.
How far away is the Milky Way from Earth?
When the Gaia and Hubble measurements are combined as anchor points, like pins on a map, astronomers can estimate the distribution of the Milky Way's mass out to nearly 1 million light-years from Earth.
How does dark matter affect the universe?
Although we cannot see it, dark matter is the dominant form of matter in the universe, and it can be weighed through its influence on visible objects like the globular clusters. The more massive a galaxy, the faster its globular clusters move under the pull of gravity. Most previous measurements have been along the line of sight to globular clusters, so astronomers know the speed at which a globular cluster is approaching or receding from Earth. However, Hubble and Gaia record the sideways motion of the globular clusters, from which a more reliable speed (and therefore gravitational acceleration) can be calculated.
Why are globular star clusters important?
"Because of their great distances, globular star clusters are some of the best tracers astronomers have to measure the mass of the vast envelope of dark matter surrounding our galaxy far beyond the spiral disk of stars," said Tony Sohn ...
What is the dark matter in the universe?
Most of the rest of the mass is locked up in dark matter, an invisible and mysterious substance that acts like scaffolding throughout the universe and keeps the stars in their galaxies. On the left is a Hubble Space Telescope image of a portion of the globular star cluster NGC 5466.
How many solar masses are there in our galaxy?
Earlier research dating back several decades used a variety of observational techniques that provided estimates for our galaxy's mass ranging between 500 billion to 3 trillion solar masses. The improved measurement is near the middle of this range.
Can we measure the mass of the Milky Way?
We can't put the whole Milky Way on a scale, but astronomers have been able to come up with one of the most accurate measurements yet of our galaxy's mass, using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the European Space Agency's Gaia satellite.
How many stars are in the Milky Way?
The Milky Way is a fairly narrow band of faint diffuse light around the celestial sphere. The Milky Way Galaxy is a spiral galaxy of about 100 billion stars.
How many light years away is the nearest galaxy?
How many galaxies like our own would it take laid edge-to-edge to reach the nearest galaxy? (Hint: The nearest galaxy to our own is about 2.5 million light-years away. The Milky Way Galaxy has a diameter of approximately 80,000 light-years.)
How far is the Moon from Earth?
The Moon is approx. 240,000 miles from Earth... Light travels at 186,000 miles per second... (the Sun is approx. 93,000,000 miles from the Earth)
How many kilometers is Titan?
The equatorial diameter of Titan is 5,150 kilometers. If a kilometer equals 0.6214 mi, what is Titan's diameter in miles?
What is the unit of measure for cosmic distance?
So for cosmic distances, we switch to whole other types of units: astronomical units, light years and parsecs. Astronomical units, abbreviated AU, are a useful unit of measure within our solar system. One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth's orbit, which is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers).
What are the units of measure for space beyond Earth?
So for cosmic distances, we switch to whole other types of units: astronomical units, light years and parsecs.
What is the unit of measure used to measure the width of the sky?
The origin of this unit of measure is a little more complicated, but it's related to how astronomers measure widths in the sky. Astronomers use "megaparsecs" — a megaparsec is 1 million parsecs — for intergalactic distances, or the scale of distances between the galaxies.
How many light years away is the nearest star system?
For example, the nearest star system to ours is the triple star system of Alpha Centauri, at about 4.3 light years away. That's a more manageable number than 25 trillion miles, 40 trillion kilometers or 272,000 AU. Light years also provide some helpful perspective on solar system ...
How far is the Sun from Earth?
One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth's orbit, which is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers). When measured in astronomical units, the 886,000,000-mile (1,400,000,000-kilometer) distance from the Sun to Saturn's orbit, is a much more manageable 9.5 AU.
How far does light travel in a year?
A light year is the distance a photon of light travels in one year, which is about 6 trillion miles (9 trillion kilometers, or 63,000 AU).

Overview
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικός κύκλος (galaktikos kýklos), meaning "milky circle." From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galile…
Etymology and mythology
In the Babylonian epic poem Enūma Eliš, the Milky Way is created from the severed tail of the primeval salt water dragoness Tiamat, set in the sky by Marduk, the Babylonian national god, after slaying her. This story was once thought to have been based on an older Sumerian version in which Tiamat is instead slain by Enlil of Nippur, but is now thought to be purely an invention of Babylonian propagandists with the intention to show Marduk as superior to the Sumerian deities.
Appearance
The Milky Way is visible from Earth as a hazy band of white light, some 30° wide, arching the night sky. In night sky observing, although all the individual naked-eye stars in the entire sky are part of the Milky Way Galaxy, the term "Milky Way" is limited to this band of light. The light originates from the accumulation of unresolved stars and other material located in the direction of the galactic plane. Brighter regions around the band appear as soft visual patches known as star clouds. Th…
Astronomical history
In Meteorologica, Aristotle (384–322 BC) states that the Greek philosophers Anaxagoras (c. 500–428 BC) and Democritus (460–370 BC) proposed that the Milky Way is the glow of stars not directly visible due to Earth's shadow, while other stars receive their light from the Sun (but have their glow obscured by solar rays). Aristotle himself believed that the Milky Way was part of the Earth's upper atmosphere (along with the stars), and that it was a byproduct of stars burning tha…
Astrography
The ESA spacecraft Gaia provides distance estimates by determining the parallax of a billion stars and is mapping the Milky Way with four planned releases of maps in 2016, 2018, 2021 and 2024. A study in 2020 concluded that Gaia detected a wobbling motion of the galaxy, which might be caused by "torques from a misalignment of the disc's rotation axis with respect to the principle axis of a non-spherical halo, or from accreted matter in the halo acquired during late infall, or fro…
Size and mass
The Milky Way is the second-largest galaxy in the Local Group (after the Andromeda Galaxy), with its stellar disk approximately 170,000–200,000 light-years (52–61 kpc) in diameter and, on average, approximately 1,000 ly (0.3 kpc) thick. To compare the relative physical scale of the Milky Way, if the Solar System out to Neptune were the size of a US quarter (24.3 mm (0.955 in)), the Milky Way would be approximately the size of the contiguous United States. There is a ring-like filame…
Contents
The Milky Way contains between 100 and 400 billion stars and at least that many planets. An exact figure would depend on counting the number of very-low-mass stars, which are difficult to detect, especially at distances of more than 300 ly (90 pc) from the Sun. As a comparison, the neighboring Andromeda Galaxy contains an estimated one trillion (10 ) stars. The Milky Way may contain ten billion white dwarfs, a billion neutron stars, and a hundred million stellar black holes. F…
Structure
The Milky Way consists of a bar-shaped core region surrounded by a warped disk of gas, dust and stars. The mass distribution within the Milky Way closely resembles the type Sbc in the Hubble classification, which represents spiral galaxies with relatively loosely wound arms. Astronomers first began to conjecture that the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy, rather than an ordinary spiral galaxy, in the 1960s. These conjectures were confirmed by the Spitzer Space Telescope observat…
About The Image
Distance Information
- Although the light year is a commonly used unit, astronomers prefer a different unit called the parsec (pc). A parsec, equal to 3.26 light years, is defined as the distance at which 1 Astronomical Unit subtends an angle of 1 second of arc (1/3600 of a degree) When we use the parsec for really large distances, we often put a prefix in front of it - like kiloparsecs (kpc), which are equal to 100…
How Do We Calculate Distances of This Magnitude
- Parallaxes give us distances to stars up to perhaps a few thousand light years. Beyond that distance, parallaxes are so small than they cannot be measured with contemporary instruments. Astronomers use more indirect methods beyond a few thousand light years. The methods to measure stellar distances greater than a few thousand light years include: Proper motions:All st…
Why Are These Distances Important to Astronomers?
- Distance is a useful tool on the galactic scale. If you can measure the average speed of stars as they move around the Galactic Center and their distance from the Galactic Center, you can make a plot called a "rotation curve". The rotation curve, which describes the motion of the galaxy can be used to determine the amount of mass within a given radius from the center. The predicted rotat…
Travel Time
- The Voyager spacecraft is traveling away from the Sun at a rate of 17.3 km/s. If Voyager were to travel to the center of our Galaxy, it would take more than 450,000,000 years to travel the 8 kpc. If it could travel at the speed of light, an impossibility due to Special Relativity, it would still take over 26,000 years to arrive! At 17.3 km/s, it would take Voyager over1,700,000,000 years to traverse t…