Quite simply an air barrier reduces the flow of air, a vapor barrier reduces the flow of water vapor and awater resistive barrier reduces the flow of liquid water. Each function is completely different. The confusion comes in when one material can provide more than one function, but they have to be used in a way to actually perform that function.
How much does it cost to install a vapor barrier?
How much does vapor barrier cost? Vapor Barrier Installation A standard 20-millimeter vapor barrier typically costs from $0.50 to $0.70 per square foot. In addition, you'll need to buy tape to secure the vapor barrier, which usually costs around $50 for a 4-inch-by-180-foot roll. How much is a moisture barrier?
What are vapor barriers and are they necessary?
Vapor barriers were originally intended to prevent assemblies from getting wet. However, they often prevent assemblies from drying. Vapor barriers installed on the interior of assemblies prevent assemblies from drying inward. This can be a problem in any air-conditioned enclosure. This can be a problem in any below grade space.
What is a vapour barrier and its use?
A vapour barrier (sometimes referred to as vapour retarder) is typically a plastic or foil sheet used for damp proofing to prevent interstitial condensation from forming in various building assemblies such as walls, roofs, foundations and floors.
What is a Class 3 vapor barrier?
- Class I – Very low permeability vapor retarders – rated at 0.1 perms or less. ...
- Class II – Low permeability vapor retarders – rated greater than 0.1 perms and less than or equal to 1.0 perms. ...
- Class III – Medium permeability vapor retarders – rated greater than 1.0 perms and less than or equal to 10 perms. ...
What is the difference between air barrier and weather barrier?
While vapor retarders and air barriers are intended to control moisture condensation within wall assemblies, weather-resistive barriers (WRBs) are intended to prevent the penetration of liquid water through the exterior walls.
What is the purpose of an air vapor barrier?
This is the function of air barriers. A vapor barrier is designed to restrict the flow of water vapor through a material, just the same as an air barrier material restricts the flow of air through a material.
What is an air barrier system?
Air barrier systems help separate the outside environment from the desired interior environment. Ultimately, an air barrier creates seamless continuity and structural integrity that helps eliminate uncontrolled air leakage and allows control over temperature, humidity, moisture and air quality throughout the building.
Is Tyvek considered an air barrier?
“It is well known that staple-up housewraps like Tyvek don't make the best air barriers,” he says. “At least they are challenging, at best, to detail as an air barrier. If you choose this type of product, taping the plywood seams is a more straightforward approach to air sealing.”
Do I need an interior air barrier?
It provides better protection against condensation risk - keeping interior humid air away from cold components. (After bulk water intrusion, air leaks and convective movement are the enclosure's biggest liabilities.)
Where are air barriers used?
Sometimes, air barrier systems do both. Air barrier systems can be located anywhere in the building enclosure – at the exterior surface, the interior surface, or at any location in between. In cold climates, interior air barrier systems control the exfiltration of interior, often moisture-laden air.
How is an air barrier installed?
0:535:08Ecohome building guide: installing air barriers - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnything that penetrates your air barrier like plumbing ventilation wiring so from the bottom theMoreAnything that penetrates your air barrier like plumbing ventilation wiring so from the bottom the sub-slab vapor barrier comes up it's attached to the sheathing.
Does an air barrier need to be continuous?
The function of an air barrier is quite specific; to stop air leakage due to differences in air pressure and temperature. It must also be continuous to be fully effective.
Do you need vapor barrier?
A vapour barrier is an important component in building construction. Its purpose is to help prevent water vapour from reaching building walls, ceilings, attics, crawlspaces or roofs, where it can condense and cause building materials to rot or grow mould.
Where should a vapor barrier be installed?
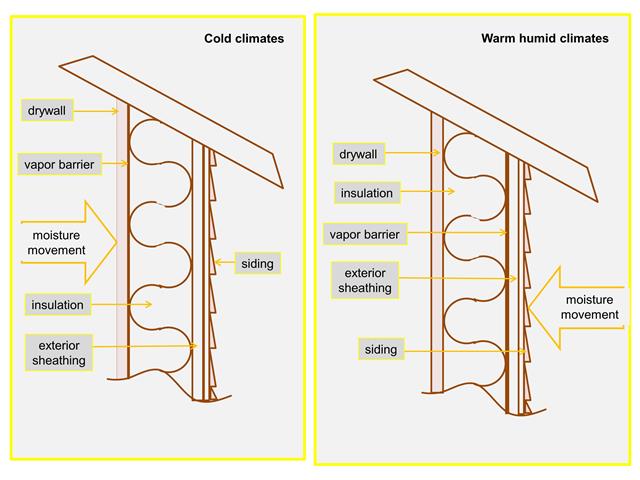
Vapor barriers are usually best installed on the side of the wall that experiences the hotter temperature and moister conditions: the inner surface in colder climates and the outer surface in hot, humid climates. In existing spaces, oil-based paints or vapor-barrier latex paints offer an effective moisture barrier.
What is the implications of a missing air vapor barrier are?
What are the implications of air/vapor barriers that are missing or incomplete? Increased air leakage and possible rot damage from condensation are the implications of a missing air/barrier.
Do interior walls need vapor barrier?
Normally interior walls do not require a vapor barrier, but there are some situations where it is highly recommended. Interior bathroom and kitchen walls, for example, are areas where there is great benefit to installing a vapor barrier. Bathrooms and kitchens produce an enormous amount of water vapor daily.
What Is An Air Barrier?
Air barriers are systems of materials designed and constructed to control airflow between a conditioned (indoor) space and an unconditioned (outdoor) space.
What does it mean when a hole is in a vapor barrier?
A hole for example in a vapor barrier will simply mean that there will be more vapor diffusion in that area compared to the other areas of the vapor barrier. To simplify, consider this wool sweater analogy: A wool sweater is insulation.
Why Do Air Barriers Really Matter?
Now that you understand the difference between air barriers and vapor barriers, the bigger question is why do they really matter? That’s a question being asked by many architects, contractors, engineers, and building owner-developers, and the answers are varied.
What is the difference between a wool sweater and a raincoat?
A wool sweater with a raincoat will keep you warm, but hold moisture inside and soak your insulation. A wool sweater with a windbreaker will keep you warm, stop the wind from stealing your heat, yet allow moisture to diffuse through it. So think of a windbreaker as an air barrier and a raincoat as a vapor barrier.
Why are air barriers important?
Here are four tangible benefits to air barriers: 1. Preventing the Loss of Conditioned Air. For most consumers, the biggest reason “why” is air barriers are important is comfort. In summer, we normally cool and dehumidify the air to a lower temperature and humidity than the exterior environment.
Why is airflow important?
In order to design and build safe, healthy, durable, comfortable and economical buildings airflow must be controlled. Airflow carries moisture that impacts a building material’s long-term performance, integrity and durability, behavior in fire (spread of smoke), indoor air quality (distribution of pollutants and location of microbial reservoirs) and thermal energy. One of the key strategies in the control of airflow is the use of air barriers.
Where is vapor barrier installed?
Vapor barrier materials are installed on the warm side of the insulation in a building assembly, as determined by climatic conditions. In warm climates, it will be on the exterior and in cold climates, it will be on the interior.
What is an air barrier?
The 2021 International Residential Code ( IRC) defines an air barrier as one or more materials joined together continuously to prevent airflow through the building’s thermal envelope and its assemblies. In comparison, the IRC defines a continuous air barrier as one that includes a combination of materials and assemblies that restrict or stop the passage of air through the building envelope.
How does an air barrier work?
An effective air barrier regulates the indoor climate by preventing the transfer of air (and the moisture attached to it) between the exterior and interior of a home. An air barrier must also stand up to the air pressure differences acting on them. They stop air from transporting moisture to the interior of a wall assembly, preventing condensation and the damaging effects of moisture accumulation. They are essential to waterproofing new foundation walls.
What is poly wall?
Poly Wall® Building Solutions (a division of Polyguard) provides homeowners quality protection against air and moisture infiltration for both above- and below-wall systems, ensuring a superior building envelope and the long-term integrity of the building or home. Poly Wall®’s air and moisture barrier systems include air barriers , below-grade waterproofing systems , liquid flashings, and window and door sheet flashings.
Why do builders put vapor barriers on the walls?
Typically, builders place vapor barriers (like polyethylene) on the interior wall and ceiling insulation to prevent vapor diffusion into the wall systems during the cold winter months when the inside of a house is warmer than the air within the wall assembly.
What is the IBC code for vapor barriers?
Deciding to use a vapor barrier on a building’s interior or exterior depends on the climate zone. For example, the 2021 International Building Code (IBC) 1404.3 and the 2021 International Residential Code (IRC) R702.7 instruct Class I or II vapor barriers and retarders inside frame walls in climate zones 5,6,7,8 and Marine 4. However, southern climate zones 1, 2, and 3 do not mandate vapor barriers and retarders.
What is the purpose of air barrier?
The design of an air barrier must control air, heat, moisture flow, and solar radiation to effectively manage the interactions between the building’s physical elements, its occupants, and the environment.
What is continuous air barrier?
A continuous air barrier system aims to control heat, moisture, and air transfer by providing a continuous airtight building envelope that separates the unheated and heated spaces between all the building enclosure components. The building enclosure includes the below- and the above-grade elements that physically separate the interior and exterior environments of the house.
What is the difference between a vapor barrier and an air barrier?
The difference between air barriers and vapor barriers. The job of a vapor barrier is to prevent vapor diffusion, and the job of an air barrier is to stop air leakage through differences in air pressure. A wall system should have one vapor barrier, but can have many air barriers. A vapor barrier can act as a very effective air barrier, ...
How does water vapor travel through walls?
How water vapor travels: There are two main ways moisture will pass through your walls that you should be concerned about — air leakage and vapour diffusion. These are two completely different things, with two completely separate solutions.
How many vapor barriers are there in a wall?
A wall system should have one vapor barrier, but can have many air barriers. A vapor barrier can act as a very effective air barrier, but an air barrier does not (and should not) always stop vapor from difusing. A wool sweater for example, is a good choice of natural insulation and will keep you warm when there is no air movement, ...
What is the best way to keep warm?
A wool sweater for example, is a good choice of natural insulation and will keep you warm when there is no air movement, but will allow the wind to howl right through it. A wool sweater with a raincoat will keep you warm but hold moisture inside and soak your insulation. A wool sweater with a windbreaker will keep you warm, stop the wind from stealing your heat, yet allow moisture to difuse through it.
What is the dewpoint of a wall?
The dewpoint in a wall is the point where the drop in temperature causes air to contract, and water vapor turns to liquid. Since the warmer the air is the more moisture it can hold, where the dewpoint will be in your wall is determined by the difference in temperature from indoor to out, and the amount of moisture in the air ...
What is the purpose of a vapor barrier?
In both cases, the vapor barrier is tasked with preventing warm, humid air from shedding its moisture as it meets a cool surface, no matter which direction it is travelling. The most important thing to realize is that there is no fixed rule regarding vapor barriers.
Why is air barrier important?
A proper air barrier is one of the most important elements of a successful building enclosure, and one of the most overlooked. Given the amount of heat loss due to air transmission and the potential moisture damage from air leaks, air barriers should be getting a lot more attention than they are.
How to Distinguish between Air Barriers and Vapor Barriers?
The flow of air contains a percentage quantity of water that affects the material relevance, purpose and integrity of buildings. Airflows can either aid or oppose the reactions of structures in any unforeseen event (including hazardous ones). Moreover, it determines the internal health conditions of buildings. Thus, the need for barriers.
Why barriers?
Construction professionals install air barriers and vapor barriers so they work in harmony as a system to effectively control moisture accumulation, resist air movement and ensure an airtight building envelope. Both barriers are needed to prevent moisture infiltration at various points depending on the zone of Site and the kind of project.
Air Barriers
These are those materials that prevent the inflow of air into a building. Any building component utilized to oppose air to indoor spaces (conditioned space) from outdoor spaces (unconditioned space) serves as an air barrier.
Vapor barriers
Vapor barriers are usually provided on building elements to prevent water diffusion (changes from gas to liquid) responsible for damage and ultimately compromised integrity of materials. They are used to reduce the transfer of water in a gaseous state. Its invention was to protect wet walls and ceilings.
Practical Application of Air Barriers and Vapor Barriers
It is a huge task to isolate the use of air and vapor barriers because they actually complement each other where the need arises. Depending on the building zone, these barriers vary in application and usage.
Create. Update. Renovate
Sign up to get updates on all of the latest innovative building products.
What is the purpose of an air barrier?
The function of an air barrier is to stop air leakage and resist differences in air pressure, keeping the indoor climate regulated. Essentially, they keep the outdoor air out and the indoor air in. An air barrier should: Be durable enough to withstand construction pressures and handling. Be impermeable to air flow.
What is a class I vapor retarder?
What we typically refer to as a vapor barrier is a Class I vapor retarder.
How many perms does a vapor membrane need?
But to be classified as vapor permeable, a membrane needs to have a permeance greater than 5 per ms, per the ASHRAE Journal, which doesn’t align with Class I Vapor Retarder attributes, requiring 0.1 perm of less. However, the higher the perms, the better vapor can diffuse out.
Can you put a vapor barrier on the warm side of the insulation?
In the words of the “uncontested king of home reno”, Jon Eakes, it’s possible to put the vapor barrier on the warm side of the insulation, without sealing it air tight, as long as you’ve created an uninterrupted air barrier someplace else, in the wall and ceiling.
Is a vapor barrier good for a building?
That said, airflow isn’t the sole cause of vapor issues, so an air barrier is a must, but a vapor barrier can still significantly benefit your building. Now that the differences in functionality and requirements are clear, the question that might be lingering is which material (s) to choose. Fortunately, there are products on the market that encompass all of these qualities. What’s more, adding the benefit of a self-adhesion only works to improve the performance of a multi-functional barrier. Look at DELTA®-VENT SA, for example. It is a high-performance, three-layer air- and water-resistive barrier that is highly vapor permeable and watertight. Check out this post to learn more about building envelope moisture control.
What happens when a vapor retarder is installed?
If a vapor retarder has been installed but not sealed around penetrations in a system with a mechanically attached membrane. When the membrane billows/flutters in high winds, humid interior air can be drawn up around penetrations into the roof system. Any subsequent condensation will likely take a long time to dry back down.
What is vapor retarder?
Vapor retarders are used within roofing assemblies to control moisture migration. They block air flow, provided they are tightly sealed around penetrations and the perimeter.
Why are vapor retarders used?
Vapor retarders are used to prevent diffusion of moisture vapor. However, they also help prevent humid air from reaching a cold surface inside the building envelope. So, by definition, they do act as barriers to vapor and air movement. But their intended purpose is not to improve energy efficiency, and they do not have to be part of the building envelope.
When is moisture not able to escape from a roof?
When the roof gets closed up, that moisture will not be able to escape if there is a tightly sealed impermeable vapor retarder further down in the assembly.
Why add insulation to a building envelope?
It's all about improving a building's energy efficiency. Adding more insulation to a building envelope has reached the point of rapidly diminishing returns. Also, insulation thicknesses are such that further increases would be difficult to accommodate without large increases in cost related to wall thickness, for example. Air leakage has been identified as a significant contributor to poor building energy efficiency. A building owner is paying a lot to heat or cool the interior air — why allow significant loss of that conditioned air to the outside?
Is it bad to use a vapor retarder on a roof?
It is considered bad practice to install materials that totally block moisture diffusion on the opposite sides of a building assembly, such as a vapor barrier at the deck level within a roof assembly. Roof membranes are vapor impermeable and any moisture that does get into the assembly, either during construction or from within the building, needs to be able to get back out. Therefore, vapor retarders should be used because they have some moisture permeability or they shouldn't be installed completely tightly.
Why are tighter buildings bad for indoor air quality?
Secondly, tighter buildings can have indoor air quality issues if the materials used to finish and furnish the interior off-gas odorous and maybe noxious chemicals. For that reason, many interior designers are selecting materials that have Environmental Product Declarations (EPD), Health Product Declarations (HPD) and similar.
What is a vapour barrier?
A vapour barrier is a material that offers a higher resistance to the diffusion of water vapour than most other materials. It is .
How much vapour is in a rier barrier?
rier. The barrier has a water vapour pexmeance of 5 ng/Pa.s-m2 (0.087 graimlh-ft2-in Hg), the
What is the moisture diffusion control of a material called?
The moisture diffusion control pmperty of a material is called its %a& vapour perme
What is the process by which water vapour migrates through a materia1?
Diffusion is the process by which water vapour migrates through a materia1 (Figure la). The
How much moisture can pass through a sheet of 0.1 mm?
ference. For -le, a sheet material, 0.1 mm thick, having a water vapour permeance of 10 will allow 10 nanograms of moisture to pass through one square metre of the material per
What is the cause of exterior wall problems?
INTRODUCTION A continuing examination of the performance of buildings in Canada has convinced the author that air leakage is the leadiig cause of exterior wall problem, It has been linked to efflorescence, spalling masonry; ice build-up under the soffits, frozen pipes and condensation in cavities, as well as rain penetration, high energy costs, and poor control over the indoor humidity conditions. Many of these problems originate early in the building process -
What is a good barrier for mpour?
sulation adhesives (mastics), metal, glass, and even concrete of s&cimt thickness may be quite suitable as mpour barriers.
