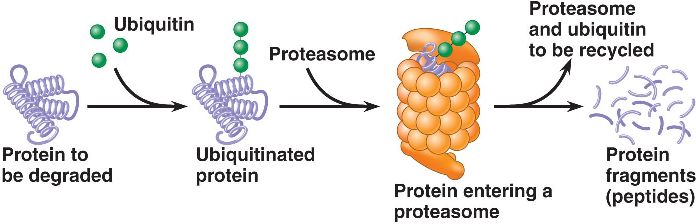
Proto-Oncogenes Explained
- Proto-oncogene vs. oncogene. ...
- Function of proto-oncogenes. Proto-oncogenes are a group of normal genes in a cell. ...
- Examples of proto-oncogenes. Over 40 different proto-oncogenes have been discovered in the human body. ...
- The takeaway. Your cells contain many important genes that regulate cell growth and division. ...
What is the difference between proto-oncogenes and oncogenic genes?
DNA sequences of proto-oncogenes can be mutated and converted into cancerous genes called oncogenes. Oncogenes are mutated or defective proto-oncogenes which produce different proteins which promote uncontrolled cell division and cancer formation. This is the difference between oncogenes and proto-oncogenes.
What is the difference between proto oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes?
Difference Between Tumor Suppressor Genes and Proto Oncogenes. The main difference between tumor suppressor genes and proto oncogenes is that the removal or inactivation of tumor suppressor genes causes cancers whereas the activation of the proto-oncogenes causes cancers.
What is an oncogene?
An oncogene is any gene that causes cancer. One of the main characteristics of cancer is uncontrolled cell growth. Because proto-oncogenes are involved in the process of cell growth, they can turn into oncogenes when a mutation (error) permanently activates the gene. In other words, oncogenes are mutated forms of proto-oncogenes.
What happens when a proto-oncogene changes to an oncogene?
A change in the DNA sequence of the proto-oncogene results in an oncogene. Oncogenes are encoded for different proteins which are responsible for uncontrollable cell division. The ultimate result of the uncontrolled cell division is the formation of a cancer.
What is the difference between a proto-oncogene and an oncogene quizlet?
Terms in this set (9) Distinguish between oncogenes and proto-oncogenes. Oncogenes are genes that induce or maintain uncontrolled cellular proliferation associated with cancer. They are mutant forms of proto-oncogenes, which normally function to regulate cell division.
What is the difference between oncogene and oncoprotein?
The key difference between oncogenes and oncoprotein is that oncogenes are cancerous genes formed due to a change or mutation in the DNA sequence of the proto-oncogene while oncoprotein is the protein coded by an oncogene which is responsible for an uncontrollable cell division.
How do proto-oncogenes become oncogenes?
The conversion of a proto-oncogene to an oncogene is called activation. Proto-oncogenes can become activated by a variety of genetic mechanisms including transduction, insertional mutagenesis, amplification, point mutations, and chromosomal translocations.
What is a proto-oncogene and what does it do?
Listen to pronunciation. (PROH-toh-ON-koh-jeen) A gene involved in normal cell growth. Mutations (changes) in a proto-oncogene may cause it to become an oncogene, which can cause the growth of cancer cells.
What is the difference between oncogene and carcinogen?
A carcinogen is a chemical that can cause cancer, by altering the DNA in a cell. Normal cells have genes called proto-onco genes (literally "before cancer genes") that control cell division. A carcinogen can change these genes into oncogenes that cause cancer.
What is meant by an oncogene?
Listen to pronunciation. (ON-koh-jeen) A mutated (changed) form of a type of gene called a proto-oncogene, which is involved in normal cell growth and division. When a proto-oncogene is changed so that too many copies are made or it becomes more active than normal, it is called an oncogene.
What is a proto-oncogene quizlet?
Proto-oncogenes. A normal gene which, when altered by mutation, becomes an oncogene that can contribute to cancer. Proto-oncogenes may have many different functions in the cell. Some proto-oncogenes provide signals that lead to cell division. Other proto-oncogenes regulate programmed cell death (apoptosis).
Are proto-oncogenes tumor suppressor genes?
Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are classes of genes that code for various proteins that are involved in the progression of the cell cycle. Oncogenes are actually mutated versions of proto-oncogenes, which are normal genes in charge of positive regulation of the cell-cycle.
What is the role of proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes?
Two classes of genes, oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, link cell cycle control to tumor formation and development. Oncogenes in their proto-oncogene state drive the cell cycle forward, allowing cells to proceed from one cell cycle stage to the next.
What happens when a proto-oncogene is turned on?
If this happens, the proto-oncogene can turn into a malfunctioning gene called an oncogene. Cells will start to grow out of control. Uncontrollable cell growth leads to cancer.
Why do we need proto-oncogenes?
Everyone has proto-oncogenes in their body. In fact, proto-oncogenes are necessary for our survival. Proto-oncogenes only cause cancer when a mutation occurs in the gene that results in the gene being permanently turned on. This is called a gain-of-function mutation.
What are the different types of mutations?
There are at least three different types of gain-of-function mutations that can cause a proto-oncogene to become an oncogene: 1 Point mutation. This mutation alters, inserts, or deletes only one or a few nucleotides in a gene sequence, in effect activating the proto-oncogene. 2 Gene amplification. This mutation leads to extra copies of the gene. 3 Chromosomal translocation. This is when the gene is relocated to a new chromosomal site that leads to higher expression.
What is the process of a mutation that leads to extra copies of a gene?
This mutation leads to extra copies of the gene. Chromosomal translocation. This is when the gene is relocated to a new chromosomal site that leads to higher expression. According to the American Cancer Society, most of the mutations that cause cancer are acquired, not inherited.
Why do cancer cells turn into oncogenes?
One of the main characteristics of cancer is uncontrolled cell growth. Because proto-oncogenes are involved in the process of cell growth, they can turn into oncogenes when a mutation (error) permanently activates the gene. In other words, oncogenes are mutated forms of proto-oncogenes. Most, but not all, oncogenes in the body arise ...
How many copies of a gene need to be mutated to cause cancer?
This means that only one copy of the gene needs to be mutated in order to encourage cancer. There are at least three different types of gain-of-function mutations that can cause a proto-oncogene to become an oncogene: Point mutation.
What is the ras gene?
In other words, Ras is one of the on/off switches in a series of steps in a major pathway that eventually leads to cell growth. When Ras is mutated, it encodes for a protein that causes an uncontrolled growth-promoting signal. Most cases of pancreatic cancer have a point mutation in the Ras gene.
What is the difference between tumor suppressor genes and proto oncogenes?
The main difference between tumor suppressor genes and proto oncogenes is that the removal or inactivation of tumor suppressor genes causes cancers where as the activation of the proto-oncogenes causes cancers. Furthermore, tumor suppressor genes suppress the cell division while proto-oncogenes activate the cell division.
What cancers are caused by oncogenes?
Retinoblastoma, colon cancers, and breast cancers are some of the cancers caused by tumor suppressor genes while chronic myeloid leukemia, breast cancer, kidney cancer are some of the cancers caused by oncogenes.
What are the causes of mutations in tumor suppressor genes?
Types of Mutations. Deletions or point mutations are the main cause of mutations in tumor suppressor genes while point mutations, gene amplification, and chromosomal translocations produce oncogenes.
How do mutations affect the development of cancer?
Mutations alter the gene products of tumor suppressor genes that inhibit the progression of the cell cycle, causing the development of tumors while mutations alter the gene products of proto-oncogenes in such a way to increase their expression, which cause cancer by increasing cell division.
What is the first tumor suppressor gene?
The first tumor suppressor genes to be identified is the RB gene ; its mutated form causes retinoblastoma. The RB gene helps in the regulation of the progression of cell cycle. There are five classes of proteins encoded by tumor suppressor genes.
Where do mutations of tumor suppressor genes occur?
Mutations of tumor suppressor genes can occur in the somatic or germ-line cells while the mutations of the proto-oncogenes occur in the somatic tissue. Therefore, mutations in the tumor suppressor genes may be inherited while the mutations of the proto-oncogenes will not be inherited to the next generation.
Which genes suppress cell division?
Furthermore, tumor suppressor genes suppress the cell division while proto-oncogenes activate the cell division. Tumor suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes are the two major classes of genes that can cause cancers upon mutation .
