What Are The Similarities And Differences Of Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells? The primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the absence of membrane bound organelles in prokaryotic cells. Moreover, prokaryotic organisms are exclusively unicellular while eukaryotic organisms can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What feature is common to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- They both have ‘chemical noses’ that keep them updated and aware of all the reactions that occur within them and in the surrounding environment.
- Both these organisms have a fluid-like matrix called the cytoplasm that fills the cells.
- Both have a cytoskeleton within the cell to support them.
What is the comparison between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
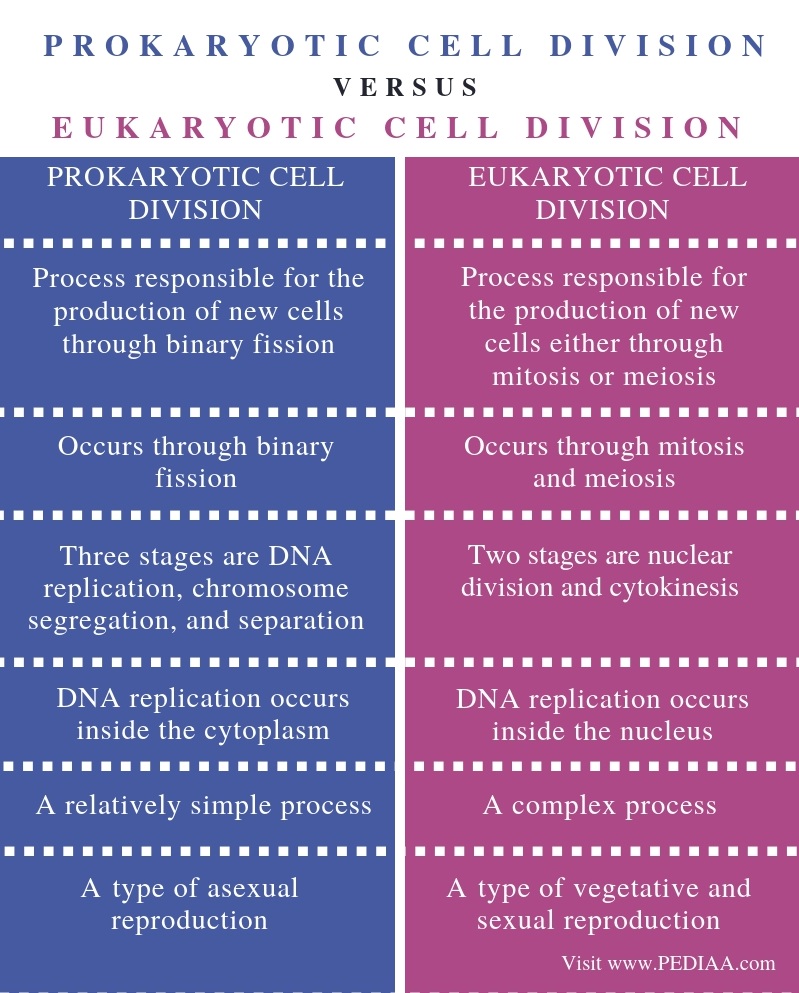
Well, to summarise, prokaryotic cells are unicellular micro-organisms, whereas eukaryotic cells are multi-cellular organisms. The nucleus is present in eukaryotic cells, while there is no nuclei present in prokaryotic cells.
Are prokaryotes more complex than eukaryotic cells?
The highest level of organization for an individual is the organism itself. Which cell is more complicated prokaryotic or eukaryotic? Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotes, and the DNA is linear and found within a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells boast their own personal “power plants”, called mitochondria.
What are two main types of eukaryotic cells?
What are the two types of eukaryotic cells?
- Kingdom Protista (not all, some are members of prokaryotes)
- Kingdom Fungi
- Plant kingdom
- Animal kingdom

What are the similarities between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell?
Some of the structural similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are cell membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material made up of DNA and ribosomes.
What are 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes don't have membrane-bound organelles whereas eukaryotes have....What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells?Prokaryotic CellEukaryotic cellEndoplasmic reticulum absentEndoplasmic reticulum presentMitochondria absentMitochondria presentCytoskeleton absentCytoskeleton presentRibosomes smallerRibosomes larger19 more rows•May 20, 2022
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information.
What are the 4 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes are exclusively unicellular organisms while eukaryotes consists of unicellular as well as multicellular organisms. Prokaryotes have circular DNA while eukaryotes have linear DNA. Eukaryotes have a true nucleus while prokaryotes do not. Eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles while prokaryotes lack these.
What are 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Class 9?
In prokaryotic cells, the true nucleus is absent, moreover, membrane-bound organelles are present only in eukaryotic cells. Another major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that prokaryotic cells are exclusively unicellular, while the same does not apply to eukaryotic cells.
What are 5 differences between plant and animal cells?
Animal cells are made up of four main parts namely nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and mitochondria. With all these parts plant cells also have a cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplasts....Difference between Animal and Plant cell.Animal CellPlant cellIt does not have a cell wall.It consists of a cellulose cell wall outside the cell membrane.8 more rows•Sep 22, 2021
What are the three major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
No prokaryotic cell has a nucleus; every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells have no mitochondria; nearly every eukaryotic cell has mitochondria. Prokaryotic cells have no organelles enclosed in plasma membranes; every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and organelles, each enclosed in plasma membranes.
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells quizlet?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA.
What is a Prokaryotic cell?
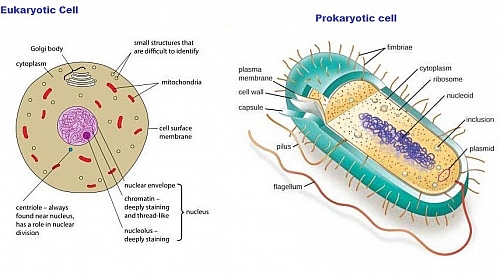
A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-...
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells?
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucle...
Define Cell?
The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of life. Cell plays a vital role in all biological activities and include membrane-bound organ...
What is Ribosome?
The ribosome is a multi-component cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein. Therefore, it is called the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes ar...
List out the unique features of Animal and Plant Cells.
Both animal and plant cells have several unique features. Listed below are some important features: In structure, both animal and plant cells are q...
List out the functions of Chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are the plastids found in all plant cells. These cell organelles comprise the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll and are involv...
Who discovered Cell and Cell Theory?
The cell was first discovered in the year 1665 by an English natural philosopher Robert Hooke. The Cell Theory was explained by Theodor Schwann and...
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
On the other hand, a prokaryote will reproduce clones of itself via binary fission and relies more on horizontal genetic transfer for variation.
What is the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell?
In prokaryotes the cytoplasm encompasses everything within the plasma membrane, including the cytoskeleton and genetic material.
How many kinds of RNA are in ribosomes?
Eukaryotic ribosomes also show more complexity than prokaryotic – they are constructed of five kinds of ribosomal RNA and about eighty kinds of proteins. In contrast, prokaryotic ribosomes are composed of only three kinds of rRNA and about fifty kinds of protein.
Why is it important to reduce the size of eukaryotic cells?
Due to the larger size of the eukaryotic cells, confining certain cellular process to a smaller area also increases the efficiency of functions by improving communication and movement within the cell.
Which cell type does not have membrane bound organelles?
Membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells contain many membrane-enclosed, large, complex organelles in the cytoplasm whereas prokaryotic cells do not contain these membrane-bound organelles. This is a key difference because it allows a high level of intracellular division of labor and contributes to the greater complexity characteristic ...
What is the basis for the genetic material of a cell?
Genetic Material. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells both use deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as the basis for their genetic information. This genetic material is needed to regulate and inform cell function through the creation of RNA by transcription, followed by the generation of proteins through translation.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell Membrane. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells bear a lipid bilayer, which is an arrangement of phospholipids and proteins that acts as a selective barrier between the internal and external environment of the cell.
What are the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
We all know that the Prokaryotes are those organisms that possess the prokaryotic cell. These are unicellular organisms and do not have membrane-bound cell organelles. Prokaryotic cells are usually the most primitive type ...
How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic plasma membranes different?
3. The prokaryotic plasma membrane is different from eukaryotic as it posses essential infolding called mesosomes. Mesosomes are formed by the extension of the plasma membrane into the cell.
What is the DNA used in prokaryotes?
1. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells use the double-stranded DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) as the genetic material of the cell. 2. In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the DNA molecules are condensed with the support of different proteins. In eukaryotes, the DNA is wrapped around proteins called Histones.
How many subunits of ribosomes are there in prokaryotes?
In Prokaryotes, 2 subunits of Prokaryotic ribosomes are: 50S and 30S units, which when present together form the 70S prokaryotic ribosomes. In Eukaryotes, 2 subunits of Eukaryotic ribosomes are: 60S and 40S units, which together form the 80S eukaryotic ribosomes. 5.
How are eukaryotic cells evolved?
Eukaryotic cells are evolutionarily developed from the prokaryotic cells over the course of millions of years of history. In eukaryotes, the cells form tissues, then organs, then organ systems, and then the body with categories of cells doing different types of metabolic activities. So, let us know the Similarities and Differences between ...
Which cell type has a semi-fluid membrane?
1. Both Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells have a semi-fluid phospholipid bilayer cell membrane. This is also known as the plasma membrane.
Where do most of the chemical reactions and metabolic pathways occur in a prokaryotic cell?
3. In Prokaryotic cell, the cytoplasm is the only place where most of the chemical reactions and metabolic pathways that run the cell takes place. In Eukaryotic cells, only a few metabolic pathways occurs in the cytoplasm and the majority occurs inside the nucleus. 4.
Which is smaller, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Scientists speculate that these organisms gave rise to the eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are comparatively smaller and much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus.
What is the meaning of eukaryotic cell?
The term “ Eukaryotes ” is derived from the Greek word “ eu “, (meaning: good) and “ karyon ” (meaning: kernel), therefore, translating to “ good or true nu clei .”. Eukaryotes are more complex and much larger than the prokaryotes. They include almost all the major kingdoms except kingdom monera.
What are the structures that help in cellular respiration?
It is also one of the smallest components within the cell. Some prokaryotic cells contain special structures called mesosomes which assist in cellular respiration.
What is the nucleus of a cell?
The nucleus contains DNA, which is responsible for storing all genetic information. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Within the nucleus exists the nucleolus, and it plays a crucial role in synthesising proteins. Eukaryotic cells also contain mitochondria, which are responsible for the creation of energy, which is then utilized by the cell.
Which type of cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the smallest part of a cell?
Right below the protective coating lies the cell wall, which provides strength and rigidity to the cell. Further down lies the cytoplasm that helps in cellular growth, and this is contained within the plasma membrane, which separates the interior contents of the cell from the outside environment. Within the cytoplasm, ribosomes exist and it plays an important role in protein synthesis. It is also one of the smallest components within the cell.
What are the biotic components of the environment?
Biotic components of the environment include all forms of life from minute bacteria to towering giant Sequoias. However, at the microscopic level, all living organisms are made up of the same basic unit – the cell.
What are the similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
For those that didn’t know, there are many similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. These are two types of cells that make up living organisms , and this article will cover all the parallelism between them. The basic unit of life is cell. Living organisms are divided into two groups on the basis of their cellular structure: prokaryotes ...
Which organisms are prokaryotic?
Animals, plants, fungi, protozoans, and algae all come under eukaryotic cells, with bacteria being the only organisms that are prokaryotes. They are smaller and simpler in structure as compared to eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cellules have a large surface-to-volume ratio, that helps the nutrients easily and rapidly reach interior parts of the cell.
What are flagella and cilia?
Flagella and cilia are found in eukaryotes; likewise endoflagella, fimbriae, pili and flagella are found in prokaryotes. They are used for motility and adhering to surfaces or moving matter outside the cells. Some prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellules have glycocalyces as a common material.
Why are eukaryotic cells so complex?
Eukaryotic cellules have a limited surface area, thus, making it very difficult for the nutrients to readily diffuse in the interior parts of the cells . Thus, eukaryotes have complex organs that help them carry out metabolism and other important functions for the survival of the organisms.
How many years ago did prokaryotes evolve?
Living organisms are divided into two groups on the basis of their cellular structure: prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The former evolved 2 billion years before the evolution of latter. Around 3.5 billion years ago, prokaryotic organisms dominated our planet. Then, about 1.5 billion years ago, a nucleated cell called eukaryote evolved.
What do cellular cytoplasmic cells regulate?
They regulate the flow of nutrients and waste matter that enters and exits the cellules.
Which layer of the cell forms the boundary between the inner and outer side of the cell?
They have a lipid bilayer, known as the plasma layer, that forms the boundary between the inner and outer side of the cell.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
A prokaryotic cell is one in which both membrane-bound cell organelles and a well-defined nucleus are absent.
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
A cell that has a well-defined nucleus and a membrane to bind it is called a eukaryotic cell.
Prokaryotic Pros and Cons
These cells add essential nutrients to the soil by decomposing dead organic matter.
Eukaryotes Pros and Cons
The lack of a cell wall helps in the efficient and fast exchange of nutrient absorption.
Considering the Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells conduct necessary living functions.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells FAQs
Yes, ribosomes are found freely floating throughout the cytoplasm in a prokaryotic cell.
The Final Words
When we compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, we see that both help in conducting necessary living functions but they have many different characteristics. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles while eukaryotic cells do have a membrane to bind the nucleus.
Which two cell types have similar mechanisms of DNA replication, transcription and translation?
The basic mechanism of DNA replication, transcription and translation is similar in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 7. Some major metabolic pathways like Glycolysis and TCA cycle are common in both cell types. 8. Similar mechanism of photosynthesis in cyanobacteria (prokaryotes) and green plants (eukaryotes). 9.
Which is the genetic material in both cell types?
3. In both cell types, DNA is the genetic material.
What is the energy that is used in cellular processes?
9. In both cell types, ATP is the chemical energy “currency”. The hydrolysis of ATP releases energy that is used for cellular processes that require energy.