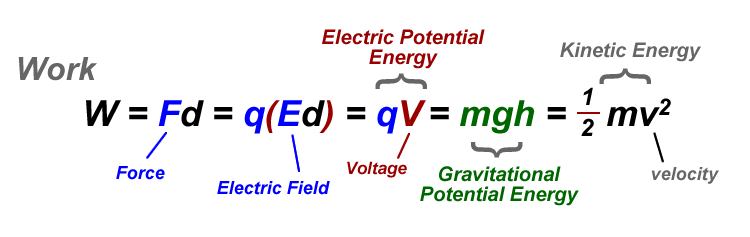
Membrane potential refers to the difference in charge between the inside and outside of a neuron, which is created due to the unequal distribution of ions on both sides of the cell. The term action potential refers to the electrical signaling that occurs within neurons.
What is an action potential and how does it work?
action potential, the brief (about one-thousandth of a second) reversal of electric polarization of the membrane of a nerve cell ( neuron) or muscle cell. In the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse, and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement.
What determines the membrane potential?
the membrane potential (V) is determined by the equilibrium potential for each ion multiplied by that ion's fraction of the total membrane conductance. How is conductance of an ion related to the type of channels in a membrane? The conductance to each ion is proportional to the total number of open channels for that ion.
What are the steps in an action potential?
- physical stimulus
- chemical stimulus
- increase in resistance
- decrease in resistance
What happens during an action potential?
- The voltage-gated ion channels are located along the axon hillock and axon; they open in response to the membrane potential reaching a threshold value
- The rising phase of the action potential is a result of sodium influx
- The falling phase of the action potential is a result of potassium efflux

What is the difference between action and potential?
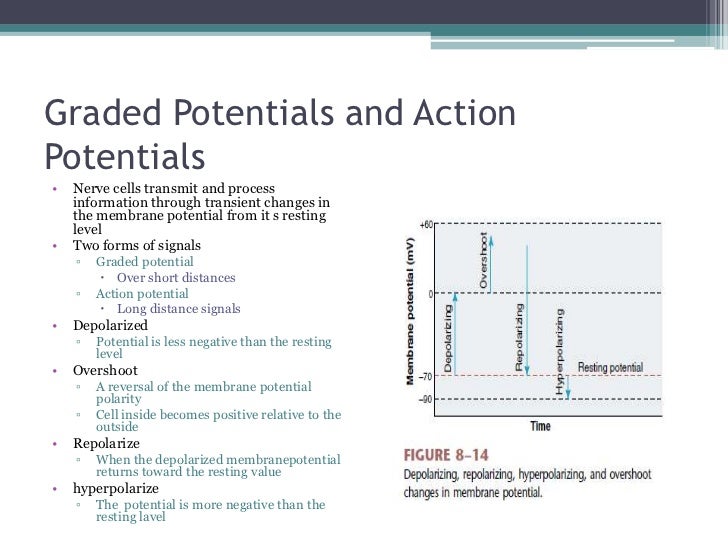
The main difference between graded potential and action potential is that graded potentials are the variable-strength signals that can be transmitted over short distances whereas action potentials are large depolarizations that can be transmitted over long distances.
What is the membrane potential difference?
Membrane potential is what we use to describe the difference in voltage (or electrical potential) between the inside and outside of a cell.
What do you mean by membrane potential?
Membrane potential is a potential gradient that forces ions to passively move in one direction: positive ions are attracted by the 'negative' side of the membrane and negative ions by the 'positive' one.
Why is it called membrane potential?
This voltage is called the resting membrane potential; it is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell. If the membrane were equally permeable to all ions, each type of ion would flow across the membrane and the system would reach equilibrium.
How does membrane potential affect action potential?
During the resting state, the membrane potential arises because the membrane is predominantly permeable to K+. An action potential begins at the axon hillock as a result of depolarisation. During depolarisation voltage-gated sodium ion channels open due to an electrical stimulus.
What is an action potential?
An action potential is a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane. The membrane voltage, or potential, is determined at any time by the relative ratio of ions, extracellular to intracellular, and the permeability of each ion.
Where is the membrane potential?
The membrane potential is the difference in electrical charge between the inside and the outside of the neuron. This is measured using two electrodes. A reference electrode is placed in the extracellular solution. The recording electrode is inserted into the cell body of the neuron.
What is membrane potential and why is it important?
The membrane potential represents a balance among the equilibrium potentials of the ions to which the membrane is permeable. The greater the conductance of an ion, the more that ion will influence the membrane potential of the cell.
What do you mean by membrane?
membrane, in biology, the thin layer that forms the outer boundary of a living cell or of an internal cell compartment. The outer boundary is the plasma membrane, and the compartments enclosed by internal membranes are called organelles.
What is membrane potential in anatomy and physiology?
The membrane potential is a distribution of charge across the cell membrane, measured in millivolts (mV).
What is the full meaning of membrane?
1 : a thin soft pliable sheet or layer especially of animal or plant origin. 2 : a limiting protoplasmic surface or interface — see nuclear membrane, plasma membrane. Other Words from membrane.
What is Membrane Potential?
So, the membrane potential is the charge difference across the cell membrane. This occurs due to the separation of positive and negative ions across the membrane. In fact, the membrane potential is the force that facilitates the passive movement of ions in one direction. Under the resting condition, this voltage difference is known as the resting membrane potential. Upon stimulation, the charges across the membrane alter and create an action potential.
What are the Similarities Between Membrane Potential and Equilibrium Potential?
Net electrochemical force is the difference between the membrane potential and the equilibrium potential.
What is the resting membrane potential of glial cells?
In glial cells, the resting membrane potential is equal to the equilibrium potential for K + ion. Moreover, in neurons, the resting membrane potential is very close to the equilibrium potential of K +.
What is the equilibrium potential of an ion?
Equilibrium potential of an ion is the membrane potential that exactly balances the concentration gradient of the ion across the membrane. In other words, equilibrium potential is the membrane potential that is required to produce electrochemical equilibrium. At the equilibrium potential, the net flow of that particular ion across ...
What determines the potential of a cell?
There are several factors that determine the membrane potential. They are ion concentrations inside and outside the cell , the permeability of the cell membrane to ions and the activity of ion channels such as Na + /K + -ATPase and Ca ++ transport pumps located in the cell membrane.
Which direction does membrane potential force ion movement?
Moreover, membrane potential forces ion movement passively in one direction, while equilibrium potential restricts the ion movements across the membrane.
How do ions and nutrients go into and out of a cell?
Different substances, especially ions and nutrients, go in and out of the cell via the cell membrane. In order to take ions and nutrients inside the cell, cells generate and maintain a membrane potential across the plasma membrane . The membrane potential is the difference of voltage or electric potential between the inside and the outside ...
What is action potential?
Action potential occurs within a neuron when it transmits electrical impulses. During this signal transmission, the membrane potential (the difference in electrical potential between the outside and inside of a cell) of the neuron (specifically the axon) fluctuates with rapid rises and falls.
Where do action potentials occur?
During an action potential, the nerve transmission of impulses takes place along the axon of the neuron up to the synaptic knobs located at the end of the axon.
What are the Similarities Between Action Potential and Synaptic Potential?
Both action potential and synaptic potential are needed for neurons to communicate with each other and send nerve impulses.
What are the two types of synaptic potentials?
There are two types of synaptic potentials as excitatory and inhibitory, based on the nature of the neurotransmitters and post-synaptic receptors. Excitatory synaptic potential depolarizes the membrane while inhibitory synaptic potential hyperpolarizes the post-synaptic membrane.
What is the difference between synaptic potential and action potential?
The key difference between action potential and synaptic potential is that action potential is the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane of excitable cells such as neurons, muscle cells and endocrine cells, etc. while synaptic potential is the post-synaptic potential change in neurons.
Why are synaptic potentials needed?
Synaptic potentials have a smaller amplitude. Hence, many synaptic potentials are needed to trigger an action potential. Moreover, they have a slower time course and do not have a refractory period. Unlike action potentials, synaptic potentials degrade quickly as they move away from the synapse.
What determines the occurrence of an action potential?
The occurrence of an action potential depends on the synaptic potential across the membrane of the neuron.
When does action potential occur?
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls.
What type of cells are action potentials?
This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells referred to as excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, en docrine cells, glomus cells and in some plant cells.
What Is Resting Potential?
Resting potential is the imbalance of electrical charge that exists between the interior of electrically excitable neurons (nerve cells) and their surroundings. If the inside of a cell becomes more electronegative (i.e if the potential is made greater than the resting potential), the membrane or the cell is said to be hyperpolarized. If the inside of the cell becomes less negative (i.e the potential decreases below the resting potential), the process is called depolarization.
What is the resting membrane potential of a cell?
The resting membrane potential of cells varies depending on the cell type; the resting potential for neurons typically ranges between -50 and -75mV. This value depends on the types of ion channels that are open and the concentrations of different ions in the intracellular and extracellular fluids.
Which is more permeable, sodium or potassium?
The membrane is more permeable to potassium ions (K+) than sodium ions (Na+).
What is the role of action potentials in neuronal communication?
In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell-to-cell communication by providing for the propagation of signals along the neuron’s axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses or to motor cells or glands.
Which channels are open at the action potential?
Voltage-gated sodium channels open up and voltage-gated potassium channels are closed at the action potential.
What is resting membrane potential?
A resting membrane potential is the difference between the electric potential in the intracellular and extracellular matrices of the cell when it isn’t excited. Every cell of the body has its own membrane potential, but only excitable cells - nerves and muscles - are capable to change it and generate an action potential .
Which pump controls membrane potential?
Sodium-potassium pump (Na-K pump) Another factor that controls membrane potential is the Na (+)-K (+) pump. This pump uses energy to expel 3 molecules of sodium in exchange for 2 molecules of potassium.
What are the pores of the excitable membrane?
Pores contribute to establishing resting membrane potential, and they are found along the entire excitable cell membrane. When the cell isn’t excited, diffusion of ions occurs only through the pores. Note that during rest, a lot more potassium pores are open than for the sodium.
How does a concentration gradient contribute to an action potential?
By concentration gradient definition, every element modifies its concentration gradient to seek equilibrium. For example, ions will diffuse from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration of the element is equal on both sides. This means that the sodium will diffuse from extra- to intracellular space, and the potassium will do the opposite. More about this process can be found in the action potential article.
What is the membrane potential of an excitable cell?
For this reason, membrane potential for excitable cells when they are not excited is called the resting membrane potential, while its changes are associated with an action potential. Key facts about the membrane potential. Definition. Difference between the electric potential of the cellular membrane matrices when the cell isn’t excited.
What are ion channels?
Ion channels are specialized proteins of the cell membrane that enable migration of the ions. There are two types of ion channels: Passive channels – which are the pores within the cell membrane, through which the molecules pass depending on their concentration gradient.
Which ions contribute the most to the cell?
Concentration of ions inside and outside the cell. Ions that contribute the most are the sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride ions. Activity of the sodium-potassium pump. Variable permeability of the cell membrane for ions.
What is the difference in electrical potential?
Difference in electrical potential- a voltage difference between the inside and outside of the cell
Which cell has a potential?
Cells like neurons, skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle- presence of a potential enables the production and transmission of an action potential
What is the E chem potential used for?
Used to calculate membrane potential where the e chem potential of an ion will be the same on both sides of a membrane with the given concentraitons
Why is there no diffusion of K or Cl?
No diffusion of K or Cl because both the permeability of the membrane to KCl is 0 and the concentration dif is 0
Is there a potential differene if it is permeable to at least one ion?
No potential differene unless it is permeable to at least one ion
How does an action potential work?
Action potential is fired by EPSP. It is a momentary event wherein the cell’s electrical membrane potential instantly rises and falls. A consistent trajectory then follows. In neurons, action potentials are also called nerve impulses or spikes. A sequence of action potentials is called a spike train. Action potentials frequently occur in human cells since humans have neurons, endocrine cells, and muscle cells. When there is a signal, the neurons communicate with each other reaching EPSP until it needs to fire an action potential. Voltage-gated ion channels produce action potentials. These channels lie inside the plasma membrane of the cell. There is a phase called resting potential. When the membrane potential is nearing the resting phase, the voltage-gated ion channels are shut, but they immediately open when there is an increase in the membrane potential value. Sodium ions will flow when these channels open which further increases the membrane potential. As membrane potentials increase, more and more electric current flows. There are two basic types of action potentials in animal cells: voltage-gated sodium channels and voltage-gated calcium channels. Voltage-gated sodium channels last for about less than one millisecond while voltage-gated calcium channels last for about a hundred milliseconds or even longer.
Where do action potentials occur?
Action potentials frequently occur in human cells since humans have neurons, endocrine cells, and muscle cells. When there is a signal, the neurons communicate with each other reaching EPSP until it needs to fire an action potential. Voltage-gated ion channels produce action potentials. These channels lie inside the plasma membrane of the cell.
What is excitatory post-synaptic potential?
Excitatory postsynaptic potential occurs when there is a flow of positively charged ions towards the postsynaptic cell, a momentary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential is created. Action potentials are also called nerve impulses or spikes.
What neurotransmitter is involved in firing an action potential?
The larger the EPSPs become, the more it reaches the limit of firing an action potential. The amino acid glutamate is the neurotransmitter associated with EPSPs. It is also the main neurotransmitter of the vertebrates’ central nervous system. Amino acid glutamate is then called the excitatory neurotransmitter. Action potential is fired by EPSP.
How long do action potentials last in animal cells?
Voltage-gated sodium channels last for about less than one millisecond while voltage-gated calcium channels last for about a hundred milliseconds or even longer.
When does a post-synaptic potential become excitatory?
A postsynaptic potential becomes excitatory when the neuron is triggered to release an action potential.
Where are the ion channels located?
These channels lie inside the plasma membrane of the cell. There is a phase called resting potential. When the membrane potential is nearing the resting phase, the voltage-gated ion channels are shut, but they immediately open when there is an increase in the membrane potential value.