
What is a lurking variable?
In a lurking variable, two variables become confounded when their effects on a response or dependent variable cannot be distinguished from each other. However, the confounding variable is not only present in the study but is related to the other study variables. This allows it to have an effect on the relationship between these variables.
What is a confounding variable in psychology?
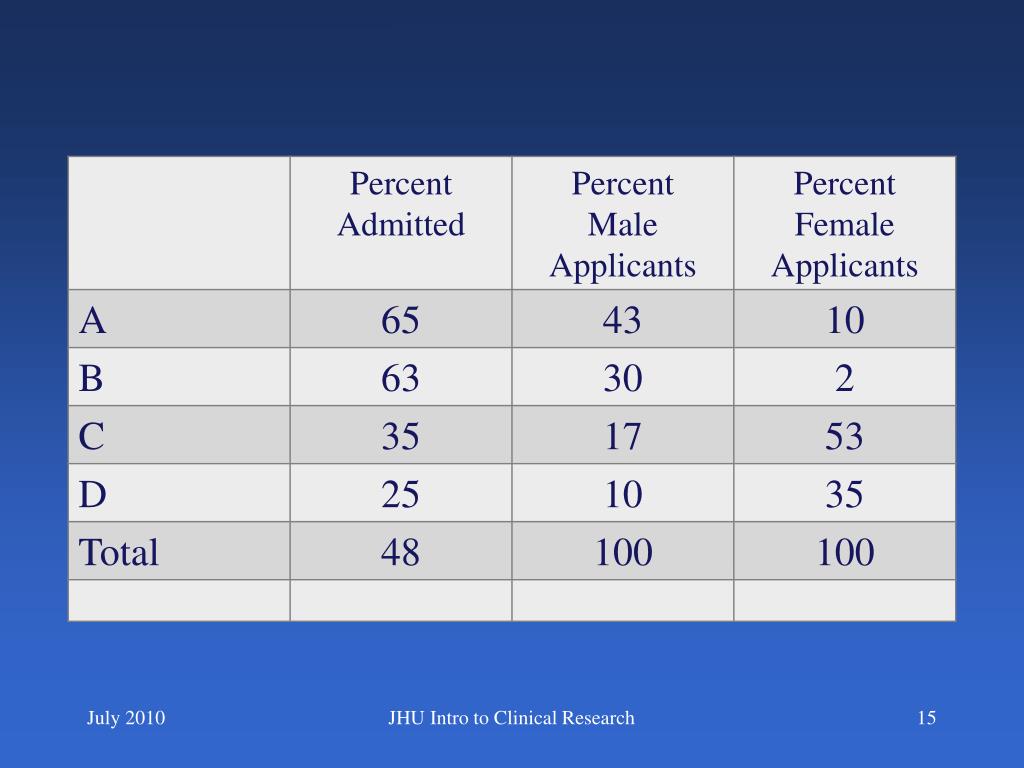
A confounding variable is a variable that affects both the response variable and the explanatory variable. Admit (yes/no) is a response variable, while GPA is an explanatory variable. General ambition is a possible confounding factor. Furthermore, what is an example of a hidden variable?
How do you eliminate the risk of lurking variables in research?
In observational studies, it can be very difficult to eliminate the risk of lurking variables. In most cases, the best you can do is simply identify, rather then prevent, potential lurking variables that may be impacting the study.
Is a latent variable the same thing as a confounder?
No, these are three different things. A latent variable is anything that you don’t directly observe. Anything related to someone else’s thought processes or attitudes is a good example. A confounder is anything that has a relationship with both the independent and dependent random variables in a causal analysis.
What's the difference between lurking and confounding variables?
A lurking variable is a variable that has an important effect on the relationship among the variables in the study, but is not one of the explanatory variables studied. Two variables are confounded when their effects on a response variable cannot be distinguished from each other.
Is a lurking variable a confounder?
A variable that is in the study and is related to the other study variables, thus having an effect on the relationship between these variables. A lurking variable, if included in the study, could have a confounding effect and then be classified as a confounding variable.
What is a lurking variable example?
A lurking variable can falsely identify a strong relationship between variables or it can hide the true relationship. For example, a research scientist studies the effect of diet and exercise on a person's blood pressure. Lurking variables that also affect blood pressure are whether a person smokes and stress levels.
What is the confounding variable in an experiment?
A confounding variable is a third variable that influences both the independent and dependent variables. Failing to account for confounding variables can cause you to wrongly estimate the relationship between your independent and dependent variables.
What's a confounding variable psychology?
A confounding variable is an unmeasured third variable that influences, or “confounds,” the relationship between an independent and a dependent variable by suggesting the presence of a spurious correlation.
What is the difference between common response and confounding?
Common response: Changes in both x and y are caused by changes in a lurking variable z. Confounding: The effect ( if any ) of x and y is confounded with the effect of a lurking variable. Even when direct causation is present. It is exactly a complete explanation of an association between two variables.
Why are lurking variables important?
A lurking variable is a variable that is unknown and not controlled for; It has an important, significant effect on the variables of interest. They are extraneous variables, but may make the relationship between dependent variables and independent variables seem other than it actually is.
What is the key idea in defining confounding?
Confounding refers to differences in outcomes that occur because of differences in the baseline risks of the comparison groups. These differences may occur due to selection bias that distributes risk factors known as confounding variables unevenly between comparison groups.
What is the best way to control for lurking variables?
Repeating, the 3 principles of good experimental design are: control the lurking variables, usually by comparing 2 or more treatments. randomize the assignments of treatments to experimental units. replicate (repeat) the treatment on many units to reduce chance variation in the results.
How do you identify a confounding variable?
Identifying Confounding A simple, direct way to determine whether a given risk factor caused confounding is to compare the estimated measure of association before and after adjusting for confounding. In other words, compute the measure of association both before and after adjusting for a potential confounding factor.
What are types of confounding variables?
Here are some confounding variables that you need to be looking out for in experiments:Order Effects.Participant variability.Social desirability effect.Hawthorne effect.Demand characteristics.Evaluation apprehension.
What kind of variable is the confounding variable?
Confounding variables are those that affect other variables in a way that produces spurious or distorted associations between two variables. They confound the "true" relationship between two variables.
What is the key idea in defining confounding?
Confounding refers to differences in outcomes that occur because of differences in the baseline risks of the comparison groups. These differences may occur due to selection bias that distributes risk factors known as confounding variables unevenly between comparison groups.
What is response and explanatory variables?
An explanatory variable is what you manipulate or observe changes in (e.g., caffeine dose), while a response variable is what changes as a result (e.g., reaction times). The words “explanatory variable” and “response variable” are often interchangeable with other terms used in research.
Do extraneous variables affect validity?
Extraneous variables can threaten the internal validity of your study by providing alternative explanations for your results. In an experiment, you manipulate an independent variable to study its effects on a dependent variable.
Is a response variable?
Response Variable is the result of the experiment where the explanatory variable is manipulated. It is a factor whose variation is explained by the other factors. Response Variable is often referred to as the Dependent Variable or the Outcome Variable.
Answer
A lurking variable is a variable that has an important effect on the relationship among the variables in the study, but is not one of the explanatory variables studied. Two variables are confounded when their effects on a response variable cannot be distinguished from each other.
Answer
Lurking variables are a common problem in observational studies when an apparent association between two variables is really just common response to a third unseen variable. A commonly cited example involves a positive association between ice cream sales and drowning.
New questions in Mathematics
A $65 meal is put on the table. The couple plans on leaving an 18% tip. How much should be left altogether?
What is the difference between lurking and confounding variables?
The difference between lurking and confounding variables lies in their inclusion in the study. If a variable was measured and included, it's associations between the explanatory and response variables can be determined and (if random assignment was performed) neutralized with methods beyond the AP Syllabus. It is a confounding (or not) variable. The associations between an unmeasured variable and the explanatory and response variables cannot be determined -- whatever its associations are remain a mystery, and it "lurks" beyond the purview of the investigator.
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable is one whose effects on the response variable cannot be distinguished from one or more of the explanatory variables in the study.
What is an extraneous variable?
An extraneous variable is one that is not one of the explanatory variables in the study, but is thought to affect the response variable. (For some folks extraneous variables are those that aren't explanatory or response variables -- in that case, some extraneous variables are thought to affect the response variable.)
What is a Lurking Variable?
A lurking variable is defined as an extraneous variable that is not included in statistical analysis.
What Problems Can Lurking Variables Cause?
Lurking variables can falsely show a strong relationship between two variables and it can also hide the relationship existing between two variables.
What is lurking variable?
A lurking variable is a variable that is not included in a statistical analysis, yet impacts the relationship between two variables within the analysis.
How to identify lurking variables?
Another way to identify potential lurking variables is through examining residual plots. If there is a trend (either linear or non-linear) in the residuals, this could mean that a lurking variable not included in the study is impacting the variables within the study in some way.
Can you eliminate lurking variables?
In observational studies, it can be very difficult to eliminate the risk of lurking variables. In most cases, the best you can do is simply identify, rather then prevent, potential lurking variables that may be impacting the study.
Can lurking variables affect both groups?
Since we randomly assign patients to groups, we can assume that the lurking variables will affect both groups roughly equally. This means any differences in blood pressure can be attributed to the pill, rather than the effect of a lurking variable.
