The main difference between Yield to Maturity and Discount Rate is that Yield to maturity is to give the total value for the bond return. But the discount rate is for finding the interest rates for the loans that are taken by us from the banks.
Full Answer
How to calculate discount yield?
Bank discount yield (or simply discount yield) is the annualized rate of return on a purely discount-based financial instrument such as T-bill, commercial paper or a repo. It is calculated as the difference between the face value and issue price divided by face value multiplied by 360 divided by number of days between issue date and maturity date.
Are discount rates and inflation rates the same?
The Discount Rate is the interest rate that the Federal Reserve charges large regional banks when it lends them money. The Inflation Rate is the rate at which prices are generally increasing. A common proxy for the inflation rate is the Consumer Price Index or CPI United States Consumer Price Index - Wikipedia.
What is the difference between rate and yield?
The yield curve is simply the spread between long-term and short-term interest rates. Short-term rates tend to be more influenced by central banks and monetary policy to stimulate the economy, support employment and maintain price stability. Long-term ...
What is the best Bond to invest in?
What are the best government bonds to watch?
- Germany: the Bund, Bobl, Schatz and Buxl. Germany’s bonds are some of the most traded and watched in the world. ...
- US: treasury bonds and T-notes. US bonds with maturities over ten years are called treasury bonds ( T-bone ), while Treasury notes (T-notes) have maturities of ten years or less.
- UK: gilts. ...
- Italy and France: BTPs and OATs. ...
Is yield same as discount rate?
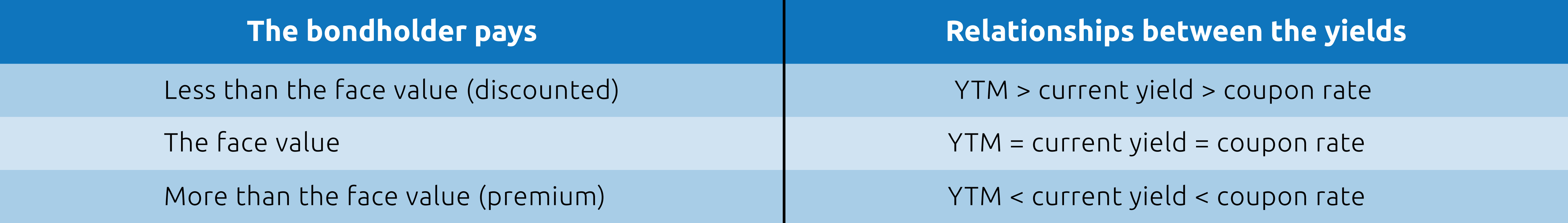
If an investor purchases a bond at par or face value, the yield to maturity is equal to its coupon rate. If the investor purchases the bond at a discount, its yield to maturity will be higher than its coupon rate. A bond purchased at a premium will have a yield to maturity that is lower than its coupon rate.
Is discount rate and yield to maturity the same?
The yield-to-maturity is the implied market discount rate given the price of the bond. A bond's price moves inversely with its YTM. An increase in YTM decreases the price and a decrease in YTM increases the price of a bond.
How do you convert discount rate to yield?
Multiply the percentage of discount by the number of times the maturity term occurs in a year. Using the same example, the equation would be: discount yield = 0.04 * 1.8947. The discount yield is 7.58 percent. By purchasing a $10,000 Treasury Bill for $9,600, you will earn 7.58 percent in interest.
What is the difference between discount and discount rate?
The word “discount” means “to deduct an amount.” A discount rate is deducted from a future value of money to provide its present value.
What means discount rate?
In corporate finance, a discount rate is the rate of return used to discount future cash flows back to their present value. This rate is often a company's Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), required rate of return, or the hurdle rate that investors expect to earn relative to the risk of the investment.
What's a yield rate?
The yield rate measures the amount of income generated by an investment over a specified period. When you invest your money, you want to make sure that it generates more than what it costs to buy and upkeep.
How is yield calculated?
How to calculate yieldDetermine the market value or initial investment of the stock or bond.Determine the income generated from the investment.Divide the market value by the income.Multiply this amount by 100.
How do I calculate a discount rate?
To calculate the percentage discount between two prices, follow these steps: Subtract the post-discount price from the pre-discount price. Divide this new number by the pre-discount price. Multiply the resultant number by 100.
What is a discount rate in NPV?
It's the rate of return that the investors expect or the cost of borrowing money. If shareholders expect a 12% return, that is the discount rate the company will use to calculate NPV. If the firm pays 4% interest on its debt, then it may use that figure as the discount rate.
What is an example of discount rate?
For example, an investor expects a $1,000 investment to produce a 10% return in a year. In that case, the discount rate for valuing this investment or comparing it to others is 10%. The discount rate allows investors and others to consider risk in an investment and set a benchmark for future investments.
What is discount rate used for?
The discount rate is the interest rate used to determine the present value of future cash flows in a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis. This helps determine if the future cash flows from a project or investment will be worth more than the capital outlay needed to fund the project or investment in the present.
Why is discount rate higher than interest rate?
Interest rates depend on a number of factors such as Borrower's creditworthiness, a risk associated with lending. Whereas, the discount rate is calculated after taking into consideration the average rate that one bank would charge to other banks for taking the overnight loans.
How do you calculate yield to maturity on a discount bond?
Yield to Maturity = [Annual Interest + {(FV-Price)/Maturity}] / [(FV+Price)/2]Annual Interest = Annual Interest Payout by the Bond.FV = Face Value of the Bond.Price = Current Market Price of the Bond.Maturity = Time to Maturity i.e. number of years till Maturity of the Bond.
How do you calculate yield on a bond?
Yield is a figure that shows the return you get on a bond. The simplest version of yield is calculated by the following formula: yield = coupon amount/price. When the price changes, so does the yield.
How do you find the original price after discount?
Calculating Original Price From Discounted Price 100 percent minus 20 percent is 80 percent, or 0.8. Expressed as an algebraic equation, $400 = 0.8(Y), where Y is the original price. Divide each side by 0.8 to solve for Y. $400 divided by 0.8 equals $500, which is the original price.
How do you calculate bond equivalent yield?
The bond equivalent yield formula is calculated by dividing the difference between the face value of the bond and the purchase price of the bond, by the price of the bond. That answer is then multiplied by 365 divided by "d," which represents the number of days left until the bond's maturity.
What Is the Discount Yield?
The discount yield is a way of calculating a bond's return when it is sold at a discount to its face value, expressed as a percentage. Discount yield is commonly used to calculate the yield on municipal notes, commercial paper and treasury bills sold at a discount .
How does discount yield work?
Discount yield computes a discount bond investor's return on investment (ROI) if the bond is held until maturity. A Treasury bill is issued at a discount from par value (face amount), along with many forms of commercial paper and municipal notes, which are short-term debt instruments issued by municipalities. U.S. Treasury bills have a maximum maturity of six months (26 weeks), while Treasury notes and bonds have longer maturity dates.
What is the $80 discount on a bond?
Since the investor receives $1,000 at maturity, the $80 discount is bond income to the owner, along with interest earned on the bond. Bond accretion means that the $80 discount is posted to bond income over the 10-year life, and an investor can use a straight-line method or the effective interest rate method. ...
What happens to the rate of return on a bond sold before maturity?
If a security is sold before the maturity date, the rate of return earned by the investor is different, and the new rate of return is based on the sale price of the security. If, for example, the $1,000 corporate bond purchased for $920 is sold for $1,100 five years after the purchase date, the investor has a gain on the sale. The investor must determine the amount of the bond discount that is posted to income before the sale and must compare that with the $1,100 sale price to calculate the gain.
Why do zero-coupon bonds rise?
Because a bond will always pay its full, face value, at maturity—assuming no credit events occur— zero-coupon bonds will steadily rise in price as the maturity date approaches. These bonds don't make periodic interest payments and will only make one payment of the face value to the holder at maturity.
What is discount yield?
Discount yield is commonly calculated for municipal bonds#N#Municipal Bond A municipal bond refers to a bond or fixed income security that is issued by a government municipality, township, or state to finance its governmental#N#, Treasury bills (T-bills), zero-coupon bonds, commercial paper, most money market instruments, and so on.
What is the Bond Equivalent Yield (BEY)?
BEY is the total yield on bonds after taking into account the total interest applicable, i.e., the simple semi-annual interest on an actual day-count basis.
Is discount yield annualized?
For simplification of calculation, the discount yield is annualized, taking into account a 360-day year rather than the actual 365-day year. It creates a slight problem because the interest on bonds and Treasury bills is paid on a 365-day basis. The calculation time convention often leads to a mismatch in values.
Is discount yield based on face value?
While there is not usually much difference, some mismatch and errors can creep up considering that the discount yield is calculated based on the bond issue’s face value rather than the actual dollar amount invested, i.e., the purchase price.
What is yield rate?
Yield refers to the earnings from an investment over a specific period. It includes the investor earning such as interest and dividends received by holding particular investments.
What is yield interest rate?
Yield is also the annual profit that an investor receives for an investment. The interest rate is the percentage charged by a lender for a loan. Interest rate is also used to describe the amount of regular return an investor can expect from a debt instrument such as a bond or certificate of deposit (CD). Ultimately, interest rates are reflected in ...
What determines the yield of a bond?
The current interest rate determines the yield that a bond will bear at the time it is issued. It also determines the yield a bank will demand when a consumer seeks a new car loan. The precise rates will vary, of course, depending on how much the bond issuer or the bank lender wants the business and the creditworthiness of the borrower.
What happens to the yield of a stock if the price doubles to $100?
If the stock price doubles to $100 and the dividend remains the same, then the yield is reduced to 2%.
What is the dividend yield?
Dividends are the investor's share of the company's quarterly profit. For example, if PepsiCo ( PEP) pays its shareholders a quarterly dividend of 50 cents and the stock price is $50, the annual dividend yield would be 4%. If the stock price doubles to $100 and the dividend remains the same, then the yield is reduced to 2%.
What is the yield on a loan at the end of the year?
At the end of the year, the yield on the investment for the lender would be $100, or 10%. If the lender incurred any costs in making the loan, those costs would reduce the yield on the investment.
What does yield mean in investment?
The yield on new investments in debt of any kind reflects interest rates at the time they are issued.
What happens to the yield to maturity of a bond when it is purchased at a discount?
If the investor purchases the bond at a discount, its yield to maturity will be higher than its coupon rate. A bond purchased at a premium will have a yield to maturity that is lower than its coupon rate.
What is the coupon rate of a bond?
The coupon rate is the annual amount of interest that the owner of the bond will receive. To complicate things the coupon rate may also be referred to as the yield from the bond.
What is the yield to maturity of a bond?
If an investor purchases a bond at par or face value, the yield to maturity is equal to its coupon rate. If the investor purchases the bond at a discount, its yield to maturity will be higher than its coupon rate. A bond purchased at a premium will have a yield to maturity that is lower than its coupon rate. YTM represents the average return of the ...
What happens to the coupon rate when a bond is issued?
At face value, when the bond is first issued, the coupon rate and the yield are usually exactly the same. However, as interest rates rise or fall, the coupon rate offered by the government or corporation may be higher or lower.
How to calculate coupon rate for IBM bond?
To calculate the bond's coupon rate, divide the total annual interest payments by the face value. In this case, the total annual interest payment equals $10 x 2 = $20. The annual coupon rate for IBM bond is thus $20 / $1,000 or 2%.
What do you look for when buying bonds?
When investors consider buying bonds they need to look at two vital pieces of information: the yield to maturity (YTM) and the coupon rate. Investment-quality bonds are low-risk investments that generally offer a rate of return slightly higher than a standard savings account.
What is coupon payment?
To an individual bond investor, the coupon payment is the source of profit. To the bond trader, there is the potential gain or loss generated by variations in the bond's market price. The yield to maturity calculation incorporates the potential gains or losses generated by those market price changes. If an investor purchases a bond at par ...
Why are bonds priced at a discount?
The same holds true for bonds priced at a discount; they are priced at a discount because the coupon rate on the bond is below current market rates.
What is yield in bond?
A yield relates a bond's dollar price to its cash flows. A bond's cash flows consist of coupon payments and return of principal. The principal is returned at the end of a bond's term, known as its maturity date .
Why is it so hard to calculate the yield on a callable bond?
For example, calculating the yield on a callable bond is difficult because the date at which the bond might be called is unknown. The total coupon payment is unknown. However, for non-callable bonds such as U.S. Treasury bonds, the yield calculation used is a yield to maturity.
Why are coupon payments smaller?
Because the coupon payments on a bond priced at a discount are smaller than on a bond priced at a premium, if we use the same discount rate to price each bond, the bond with the smaller coupon payments will have a smaller present value. Its price will be lower.
What happens to a bond when it matures?
That is, if you buy a bond that pays 1% interest for 3 years, that's exactly what you'll get. And when the bond matures, its face value will be returned to you.
What is the dollar price of a bond?
A bond's dollar price represents a percentage of the bond's principal balance, otherwise known as par value. A bond is simply a loan, after all, and the principal balance, or par value, is the loan amount. So, if a bond is quoted at 99-29, and you were to buy a $100,000 two-year Treasury bond, you would pay $99,906.25.
How much discount is on a T bill?
T-bills are quoted at a discount from face value, with the discount expressed as an annual rate based on a 360-day year. 1 For example, you will get a 0.07*90/360=1.75% discount when you purchase the T-bill.
How to calculate yield?
Yield is determined through basic math. Take your initial investment, and simply divide it by the interest rate. This will give your basic term yield. Whether a term is 6 months, a year, or 12 years, you multiply your annual yield into the number of terms you’ll be allowing the investment to sit (if you’re not compounding), and you will derive your total yield. If you’re compounding, you’ll have to continually adjust the initial amount for each time the yield is compounded back into the investment. So, if you invested $10,000 for three years, at a term of one year, your second term would be calculated by multiplying $10,300 by the interest rate.
What is yield in investing?
The yield is how much you actually profited from the investment. While you can put the yield into terms of percentages, you can also do it simply in dollar amounts. If you bought an investment for $10,000, with a 3% interest rate for one year, your yield would be about $300. Of course, if you’re compounding your interest back into the investment, your yield increases. You can’t compound an interest rate.
What is yield expressed in?
4. Yield can be expressed in dollars or percentages.
What is the coupon rate of a bond?
A bond's coupon rate is the rate of interest it pays annually, while its yield is the rate of return it generates. A bond's coupon rate is expressed as a percentage of its par value. The par value is simply the face value of the bond or the value of the bond as stated by the issuing entity.
How to measure bond yield?
A bond's yield can be measured in a few different ways. Current yield compares the coupon rate to the current market price of the bond. 2 Therefore, if a $1,000 bond with a 6% coupon rate sells for $1,000, then the current yield is also 6%. However, because the market price of bonds can fluctuate, it may be possible to purchase this bond for a price that is above or below $1,000.
How much interest does a $1,000 bond pay?
Thus, a $1,000 bond with a coupon rate of 6% pays $60 in interest annually and a $2,000 bond with a coupon rate of 6% pays $120 in interest annually.
What does it mean to buy a bond at a premium?
To buy a bond at a premium means to purchase it for more than its par value. To purchase a bond at a discount means paying less than its par value. Regardless of the purchase price, coupon payments remain the same. To understand the full measure of a rate of return on a bond, check its yield to maturity.
What happens to a coupon rate if the government increases the minimum interest rate?
Coupon rates are largely influenced by the interest rates set by the government. Therefore, if the government increases the minimum interest rate to 6%, then any pre-existing bonds with coupon rates below 6% lose value. 1
Does credit rating affect bond price?
In addition, a bond's designated credit rating will influence its price and it can happen that when looking at a bond's price, you will find it does not honestly show the relationship between other interest rates and the coupon rate at all.
What is discount rate vs interest rate?
A discount rate is a broader concept of Finance which is having multi-definitions and multi-usage. Whereas Interest rate has a narrow definition and usage, however, multi things are to consider before determining the interest rates. In some cases, you have to pay to borrow money then it is a direct financial cost. In other cases, when you invest money in an investment, and the invested money cannot be utilized in anything else, then there is an opportunity cost. Discount Rates vs Interest rates both are related to the cost of money but in a different way. If you have an interest in Finance and want to work in the Financial Sector in the future, then you should know the difference between Interest rates and Discount rates.
What is discount rate?
Discount Rate is the interest rate that the Federal Reserve Bank charges to the depository institutions and to commercial banks on its overnight loans. It is set by the Federal Reserve Bank, not determined by the market rate of interest. An interest rate is an amount charged by a lender to a borrower for the use of assets. Interest rates are mostly calculated on an annual basis, which is also known as the annual percentage rate. The assets borrowed can be cash, large assets such as a piece of machinery, vehicles or building.
What is interest rate?
An interest rate is an amount charged by a lender to a borrower for the use of assets. Interest rates are mostly calculated on an annual basis, which is also known as the annual percentage rate. The assets borrowed can be cash, large assets such as a piece of machinery, vehicles or building.
Can you pay interest on a 10 year bond?
Buy a 10- Year bond or make a Fixed Deposit in the bank, and you’ll be getting the interest. However, someone will pay you interest for using your money. Interest rates are directly proportional to the risk profile of the borrower. The interest rate will be higher if the borrower’s profile is considered risky, the rate of interest charged on them will be on the higher side.

How Is The Discount Yield calculated?
- Discount yield is calculated as follows: The components of the discount yield formula are as follows: 1. (Face Value – Purchase Price)is the total discount amount applied to the face value of the bond. 2. (Face Value – Purchase Price) / Face Value is the percentage value of the total discount on the bond to its face value. 3. 360 / No. of Days (or ...
Popular Usage
- Discount yield is commonly calculated for municipal bonds, Treasury bills (T-bills), zero-coupon bonds, commercial paper, most money market instruments, and so on. 1. Municipal bonds: Municipal bonds are low-risk debt securities issued by the government, or municipality, primarily to finance its public expenditures. These are exempt from most federal and provincial taxes. 2. …
Practical Example
- Say, for example, you purchase a bond for $9,600. It matures to a total value of $10,000. It means the bond was purchased at a discount of $400. It was issued on December 1, 2019, and is to mature in 90 days. Consequently, the discount yield for this bond can be calculated as follows: Therefore, the discount yield of the bond is 0.16 or 16%.
What Is The Bond Equivalent Yield (Bey)?
- Bond equivalent yields (BEY) are often considered along with bank discount yields and sometimes also confused with each other. BEY is the total yield on bonds after taking into account the total interest applicable, i.e., the simple semi-annual interest on an actual day-count basis. The bond equivalent yield (BEY) is calculated as follows: Where: 1. DRis the discount rate (which is basical…
More Resources
- CFI is the official provider of the global Capital Markets & Securities Analyst (CMSA)™certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional resources below will be useful: 1. Commercial Paper 2. Money Market 3. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) 4. Zero-Coupon Bond
Yield vs. Interest Rate: An Overview
Yield
- Yieldrefers to the return that an investor receives from an investment such as a stock or a bond. It is usually reported as an annual figure. In bonds, as in any investment in debt, the yield is comprised of payments of interest known as the coupon. In stocks, the term yield does not refer to profit from the sale of shares. It indicates the return ...
Interest Rates
- The interest rate on any loan is the percentage of the principle that a lender will charge annually until the loan is repaid. In consumer lending, it is typically expressed as the annual percentage rate(APR) of the loan. As an example of interest rates, say you go into a bank to borrow $1,000 for one year to buy a new bicycle, and the bank quotes you a 10% interest rate on your loan. In additi…
Example
- For example, a lender might charge an interest rate of 10% for a one-year loan of $1,000. At the end of the year, the yield on the investment for the lender would be $100, or 10%. If the lender incurred any costs in making the loan, those costs would reduce the yield on the investment.
Special Considerations
- Current interest rates underpin the yield on all borrowing, from consumer loans to mortgages and bonds. They also determine how much an individual makes for saving money, whether in a simple savings account, a CD, or an investment-quality bond. The current interest rate determines the yield that a bond will bear at the time it is issued. It also determines the yield a bank will deman…