Stereotactic biopsy refers to a needle biopsy using mammography to locate the area of concern and getting the sample with guidance under mammography. This procedure is done on "spots" that cannot be felt. A needle biopsy that is not done stereotactically, refers to a biopsy that is done with a needle.
Full Answer
What is stereotactic biopsy and what is the technique used?
A stereotactic biopsy is an innovative technique used most often to obtain a sample of a mass to see if it is cancerous. With this tissue sample, a pathologist can identify the grade and type of tumorfound. This operation is used in brain cancers to help facilitate a clear understanding of the tumor in the most minimally invasive way.
How accurate are needle biopsies?
The Disposable Biopsy Needle Market in the Global Environment ... Investors can use the report to make accurate predictions about market growth potential by examining key trends and changes, which will enable the company to calculate future market growth ...
How do they do a needle biopsy?
Your doctor will:
- make a small cut
- remove the lymph node or portion of the lymph node
- stitch the biopsy site closed
- apply a bandage
How serious is stereotactic breast biopsy?
These are all signs of infection. A stereotactic breast biopsy is a relatively simple and low-risk procedure. However, it does carry some risks: Following your doctor’s instructions on how to care for your wound will greatly reduce your risk of infection. to your unborn child.
Is the stereotactic biopsy the same as core needle biopsy?
What is a stereotactic needle biopsy? A stereotactic needle biopsy, also called stereotactic core needle biopsy, is a medical test to remove a piece of tissue from your body. The tissue is then tested to find out what it is.
Why do I need a stereotactic biopsy?
A stereotactic breast biopsy is an option when a mammogram shows a breast abnormality such as: A suspicious solid mass. Microcalcifications — tiny clusters of small calcium deposits. A distortion in the structure of the breast tissue.
What is the best type of breast biopsy?
A core needle biopsy (CNB) uses a larger hollow needle to sample breast changes felt by the doctor or seen on an ultrasound, mammogram, or MRI. This is often the preferred type of biopsy if breast cancer is suspected.
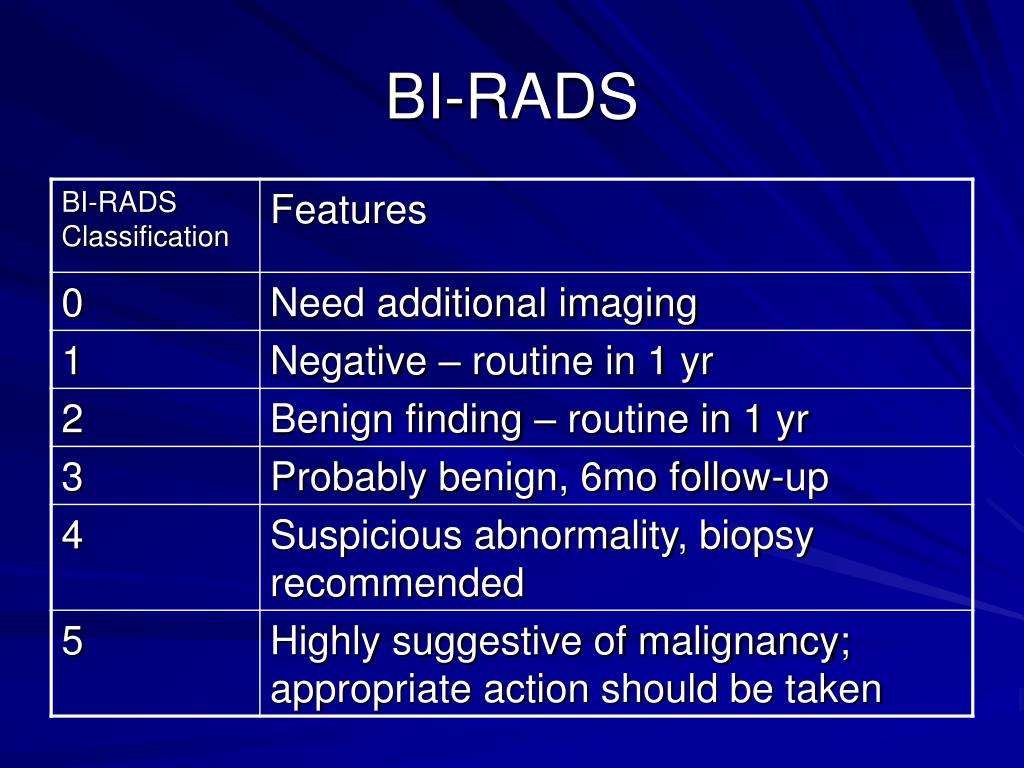
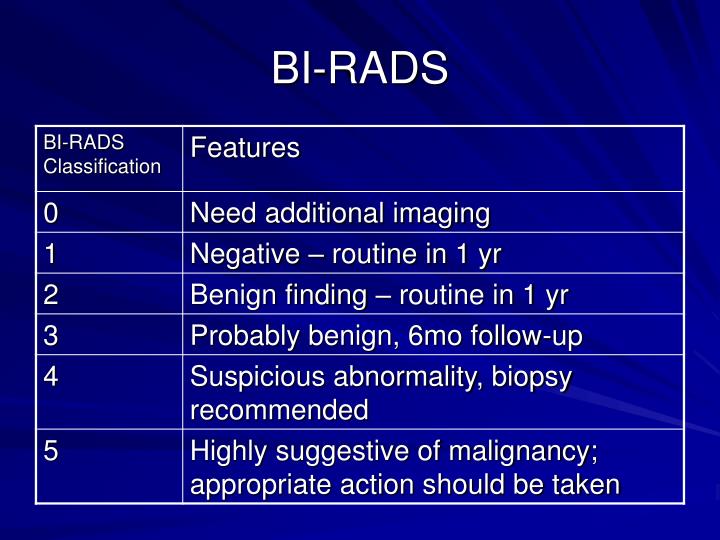
What percent of stereotactic biopsies are benign?
Because 70% to 80% of breast biopsies are performed for benign lesions, only the volume of tissue necessary to make the diagnosis of a benign process is needed by the pathologist.
What percent of breast calcifications are malignant?
The rate of malignancy was 40.0% (543 of 1357) for cases with a single cluster of microcalcifications, 50% (112 of 224) for those with multiple clusters and 60.0% (303 of 505) for those with dispersed microcalcifications.
How long does it take to heal from a stereotactic breast biopsy?
Watch for excessive bleeding, redness, skin changes, swelling or pain. Bleeding under the skin could present as a hard area (lump) that could take up to 6 weeks to resolve.
How painful is a core needle breast biopsy?
This can be uncomfortable, but most patients describe it as perfectly tolerable (experience does vary somewhat). The recovery time is likewise usually quick, though there might be some bleeding and/or bruising. Core needle biopsies usually result in more bruising than a breast fine needle biopsy.
What are the two types of breast biopsy?
There are two basic types of breast biopsy: surgical and needle. A breast biopsy done surgically through an incision in the skin is called a surgical breast biopsy. A breast biopsy done by inserting a needle through the skin is called a breast needle biopsy.
Why do they put a clip in your breast after a biopsy?
A small metal clip may be inserted into the breast to mark the site of biopsy in case the tissue proves to be cancerous and additional surgery is required. This clip is left inside the breast and is not harmful to the body. If the biopsy leads to more surgery, the clip will be removed at that time.
What if my breast calcifications are malignant?
Although breast calcifications are usually noncancerous (benign), certain patterns of calcifications — such as tight clusters with irregular shapes and fine appearance — may indicate breast cancer or precancerous changes to breast tissue.
How often are breast calcifications malignant?
They're often benign, but calcifications can sometimes be an early sign of breast cancer. “The most common form of cancer we see with calcifications is ductal carcinoma in situ, which is considered stage 0 cancer,” Dryden says. Benign calcifications are often scattered throughout both breasts.
How often are suspicious calcifications malignant?
No further evaluation or treatment is needed. ''Probably benign'' calcifications have a less than 2% risk of being cancer. In other words, about 98% of the time, these type of calcifications are considered not to be cancer. Typically, they will be monitored every six months for at least one year.
How often are breast calcifications cancerous?
Sometimes, breast calcifications are the only sign of breast cancer, according to a 2017 study in Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. The study notes that calcifications are the only sign of breast cancer in 12.7 to 41.2 percent of women who undergo further testing after their mammogram.
Why would a radiologist recommend a biopsy?
Your physician and a Radiology & Imaging radiologist recommend a biopsy when a finding has an appearance that could possibly be cancerous. As medical procedures go, a biopsy or aspiration is minor.
What if my breast calcifications are malignant?
Although breast calcifications are usually noncancerous (benign), certain patterns of calcifications — such as tight clusters with irregular shapes and fine appearance — may indicate breast cancer or precancerous changes to breast tissue.
Should I worry about breast calcifications?
Should I be worried? A: While calcifications could be a cause for concern and need further investigation, they're actually a common mammographic finding and are most often noncancerous (benign). However, additional imaging and testing is often necessary, as they could indicate cancer.
10 Things Young Women Should Know About Breast Cancer
Is breast cancer genetic? Should I get tested for the BRCA gene? What every young women should know about breast cancer. Discover...
Breast Cancer: Visual Guide to Male Breast Cancer
Breast cancer isn't just a woman's disease. Learn about the symptoms and treatment of male breast cancer, and find out what can...
Everyday Habits to Lower Breast Cancer Risk
Concerned about your breast cancer risk? Here are everyday health habits you can adopt to improve your odds.
Breast Cancer: Where It Can Spread
When breast cancer spreads, or metastasizes, it often goes to these five places: the lymph nodes, bones, liver, lungs, and brain....
Breast Cancer Quiz: Symptoms & Signs
This Breast Cancer Quiz features signs, symptoms, facts, causes, common forms, terms, risk factors, statistics, and more. ...
Breast Cancer: 9 Surprising Benefits of Pet Ownership for Breast Cancer
Owning a pet can help you ease stress and anxiety, manage high blood pressure, and stay active, even when you have breast cancer.
Breast Cancer: Surprising Things That Can Help During and After Treatment
When you have breast cancer, help can come from some unexpected places. WebMD shares a few.
What is Stereotactic Biopsy?
Stereotactic biopsy is a kind of mammographically guided biopsy that uses x-ray to detect breast cancer or abnormality in breasts. In order to place the biopsy needle precisely at the correct location, stereotactic biopsy utilizes x radiation. Once placed, a small sample of tissue is removed for further examination in the laboratory.
What is Ultrasound Biopsy?
Ultrasound biopsy is an image-guided biopsy that uses ultrasound waves to place the biopsy needle precisely at the correct location. Therefore, ultrasound biopsy does not use radiation. Instead, it uses high-frequency sound.
What are the Similarities Between Stereotactic Biopsy and Ultrasound Biopsy?
In both stereotactic biopsy and ultrasound biopsy, a small sample of tissue is removed for further examination.
What is the Difference Between Stereotactic Biopsy and Ultrasound Biopsy?
Stereotactic biopsy uses an x-ray to examine and place the needle, while ultrasound biopsy uses ultrasound waves to place the biopsy needle. Thus, this is the key difference between stereotactic biopsy and ultrasound biopsy. Unlike stereotactic biopsy, ultrasound biopsy does not use ionizing radiation.
Summary – Stereotactic Biopsy vs Ultrasound Biopsy
Stereotactic biopsy and ultrasound biopsy are two relatively simple and less invasive biopsies than surgical biopsy. Stereotactic biopsy uses x radiation to guide the biopsy needle to the accurate location. In contrast, ultrasound biopsy uses sound waves to locate the biopsy needle to the accurate place.
