The main difference between acid fast and non acid fast bacteria is that acid fast bacteria resist decolorizing by acid after accepting a stain whereas non acid fast bacteria are readily decolorized by acid after staining.
What is the difference between acid fast and non acid fast?
Non Acid Fast Bacteria: The non acid fast bacteria are a type of bacteria that are readily decolorized by acid after staining. Acid Fast Bacteria: The final color of the acid fast bacteria is pink or red. Non Acid Fast Bacteria: The final color of the non acid fast bacteria is blue.
What is acid fast in microbiology?
Acid fastness is a physical character of bacteria, which can be described as the resistance to decolorization by acids during staining procedures such as Gram staining. The acid-fast staining is used to differentiate bacteria as acid fast and non acid fast bacteria. The most commonly used acid-fast staining technique is Ziehl-Neelsen stain.
What is an example of non acid fast bacteria?
Nonacid fast bacteria can be stained using gram stain or any other simple staining procedure. Examples of nonacid fast bacteria are Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas sp. Non acid fast bacteria is in blue What is the difference between Acid Fast and Non Acid Fast Bacteria?
What is the effect of acid fast staining on nonacid fast bacteria?
After following the acid fast staining procedure, these bacteria will stain with blue. This is because nonacid fast bacteria have a thin cell wall and lack mycolic acid in the cell wall. This allows the penetration of carbolfuchsin into the cytoplasm. However, it is removed with acid alcohol treatment, making nonacid fast bacterial cells colorless.

What is the difference between acid-fast and non acid-fast organisms?
Acid fast bacteria have a high content of mycolic acids in their cell walls. Acid fast bacteria will be red, while nonacid fast bacteria will stain blue/green with the counterstain with the Kinyoun stain.
What does it mean if a bacteria is non acid-fast?
Bacteria that cannot retain the red color of carbol fuchsin after decolorization with acid-alcohol are known as non-acid fast bacteria. These bacteria lack high amounts of lipids in their cell walls that can firmly retain the dye.
Why are some bacteria acid-fast and others not?
Principle: Some bacteria contain a waxy lipid, mycolic acid, in there cell wall. This lipid makes the cells more durable and is commonly associated with pathogens. Acid fast cell walls are so durable that the stain (carbol fuschin) must be driven into the cells with heat.
What are acid-fast bacteria?
Acid-fast bacillus (AFB) is a type of bacteria that causes tuberculosis and certain other infections. Tuberculosis, commonly known as TB, is a serious bacterial infection that mainly affects the lungs. It can also affect other parts of the body, including the brain, spine, and kidneys.
Why is E coli non acid-fast?
Most bacteria, such as E. coli and Staphylococcus, lack this high mycolic acid content and are easily decolorized by the acid-alcohol. Therefore, these organisms are described as “non-acid-fast”. They absorb the counterstain, methylene blue.
Why do non acid-fast bacteria stain blue?
The non-acid fast organism lack the lipoidal material in their cell wall due to which they are easily decolorized, leaving the cells colorless. Then the smear is stained with counterstain, methylene blue.
What are examples of non acid-fast bacteria?
In order to clearly observe and differentiate from acid fast bacteria, methylene blue will be useful here. Nonacid fast bacteria can be stained using gram stain or any other simple staining procedure. Examples of nonacid fast bacteria are Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas sp.
Why do acid-fast positive bacteria grow more slowly?
Functions of the Acid-Fast Cell Wall Components Layer 3: The mycolic acids and other glycolipids also impede the entry of chemicals causing the organisms to grow slowly and be more resistant to chemical agents and lysosomal components of phagocytes than most bacteria (Figure 2.3C. 2).
Why is Mycobacterium called acid-fast bacteria?
Mycobacterium and many Nocardia species are called acid-fast because during an acid-fast staining procedure they retain the primary dye carbol fuchsin despite decolorization with the powerful solvent acid-alcohol. Nearly all other genera of bacteria are nonacid-fast.
Why is it important to study acid-fast bacteria?
An acid-fast bacteria (AFB) culture is done to find out if you have tuberculosis (TB) or another mycobacterial infection. Besides TB, the other main mycobacterial infections are leprosy and a TB-like disease that affects people with HIV/AIDS.
Are all Gram positive bacteria acid-fast?
Posted June 1, 2020. Acid-fast bacteria are gram-positive in terms of structure because they contain peptidoglycan in the cell wall. However, they stain poorly with Gram stain procedure, appearing weakly Gram-positive.
Why acid-fast bacteria Cannot be Gram stained?
Although gram positive, acid-fast bacteria do not take the crystal violet into the wall well, appearing very light purple rather than the deep purple of normal gram positive bacteria (the waxy lipid in the acid-fast wall repels the aqueous crystal violet stain).
What is the purpose of the acid-fast stain?
The acid-fast stain is a laboratory test that determines if a sample of tissue, blood, or other body substance is infected with the bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB) and other illnesses.
What is acid-fast bacilli test?
Brief Description. Acid- Fast Bacilli (AFB) smear and culture are two separate tests always performed together at the MSPHL, Tuberculosis (TB) Unit. AFB smear refers to the microscopic examination of a fluorochrome stain of a clinical specimen.
What is the acid-fast stain procedure?
Acid-Fast Staining InstructionsAir dry and heat fix a thin film of microorganisms. ... Flood the slide with Carbolfuchsin. ... Flood slide with Acid Alcohol for 30 seconds. ... Counterstain by flooding the slide with Methylene Blue for 30 seconds. ... Dry the slide by putting it between the pages of a book of Bibulous paper.More items...
Acid Fast vs Non Acid Fast Bacteria
The difference between acid fast and non acid fast bacteria is in their cell wall, basically. Bacteria are generally identified and observed with d...
Acid Fast Staining Procedure
In order to complete the understanding of the acid fast and non acid fast bacteria, first we will go through the staining procedure. Acid fastness...
What Are Acid Fast Bacteria?
Bacteria that have acid fastness are known as acid fast bacteria. In other words, bacteria that are still stained with red color after the decolori...
What Are Non Acid Fast Bacteria?
If a bacterium lacks the acid fastness it is called nonacid fast bacteria. After following the acid fast staining procedure, these bacteria will st...
What is the difference between acid fast and non acid fast bacteria?
The difference between acid fast and non acid fast bacteria is in their cell wall, basically. Bacteria are generally identified and observed with differential staining procedures. Acid fast staining is one of such methods to distinguish a certain type of bacteria from others. This method was first discovered by Franz Ziehl and Friedrich Neelsen. At that time, Mycobacterium that cause tuberculosis, was unable to be stained and observed using other staining procedures such as gram stain. Neelsen and Ziehl stained this bacteria by adding phenol (carbolic acid) and basic fuchsin (e) along with acid alcohol, so the dye is known as Carbol Fuchsin (e) solution or Ziehl – Neelsen stain.
What are Acid Fast Bacteria?
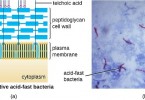
Bacteria that have acid fastness are known as acid fast bacteria. In other words, bacteria that are still stained with red color after the decolorization step during the acid fast staining procedure are known as acid fast bacteria . What makes these bacteria to have acid fastness? Well, if we consider a cross section of the cell wall of an acid fast bacterium, it can be easily understand.
Why do nonacid fast bacteria stain?
This is because nonacid fast bacteria have a thin cell wall and lack mycolic acid in the cell wall. This allows the penetration of carbolfuchsin into the cytoplasm. However, it is removed with acid alcohol treatment, making nonacid fast bacterial cells colorless. In order to clearly observe and differentiate from acid fast bacteria, methylene blue will be useful here.
What is the primary die that is flooded over a smear of bacteria that is heat fixed on?
This is initially described by Paul Ehrlich. Following three steps are carried out during the staining procedure. 1. Application of primary dye – Carbolfuchsin is the primary die that is flooded over a smear of bacteria that is heat fixed on a clean slide. Heat is applied to ensure the penetration of dye up to the cytoplasm.
What are some examples of nonacid fast bacteria?
Nonacid fast bacteria can be stained using gram stain or any other simple staining procedure. Examples of nonacid fast bacteria are Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas sp.
Does acid alcohol decolorize bacteria?
During the acid alcohol decolor ization step, the acid alcohol is prevented entering the cytoplasm due to the presence of hydrophobic mycolic acid, thus it is unable to remove carbolfuchsin from the bacteria cell. So the primary dye will remain in the cytoplasm even after the decolorization step.
Which bacteria are pathogenic to humans?
Acid fast bacteria includes several genera such as Mycobacterium and Nocardia, which are pathogenic to human, causing tuberculosis and nocardiosis, respectively.
What is Acid Fast?
Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacteria, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during staining procedures. Once stained, these organisms resist dilute acid and or ethanol based decolorization procedures common in many staining protocols. Thus, the name ‘acid fast’ is given to those organisms. This property is shown due to having a high level of waxy material (mycolic acids) in their cell walls. This test is critical for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
What is the difference between acid fast and gram stain?
Gram staining is a differential staining technique, which separates bacteria into two groups known as Gram-posi tive bacteria and Gram-nega tive bacteria. The acid-fast stain is a differential stain used to identify acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium from non-acid fast organisms. This is the key difference between Gram stain ...
What is the Difference Between Gram Stain and Acid Fast?
Gram staining is a differential staining technique, which separates bacteria into two groups Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria.
What is the primary stain for Grams?
Grams staining is performed using four different reagents namely; primary stain, mordant, decolorizing agent and counter stain. Crystal violet and safranin are used as the primary and counter stains, respectively while grams iodine and 95% alcohol are used as the mordant and decolourizer, respectively. The basic steps of grams stain are as follows;
What is Gram staining?
Gram staining categorizes bacteria into two major groups named gram positive and gram negative, which are very important in bacterial classification and identification. Microbiologists perform gram staining as an initial step in bacterial characterization during their studies.
Why is the primary stain not effective for Gram positive bacteria?
The counter stain will not be effective for gram positive bacteria due to the retention of the primary stain. Thus, grams positive bacteria will be visible in primary stain colour, that is, purple colour.
What is the primary stain used in acid fast?
Crystal violet is the commonly used primary stain in gram staining. Carbol fuchsin is the primary stain used in acid fast. Decolourizing Agent. 95% alcohol is used as a decolourizing agent in gram stain. Acid alcohol is used as a decolourizing agent in acid fast.
What makes acid fast bacteria difficult to stain?
acid fast bacteria have a waxy cell wall (mycolic acid) that makes them difficult to stain with traditional methods
Why do cells turn pink after safranin?
cells will appear pink after the safranin is applied because the CV-i complex is stripped during decolorizer step
What is used to remove primary stain from cells?
ethyl alcohol, used to remove the primary stain from the cells
Can you spread bacteria on a slide?
spread bacteria on a clean slide and allow to air dry on electric warmer
