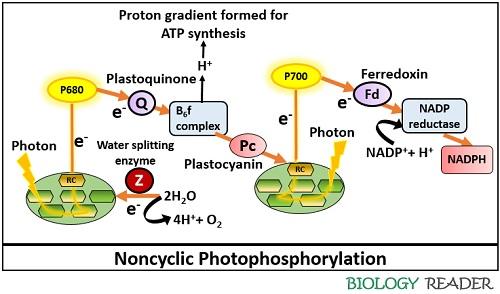
What is the difference between cyclic and noncyclic electron transport? As the name suggests, in cyclic photophosphorylation the electrons move in a circular pattern. Electron movement is non-cyclic in noncyclic photophosphorylation.
What is cyclic and non cyclic electron transport pathway?
Cyclic electron transport pathway Two photosystems, PSI (P700) and PSII (P680) are involved. Only one photosystem, PSI (P700)is involved. The electron flow is non-cyclic and the final electron acceptor is NADP. The electron flow is cyclic and the final electron acceptor is P700.
What is the difference between noncyclic and cyclic electron flow?
What is the difference between noncyclic and cyclic electron flow in terms of the products and the pathways the electrons follow? Cyclic photo-phosphorylation in photosynthesis light dependent reaction leads to the formation of ATP and NADPH, and the electrons go from water to PSII to PSI and eventually to NADPH.
What is the difference between cyclic and non-cyclic photo-phosphorylation?
Cyclic photo-phosphorylation in photosynthesis light dependent reaction leads to the formation of ATP and NADPH, and the electrons go from water to PSII to PSI and eventually to NADPH. In non-cyclic photo-phosphorylation only some ATP is produced and the electrons go from PSII to PSI and back again.
Does cyclic photophosphorylation produce NADPH and O2?
Under certain conditions, the photoexcited electrons take an alternative path called cyclic electron flow, which uses photosystem I (P700) but not photosystem II (P680). This process produces no NADPH and no O2, but it does make ATP. This is called cyclic photophosphorylation.

What is the difference between cyclic and noncyclic electron flow quizlet?
What is the difference b/w the noncyclic and cyclic electron flow? Only photosystem I is used in cyclic photophosphorylation where the electrons are passed back to the same photosystem, while non-cyclic phosphorylation uses both photosystems.
Which of the following is the main difference between cyclic and non cyclic photophosphorylation?
What is the difference between cyclic and non cyclic Photophosphorylation? In cyclic photophosphorylation, only PSI is involved and only ATP is synthesised, whereas, in the non-cyclic photophosphorylation both PSI and PSII are involved and both ATP, as well as NADPH, are produced.
What are the similarities between cyclic and non cyclic electron transport during photosynthesis?
Ø Both cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylations are light reactions. Ø Both are dependent on light. Ø Both are electron transport systems. Ø Both pathways produce assimilatory powers.
What are the main differences between cyclic and non cyclic electron flow with respect to the way the electrons flow and what is produced?
1 Answer. Cyclic photo-phosphorylation in photosynthesis light dependent reaction leads to the formation of ATP and NADPH, and the electrons go from water to PSII to PSI and eventually to NADPH. In non-cyclic photo-phosphorylation only some ATP is produced and the electrons go from PSII to PSI and back again.
What is the difference between ps1 and ps2?
The key difference between both the photosystems – Photosystem I and photosystem II is that PS I tends to absorb light of longer wavelengths > 680nm, whereas PS II absorbs light of shorter wavelengths <680 nm.
What is non cyclic electron transport?
In a process called non-cyclic photophosphorylation (the "standard" form of the light-dependent reactions), electrons are removed from water and passed through PSII and PSI before ending up in NADPH. This process requires light to be absorbed twice, once in each photosystem, and it makes ATP .
What is cyclic electron transport?
Cyclic electron transfer involves only PSI and cyt bf and was first described by Arnon (1). It involves electron flow to generate an electrochemical proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane without net production of reducing equivalents.
How is cyclic electron flow different than linear electron flow in photosynthesis?
In linear electron flow (LEF), the PSs function in series and electrons are transferred all the way from water to NADP+ with concomitant production of NADPH and ATP. Cyclic electron flow (CEF), in contrast, recycles electrons around PSI by re-routing them from ferredoxin (Fd) to the plastoquinone (PQ).