
What is cytology and cytopathology?
Technically speaking, cytology is the study of individual normal cells, but it is always used in conjunction with cytopathology, which is the study of diseased cells. The human body is born with a single cell; it then divides and differentiates into tissues, organs, organ systems, and then an entire human being.
What is the difference between histology and cytology?
The main difference between histology and cytology is that histology is the examination of tissue under a microscope while cytology is the examination of cells under a microscope. Histology focuses on providing excellent details of tissues and cytology on offering excellent details of cells.
What is cytopathology in lymphoma?
More in Lymphoma. Cytopathology is the study of disease at the cellular level. "Cyto" refers to cell and "pathology" to disease. Cytology tests are done on cells in fluid aspirations, scrapings or brushings to look at single cells or small clusters of cells and assess whether they are normal or show signs of disease.
How do you do a cytopathology procedure?
Cells examined for cytopathology can come from fluids such as urine or sputum or may be extracted from tissue, such as from inside the chest or abdomen. Cells can also be extracted by inserting needles into growths or diseased areas or tissues—such as with a fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) procedure.
What is cytopathology used for?
Diagnosing diseases by looking at single cells and small clusters of cells is called cytology or cytopathology. It's an important part of diagnosing some types of cancer.
What are the two types of cytology?
After sampling, two main techniques can be used: conventional cytology and liquid-based cytology.
What do you mean by cytopathology?
Definition of cytopathology 1 : a branch of pathology that deals with manifestations of disease at the cellular level.
What tests are done in cytopathology?
Cytopathology Test ListAnal pap.Body cavity fluids, cytopathology.Bronchoalveolar lavage.Brush biopsy specimen.Cerebrospinal fluid, cytology.Cyst fluid, cytology.Fine needle aspiration - clinician obtains sample.Fine needle aspiration - pathologist obtains sample.More items...
How accurate is cytology?
Urinary cytology is most helpful in diagnosing invasive high-grade (the cancer cells grow and spread quickly) tumors and carcinoma in situ (a group of abnormal cells that are found only in the place where they first formed in the body). It has a 95% accuracy rate for diagnosing these two conditions.
Which instrument is used in cytopathology?
Microscopes, vortex, and centrifuge are maintained daily, or as used.
Who is the father of cytology?
George N. Papanicolaou, M.D. Father of modern cytology.
What is the most common lab test that involves cytopathology?
A popular type of cytology screening test is a Pap smear. Other uses for cytology tests include: To diagnose infectious diseases.
Why it is called cytology?
Cytology is the study of individual cells of the body, as opposed to histology which is the study of whole human tissue itself.
Is cytopathology a Pap smear?
Cytopathology is a diagnostic technique that examines cells from various body sites to determine the cause or the nature of disease. The first cytopathology test developed was the Pap test, which has been widely utilized in the last 50 years for screening and diagnosing of cervical cancer and its precursors.
What is the difference between biopsy and cytology?
A cytology test is different from a biopsy. During a biopsy, tissue from a certain area of the body is removed and analyzed for cancer. A cytology test removes and studies a fewer number of cells. With a cytology test, the cytological morphology of the cells collected are studied under a microscope.
What are the cytological techniques?
Cytological techniques are methods used in the study or manipulation of cells. These include methods used in cell biology to culture, track, phenotype, sort and screen cells in populations or tissues, and molecular methods to understand cellular function.
Who is the father of cytology?
George N. Papanicolaou, M.D. Father of modern cytology.
What is cytology test?
Cytology is a common method for determining a diagnosis in the medical world. Cytology tests use small amounts of bodily tissue or fluid in order to examine certain types of cells. Healthcare providers can use cytology tests for almost all areas of your body.
What are the two branches of cytology?
There are two main kinds, or branches, of cytology: exfoliative cytology and intervention cytology.
What is intervention cytology?
Intervention cytology is a branch of cytology in which your healthcare provider has to “intervene” with your body to get a sample of cells to test, meaning they have to pierce your skin in some way to get a sample of cells.
What is exfoliative cytology?
Exfoliative cytology is a branch of cytology in which the cells that a pathologist examines are either “shed” by your body naturally or are manually scraped or brushed (exfoliated) from the surface of your tissue.
How long does it take to get a cytology test?
Some routine cytology screenings could take as little as 1 to 2 days to get your results while other tests could take 1 to 2 weeks. Factors that affect how long it takes to get cytology test results include:
What is the name of the test that a pathologist performs to determine if a cell is abnormal?
Since cytology only examines cells, which are so tiny, pathologists only need a very small sample of tissue to do a cytology test.
How many steps are there in cytology?
Each cytology test is slightly different depending on what kind of cells are being tested and if the sample is tissue or fluid. In general, there are four steps to a cytology test including:
What is cytology and cytology?
Cytopathology and cytology are diagnostic processes by which the cells obtained from biopsy, fluid samples, scrapings, or brushings are specially prepared and examined with a microscope. These tests are used to examine single cells or small clusters of cells and to assess whether they are normal or show signs ...
Where do cells come from for cytopathology?
Cells examined for cytopathology can come from fluids such as urine or sputum or may be extracted from tissu e, such as from inside the chest or abdomen. Cells can also be extracted by inserting needles into growths or diseased areas or tissues—such as with a fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) procedure.
What is the role of histopathology in cancer?
While cytopathology relates to abnormalities found within—or expressed by—individual cells, histopathology extends the analysis so that pathologists can see abnormalities related to attachments between cells , and explore whether the cell appears normal given its location within the tissue. This is sometimes referred to as "histological architecture," which can be important in the evaluation of the appearance of conditions such as cancer. 3
Why do we do cytology?
Cytology can also be done to assist in the diagnosis when there is a known or suspected disorder, such as when a fine needle aspiration is used to sample cells from a tumor.
What is the study of disease at the cellular level?
Cytopathology is the study of disease at the cellular level. "Cyto" refers to cell and "pathology" to disease.
What is the Difference Between Histopathology and Cytology?
Histopathology is the science of looking at tissues related to diseases. Meanwhile, cytology is the science of looking into individual cells. Thus, this is the key difference between histopathology and cytology.
Why is cytology used in medicine?
Cytology is often used in medicine in order to prevent and diagnose diseases.
Why is histopathology and cytology important?
Both histopathology and cytology are widely used in medicine in order to diagnose and prevent diseases. In both studies, it is necessary to make glass slides of specimens, stain them using suitable dyes and examine under a microscope.
What is the study of cells in relation to disease called?
The study of tissues in relation to disease is known as histopathology. In contrast, the study of a single cell type is known as cytology. Therefore, histopathology looks at tissues while cytology looks at individual cells.
What is the study of tissues?
Therefore, histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of tissues in order to study the manifestations of diseases. In simple words, histopathology is the study of tissues related to diseases. In histopathology , a pathologist (specialized doctor) examines changes in any tissue associated with a disease using a microscope ...
What are the two branches of biology?
Histopathology and cytology are two branches of biology.
What is the study of cells in the body?
Cytology is the study of individual cells of the body in terms of structure, function and chemistry. Therefore, normal cells are studied in cytology. However, in cytopathology, cells related to the diseases are examined and analyzed to diagnose medical conditions. In cytology , individual cells are observed for abnormal changes in ...
What is pathology in medical terms?
the branch of medical science that studies the causes and nature and effects of diseases. Pathology noun. any deviation from a healthy or normal condition. Pathology noun. the science of the causes and effects of diseases, especially the branch of medicine that deals with the laboratory examination of samples ...
What is the branch of biology that studies the structure and function of cells?
Cytology noun. the branch of biology that studies the structure and function of cells. ADVERTISEMENT. Pathology noun. The science which treats of diseases, their nature, causes, progress, symptoms, etc.
What is the branch of medicine that studies the nature of disease?
Pathology no un. The branch of medicine concerned with the study of the nature of disease and its causes, processes, development, and consequences.
What is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury?
Pathology . Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word pathology also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a more narrow fashion to refer ...
What is the scientific study of cells, their origin and functions?
Cytology is the scientific study of cells, their origin and functions.
Can histopathology and cytology overlap?
There is a close association between histopathology and cytopathology, which can overlap technically and diagnostically. Histologic tissue specimens and cytologic cellular samples can replace each other but often are complementary to each other.
What is the difference between histopathology and cytology?
Histopathology concerns whole tissues where cells dwell. Cytopathology studies individual cells. Mucosal cells that loosen themselves or are exfoliated from tissues can be studied, Blood cells are also main cytology targets because blood and bone marrow are liquid tissues.
What is cytology in cancer?
Cytology looks at exfoliated cells on a slide stained with pap stain for cancer screening.
What is histopathology sputum?
Histopathology looks at chunks of biopsy tissue that are processed (dehydrated) sliced very thinly and placed on a slide for various staining for various reasons. They can also take fluids and spin them down and slice the plug as a piece of tissue and stain with various stains. Silver stains were used on sputum to identify Pneumocystis Carnii in the old days (70’s) before HIV had a name. It was just a strange Immunodeficiency syndrome and people’s immune system got so weak that spores we are exposed to ev
What does a pathologist do when a slide is abnormal?
The pathologist will take out a thin layer of cells and prepare a smear from there. This smear will then be processed appropriately and visualised under microscope. If the Pathologist finds any abnormalities in the slide, then the pathologist will inform the surgeon that a biopsy is needed for confirmation.
What is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic structure of tissues?
Cytology is the branches of Biology and Medicine concerned with the structure and function of plant and animal cells. But, Histopathology is the study of the microscopic structure of tissues.
What is the study of cells in bodily fluids?
Histology is the study of cells in bodily tissues. Cytology is the study of cells in bodily fluids. That’s the simplest version.
What is the study of cells called?
Cytology is the study of cells. The cells can be retrieved by a needle to withdraw a certain cell type from the body. The cells can then be viewed under a microscope.
How is cytology used in medicine?
Cytology is widely used in medicine for the prevention and diagnosis of disease. In 2016 over 3,000,000 cervical screening samples were taken in England as part of the cervical screening programme.
What is cytology used for?
Cytology can also be used to diagnose many non-cancerous medical conditions such as infections and systemic diseases. There are two main branches of cytology. There are those involved with the assessment of pre-cancerous and, occasionally, cancerous, changes of the cervix (mouth of the womb) such as in cervical cancer screening, ...
What is the study of individual cells of the body?
What is Cytology ? Cytology is the study of individual cells of the body, as opposed to histology which is the study of whole human tissue itself.
Why do we look at cells under the microscope?
The human body is made up of millions of cells and these can be sampled and looked at under the microscope, after suitable preparation, to help diagnose medical conditions. This involves looking at the individual cells for abnormal changes of both the nucleus and also the cytoplasm (body) of the cell. The nucleus contains the genetic material that ...
What Is Cytology?
Cytology is the study of the chemical composition, structure, and functions of animal and plant cells. The field provides a microscopic examination of plant and animal cell samples.
What is the difference between histology and cytology?
The main difference between histology and cytology is that histology is the examination of tissue under a microscope while cytology is the examination of cells under a microscope. Histology focuses on providing excellent details of tissues and cytology on offering excellent details of cells. But histological studies are wider than that of cytology.
What is the study of cell biology?
Cell biology involves the study of structure, functions, constituents, physical features, division, death, and life cycle of cells. Besides that, cytogenetics and cytopathology deal with the study of cellular diseases. But cytogenetics provides guidance on the genetic basis of cellular disease.
What is the difference between a cell and a tissue?
The former is the study of chemistry, structure, and function of living organisms cells while the latter is the study of chemical composition, microscopic structure, and functions of tissues or tissue systems. A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of life. A tissue is a group of cells with different origins but performs ...
Why is histology important in medicine?
Histology is a crucial field in medicine since it helps to understand the properties of various diseases. Histopathology is a branch of histology which deals with the study of diseased tissues. You May Also Like: Difference between Marasmus and Kwashiorkor.
Is histopathology the study of tissues?
Not really. Histology is the study of tissues and histopathology is the study of tissues in relation to their diseases.
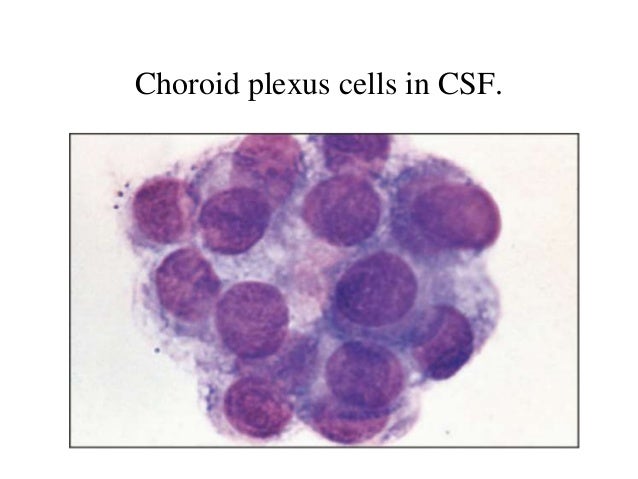
Cytology Uses
Cytopathology Process
Cytology vs. Cytopathology
- Cytopathology tests are used to examine single cells or small clusters of cells and to assess whether they are normal or show signs of disease. A report from a cytopathology test describes findings that help determine whether or not the examined cells have characteristics of illnesses, like infection, inflammation, or cancer.2 Cytopathology is the study of disease at the cellular leve…
Cytology vs. Pathology
- Cytology is the study of cells. When cytopathology is used to look at cells for signs of disease, it falls under the umbrella of pathology.3 Pathology is a field of medicine that studies diseases. Lab tests, like cytology smears, can be a tool that pathologists use when researching a disease.4
Cytopathology vs. Histopathology
- A pathology department in a hospital is set up to do different kinds of cytology tests on cells and tissue samples, whether from FNAC or from a larger sample, such as an excisional biopsy. In cytopathology, some aspects of a disease can be inferred based on the characteristics of individual cells—including the appearance of the nucleus, the presence of cellular proteins, and t…
Summary
- Cytology is the study of normal cells. When cells are looked at for abnormalities or signs of disease, it's usually called cytopathology. Pathology is the branch of medicine that looks at why and how diseases happen. Cytology smears, histology samples, and other cytopathology tests can help pathologists learn about diseases and help providers diagn...