
What does diatonic and chromatic mean?
The chromatic scale is the musical scale with twelve pitches that are a half step apart. Definition 1.2. A diatonic scale is a seven-note musical scale with 5 whole steps and 2 half steps, where the half steps have the maximum separation usually 2 or 3 notes apart.
Which key of diatonic harmonica should I buy?
Which harmonica key should I buy? Usually the key of “C” is the best first key for diatonic. Recommended diatonic keys after the key of “C” include: “A”, “D”, “F”, “G”, and “Bb” (roughly in that order—or you can buy all six keys packaged together). Of course, if there is a song in a particular key that you want to play along with, then you would need the correct diatonic key for that song.
What are diatonic scales?
The diatonic scales are the basic scales, or natural scales, in music. Another way to think of it is like this: Musical scales are like loaves of bread. White bread is the most basic kind of bread,...
What is the diatonic scale?
In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps (whole tones) and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, depending on their position in the scale.

Is piano chromatic or diatonic?
Any sequence of 7 natural notes on a piano, such as F to F, G to G, B to B, etc. is diatonic.
What does diatonic mean in music?
diatonic, in music, any stepwise arrangement of the seven “natural” pitches (scale degrees) forming an octave without altering the established pattern of a key or mode—in particular, the major and natural minor scales.
What is an example of diatonic?
F–C–G–D–A–E–B. Any sequence of seven successive natural notes, such as C–D–E–F–G–A–B, and any transposition thereof, is a diatonic scale. Modern musical keyboards are designed so that the white notes form a diatonic scale, though transpositions of this diatonic scale require one or more black keys.
What is the difference between a chromatic and major scale?
The tones of the chromatic scale (unlike those of the major or minor scale) are all the same distance apart, one half step. The word chromatic comes from the Greek chroma, color; and the traditional function of the chromatic scale is to color or embellish the tones of the major and minor scales.
What are the 2 types of diatonic scales?
Scales: Diatonic scales include both the major scale, or Ionian mode, which is the most frequently used musical scale, and the natural minor scale, or Aeolian mode, which uses the same number of notes as the major scale, but in a different pitch.
What is chromatic in music?
Chromatic tones in Western art music are the notes in a composition that are outside the seven-note diatonic (i.e., major and minor) scales and modes.
What is the opposite of diatonic?
The term chromatic inflection (alternatively spelt inflexion) is used in two senses: Alteration of a note that makes it (or the harmony that includes it) chromatic rather than diatonic.
What is an example of a chromatic scale?
Chromatic Scales Put simply, the chromatic scale is a musical scale that uses all the musical pitches. For example, if you were to start the chromatic scale on a C, the scale would read as: C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#, A, A#, B, C… and so on.
How many notes are in a chromatic scale?
12 notesThere are 12 notes in the chromatic scale. To fully convey the sound of chromaticism, you must play several of these notes in a row.
What are the 12 chromatic scales?
Chromatic scales are the scales that includes all twelve tones in sequential order: A, A#/Bb, B, C, C#/Db, D, D#/Eb, E, F, F#/Gb, G, and G#/Ab. Chromatic scales can start from any of the twelve tones, so there are twelve different iterations or inversions of the scale.
Why are there 12 notes in the chromatic scale?
The idea behind twelve is to build up a collection of notes using just one ratio. The advantage to doing so is that it allows a uniformity that makes modulating between keys possible.
Why is it called chromatic scale?
The set of all musical notes is called the Chromatic Scale, a name which comes from the Greek word chrôma, meaning color. In this sense, chromatic scale means 'notes of all colors'. Colors, in fact, are also made up from different frequencies, those of light waves.
What is the difference between pentatonic and diatonic?
Diatonic scales have 7 notes. A pentatonic scale is a a diatonic scale that has two notes removed, using a the major scale as our basis we'd remove the 4th and 7th notes as they are only a half step from their neighbors and offer the most friction.
Are all major scales diatonic?
Many scales are diatonic including Major, Minor (the Harmonic minor is an exception) and modal scales. Examples of non-diatonic scale are pentatonic, octatonic and whole-tone scales. Also, as a more obscured example, the Acoustic Scale (a.k.a. Lydian Dominant).
What is a diatonic chord?
What are Diatonic Chords? A chord which is diatonic is simply a chord built from notes of the key. In the key of C again (C, D, E, F, G, A and B), the chord C major (C, E, G) would be diatonic to the key of C because its 3 notes are part of the C major scale.
What is the most commonly used example of a diatonic scale?
The major scale is probably the most familiar and easily recognisable of all diatonic scales. If you were to play all the white notes on a piano keyboard starting on C you'll not only play a major scale but a diatonic scale.
What is chromatic scale?
Chromatic most often refers to structures derived from the twelve-note chromatic scale, which consists of all semitones.
What is a diatonic tetrachord?
A diatonic tetrachord comprised, in descending order, two whole tones and a semitone, such as A G F E (roughly). In the chromatic tetrachord the second string of the lyre was lowered from G to G ♭, so that the two lower intervals in the tetrachord were semitones, making the pitches A G ♭ F E.
What is fugue diatonic?
I, fugue subject: diatonic variant Play (help·info). Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features ...
How many tones are there in Melodies?
Melodies can be based on a diatonic scale and maintain its tonal characteristics but contain many accidentals, up to all twelve tones of the chromatic scale, such as the opening of Henry Purcell 's Thy Hand, Belinda, Dido and Aeneas (1689) ( Play (help·info), Play (help·info) with figured bass ), which features eleven of twelve pitches while chromatically descending by half steps, the missing pitch being sung later.
When one note of an interval is chromatic or when both notes are chromatic, the entire interval is called?
When one note of an interval is chromatic or when both notes are chromatic, the entire interval is called chromatic . Chromatic intervals arise by raising or lowering one or both notes of a diatonic interval, so that the interval is made larger or smaller by the interval of half step ["altered diatonic intervals"].
What is the color of a note called?
The term cromatico (Italian) was occasionally used in the Medieval and Renaissance periods to refer to the coloration (Latin coloratio) of certain notes. The details vary widely by period and place, but generally the addition of a colour (often red) to an empty or filled head of a note, or the "colouring in" of an otherwise empty head of a note, shortens the duration of the note. In works of the Ars Nova from the 14th century, this was used to indicate a temporary change in metre from triple to duple, or vice versa. This usage became less common in the 15th century as open white noteheads became the standard notational form for minims (half-notes) and longer notes called white mensural notation. Similarly, in the 16th century, a form of notating secular music, especially madrigals in was referred to as "chromatic" because of its abundance of "coloured in" black notes, that is semiminims (crotchets or quarter notes) and shorter notes, as opposed to the open white notes in , commonly used for the notation of sacred music. These uses for the word have no relationship to the modern meaning of chromatic, but the sense survives in the current term coloratura.
Is there a difference in tuning between enharmonic intervals?
In equal temperament, there is no difference in tuning (and therefore in sound) between intervals that are enharmonically equivalent. For example, the notes F and E ♯ represent the same pitch, so the diatonic interval C–F (a perfect fourth) sounds the same as its enharmonic equivalent—the chromatic interval C–E ♯ (an augmented third).
What does diatonic mean on the piano?
The origin of the term diatonic is Greek, and it means progressing through tones. From a literal standpoint, a progression through the white notes on the piano from C to C: …without any of the black notes: …can be considered to be diatonic.
What is a chromatic note?
Two or three notes that have the same letter names, are chromatically related. For example, Db, D and D#: …are chromatically related. In a nutshell, the term chromatic is basically used to describe a musical idea [be it a note, scale, chord, or chord-progression] that is foreign to a particular key environment.
What is a diatonic scale?
Diatonic scales: The traditional scales of the major and minor key. Diatonic intervals: Intervals that are formed from two notes that belong to a particular key. Diatonic chords: Chords that are made up of the notes of a given key. Diatonic chord progression: Chord movement from one diatonic chord to another.
Is F# diatonic or non-diatonic?
Although F# and C#: …are literally non-diatonic, due the fact that they belong to the prevalent key, they are considered to be diatonic. “In A Nutshell…”. Any musical element (be it a note, scale, interval, chord, or chord progression) that is based on the notes of a particular key is diatonic.
Diatonic vs. Chromatic Accordion: Which is right for you?
BrandNewTune.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. As an affiliate, this website earns from qualifying purchases.
Diatonic vs. chromatic accordion: Which is right for you?
Now that you understand how accordions are designed, and what features you want to look for you can determine whether a diatonic vs. chromatic accordion is better for your situation.
What is the difference between a diatonic and a diatonic harmonica?
The diatonic harmonica is set to one key. This means it is the equivalent to playing a piano with just the white keys. This may be more restricting but the diatonic harmonica is much easier to play. This is a great harmonica for beginners.
How many sections are there in a diatonic harmonica?
The diatonic harmonica is divided into three sections. The first section is holes 1 2 and 3. When you blow air into this section you will be playing a c major chord where drawing in air will play a g major.
What type of harmonica is used in classical music?
This type of harmonica allows you to play all the keys rather than just one but it is arguably harder to master. Chromatic harmonicas are typically used more in classical and jazz music. The harmonica is able to bend notes on both draw and blow which is perfect for these genres.
How to play a harmonica?
The easiest way to play a harmonica is to blow out and draw in air within the harmonica to create a note. Depending on which hole/holes you are blowing or sucking, depends on what chord or note is played. Have a play around with the harmonica to see if you can point out what notes and chords you can hear. It’s best practice to point out ...
What are the different types of harmonicas?
There are two types of harmonica: a chromatic and a diatonic harmonica. Both types are used in a wide range of genres of music but typically stick to ones that they are most suited to. This section will discuss which harmonica you should use for each genre and the differences between them.
How many harmonicas can you play at the same time?
It is perfect for these genres as typically two harmonicas are played at the same time to create a harmony. For example, one person can play the first 3 holes whilst the other play the last three holes.
Is the harmonica easy to play?
The harmonica is a simple instrument to play and is quite easy to understand as a beginner. It will take some practice to complete a song and remember what chords are where on the harmonica.
Diatonic Vs Chromatic Harmonica
The diatonic and chromatic harmonica have noticeable differences in how they are played, the styles of music they are used for, and the cost for each instrument.
Should You Buy a Diatonic Harmonica?
The diatonic harmonic gets its name because it is easy to play the notes of a diatonic scale on it. A diatonic scale is a scale that starts at a certain note and progresses 6 more unique notes in a series of steps and half steps until ending with the 8 note which is exactly the same as the starting note except for one octave higher.
Should You Buy a Chromatic Harmonica?
Diatonic harmonicas are relatively limited in the notes you are able to play, but chromatic harmonics function in the opposite way. If you have a chromatic harmonica, you will be able to play any note you want, regardless of if it is on a certain scale.
Diatonic Vs Chromatic Harmonica, Final Thoughts
Although diatonic and chromatic harmonicas may look similar to someone who knows little about them, there are in fact many nuances to consider before making a purchase. From your current skill level with harmonica to the types of music you plan to play, there are variables to choose from when it is time for your decision.
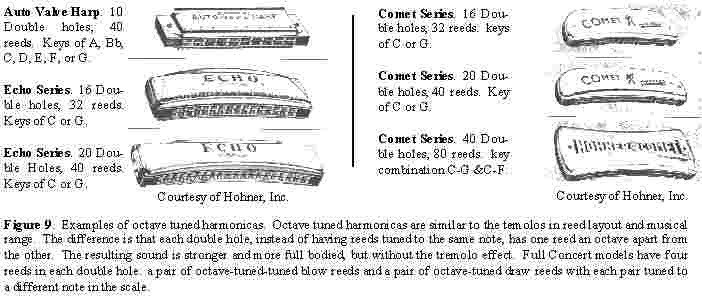
Overview
Intervals
When one note of an interval is chromatic or when both notes are chromatic, the entire interval is called chromatic. Chromatic intervals arise by raising or lowering one or both notes of a diatonic interval, so that the interval is made larger or smaller by the interval of half step ["altered diatonic intervals"].— Allen Forte (1979)
Because diatonic scale is itself ambiguous, distinguishing intervals is also ambiguous. For exam…
History
In ancient Greece there were three standard tunings (known by the Latin word genus, plural genera) of a lyre. These three tunings were called diatonic, chromatic, and enharmonic, and the sequences of four notes that they produced were called tetrachords ("four strings"). A diatonic tetrachord comprised, in descending order, two whole tones and a semitone, such as A G F E (roughly). …
Diatonic scales
Medieval theorists defined scales in terms of the Greek tetrachords. The gamut was the series of pitches from which all the Medieval "scales" (or modes, strictly) notionally derive, and it may be thought of as constructed in a certain way from diatonic tetrachords. The origin of the word gamut is explained in the article Guidonian hand; here the word is used in one of the available senses: the all-e…
Chromatic scale
Chromatic scale on C: full octave ascending and descending
A chromatic scale consists of an ascending or descending sequence of pitches, always proceeding by semitones. Such a sequence of pitches is produced, for example, by playing all the black and white keys of a piano in order. The structure of a chromatic scale is therefore uniform throughout—unlike major and minor scales, which have tones and semitones in particular arrang…
Musical instruments
Some instruments, such as the violin, can play any scale; others, such as the glockenspiel, are restricted to the scale to which they are tuned. Among this latter class, some instruments, such as the piano, are always tuned to a chromatic scale, and can be played in any key, while others are restricted to a diatonic scale, and therefore to a particular key. Some instruments, such as the
Chords
By chromatic linear chord is meant simply a chord entirely of linear origin which contains one or more chromatic notes. A great many of these chords are to be found in the literature.— Allen Forte (1979)
Diatonic chords are generally understood as those that are built using only notes from the same diatonic scale; all other chords are considered chromatic. How…
Harmony
The chromatic expansion of tonality which characterizes much of nineteenth century music is illustrated in miniature by the substitution of a chromatic harmony for an expected diatonic harmony. This technique resembles the deceptive cadence, which involves the substitution of another diatonic chord for the expected diatonic goal harmony. ... In the major mode a substitute chromatic consonance often proves to be a triad which has been taken from the parallel minor …