The main difference between directional and disruptive selection is that directional selection favors a phenotype most fitted to the environment whereas disruptive selection favors extreme values for a trait over intermediate values.
What is the difference between directional and disruptive natural selection?
Definition. Directional selection refers to a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction, while disruptive selection refers to a mode of natural selection in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values.
What is the difference between stabilizing and disruptive selection?
The key difference between disruptive selection and stabilizing selection is that disruptive selection favours both extreme phenotypes while stabilizing selection favours average phenotypes in a population, eliminating both extremes. Disruptive selection and stabilizing selection are two types of natural selection processes.
What is the directional selection theory of evolution?
The directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype.
How does directional selection result in population graph drift?
Directional selection is one way of natural selection. One extreme trait or phenotype prefers over the other during the directional selection. Thus, one extreme trait is selected against the other extreme trait. Therefore, this results in a population graph drift.

What is the difference between directional and disruptive?
The key difference between directional and disruptive selection is that the directional selection prefers and selects only one extreme trait among the two extreme traits whereas the disruptive selection favours both extreme traits together.
What is the difference between disruptive stabilizing and directional selection?
Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes, different from one extreme in directional selection. Stabilizing selection favors the middle phenotype, causing the decline in variation in a population over time.
What is an example of directional selection?
An example of directional selection is giraffe neck lengths. The environment created a selection pressure which favored giraffes with longer necks who could reach more food in the trees. At the same time, there was selection pressure against giraffes with shorter necks.
What is an example of disruptive selection?
One example of disruptive selection is dark and light-colored oysters. Both dark-colored oysters and light-colored oysters have camouflage advantages. Light-colored oysters will blend with the rocks and dark-colored oysters can hide under the rock shadow.
What is meant by directional selection?
Directional selection occurs when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or reproduce more than those on the other. It has been demonstrated many times in natural populations, using both observational and experimental approaches.
Which best describes directional selection?
Which statement best describes directional selection? a. Directional selection occurs when phenotypes at both extremes of the phenotypic distribution are selected against.
How are directional and disruptive selection similar?
Similarities Between Directional and Disruptive Selection Both increase the allele frequency of the favored phenotypes within the population. However, they may increase or decrease biological phenotypes within a population. The decrease in the number of phenotypes within a population reduces variation.
What is disruptive selection in simple terms?
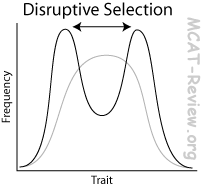
Disruptive selection, also called diversifying selection, describes changes in population genetics in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values.
What causes disruptive selection?
Disruptive selection occurs when individuals of intermediate phenotype are less fit than those of both higher and lower phenotype, such that extremes are favored. This may occur if there are two diverse food sources or predators with diverse preferences for, say, size of prey.
What is the disruptive selection in evolution?
Disruptive selection occurs when extreme phenotypes have a fitness advantage over more intermediate phenotypes. The phenomenon is particularly interesting when selection keeps a population in a disruptive regime.
What are the 3 types of selection?
There are three types of selection: Stabilising selection. Disruptive selection. Directional selection.
Why is disruptive selection important?
Disruptive selection has long been viewed as important in maintaining and increasing variation within natural populations [1–3]; favoring the evolution of alternative phenotypes [4, 5] and sexual dimorphism [6–8]; and even initiating speciation [6, 8–12].
What is the difference between directional selection and stabilizing selection?
Stabilizing selection results in a decrease of a population 's genetic variance when natural selection favors an average phenotype and selects against extreme variations. In directional selection, a population's genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes.
What are the 3 types of selection?
There are three types of selection: Stabilising selection. Disruptive selection. Directional selection.
What are the 3 different types of natural selection?
Natural selection on traits determined by multiple genes may take the form of stabilizing selection, directional selection, or disruptive selection.
What are the three modes of natural selection?
Natural selection can produce three different effects on the genetic variation of a population. These three modes, known as directional, stabilizing, and disruptive selection, are demonstrated in the following activity.
What is the difference between directional and disruptive selection?
Directional selection refers to a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction, while disruptive selection refers to a mode of natural selection in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values.
What is directional selection?
Directional selection is a type of natural selection that leads to the selection of the phenotype that is most fitted to the environment. Therefore, environmental changes are the driving force of the directional selection. Moreover, as it selects a particular phenotype over its opposite phenotype, the existing variation moves towards one end.
What is the selection of dark-colored moths over light-colored moths after industrial evolution?
Selection of the dark-colored moths over light-colored moths after industrial evolution is an example of directional selection while selection of alpha males and “sneaking” males over intermediate males in a lobster population is an example of disruptive selection.
What are the two types of natural selection mechanisms?
Directional and disruptive selection are two types of natural selection mechanisms.
What is the decrease in the number of phenotypes within a population?
The decrease in the number of phenotypes within a population reduces variation.
What is the difference between directional selection and disruptive selection?
Although both of them result in a population adapting to biotic and abiotic environments, they differ in many ways. Directional selection occurs when one extreme phenotype is favored over the other phenotypes, whereas disruptive selection occurs when two or more phenotypes are favored over the others. Another difference is that disruptive selection favors polymorphism and directional selection causes species to evolve over time and leads to the extinction of those lacking the phenotypes causing the distribution curve to shift.
What are some examples of directional selection?
A common example of directional selection is the human struggle against malaria. Plasmodium is spread by the bites of
Why Is The Brush Tail Possums Considered Microevolution?
It can also be a gradual process such as the formation of mountains, or it can be a rapid and unexpected change, such as a natural disaster. When changes in organism’s environments occur, they must adapt to their new environment, this can cause ample amounts of selective stress and pressure on organisms, causing some species to eventually die out, while other organisms strive and evolve to be better adapted to this change .
What is the mechanism of evolution?
The next mechanism is gene flow, which is when alleles from one population migrate to another population and changes the genetic variation of both populations. Sexual selection is another mechanism of evolution that involves the passing down of more attractive and appealing traits. The final mechanism is natural selection and this mechanism is the most important for evolution. Natural selection is the selection of individuals that possess more favorable traits in an environment. These favorable traits will be passed down to future
Which mechanism of evolution involves the passing down of more attractive and appealing traits?
Sexual selection is another mechanism of evolution that involves the passing down of more attractive and appealing traits. The final mechanism is natural selection and this mechanism is the most important for evolution. Natural selection is the selection of individuals that possess more favorable traits in an environment. These favorable traits will be passed down to future
Why is malaria a recessive gene?
This occurs due to wrong coding for the protein in haemoglobin which causes haemoglobin to not form properly. This anaemia is a recessive gene and when an individual is a carrier, it provides an advantage against malaria. Malaria is a life-threatening blood disease caused by a parasite called Plasmodium that is transmitted to humans by an infected Anopheles mosquito through biting. Malaria is a preventable and treatable disease (MNT). Both sickle cell anaemia and malaria happen in Africa, South America and in some parts of Asia and the most deaths caused by the malarial
What is directional selection theory?
The directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype. In other words, if a particular trait is favorable, ...
What are some examples of directional selection?
An example of directional selection is giraffe neck lengths. The environment created a selection pressure which favored giraffes with longer necks who could reach more food in the trees.
What are the three types of natural selection?
Directional selection, stabilizing selection and disruptive selection are three types of natural selection. They are also examples of adaptive evolution. Natural selection is the mechanism of evolution which favors organisms that are better adapted to their environments.
Why is stabilizing selection considered the most common mechanism for natural selection?
Because most traits do not change drastically over time , stabilizing selection is considered to be the most common mechanism for natural selection. Other examples of stabilizing selection are the birth weight of humans and the number of eggs a bird lays (clutch size).
What is stabilizing selection?
Stabilizing selection can be thought of as “middle-of-the-road” selection, meaning a non-extreme trait is favored instead of one of the two extreme traits. An example of this is plant height. In a population of plants, those that are short may not get enough sunlight, but those that are tall may be subjected to wind damage.
Which type of natural selection favors both extreme traits in a population?
Disruptive Selection . This type of natural selection is bimodal and favors both extreme traits in a population. For example, in a population of plants, there are some pollinators that visit the tallest plants, a different species of pollinator visits medium-height plants and a third species of pollinator that prefers the shortest plants.
Who was the first to describe directional selection?
The English naturalist and scientist Charles Darwin was the first to describe directional selection as a form of natural selection in his foundational 1859 work On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favored Races in the Struggle for Life.#N#The directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype. In other words, if a particular trait is favorable, it will be expressed at the most beneficial frequency in the population.
What is disruptive selection?
As a result, the population’s genetic variance decreases. In contrast, disruptive selection is a type of natural selection which favours both extreme traits together. It increases the genetic variance of the ...
What is the Difference Between Disruptive Selection and Stabilizing Selection?
Stabilizing selection is a mode of natural selection which favours an average trait value over two extreme trait values . So, this is the key difference between disruptive selection and stabilizing selection. Disruptive selection increases the population’s genetic variance while stabilizing selection decreases the population’s genetic variance.
What is Stabilizing Selection?
Stabilizing selection is a type of natural selection which favours the average or middle phenotypes in a population. In other words, stabilizing selection pushes a population towards the average or median while eliminating the two extreme phenotypes. The environment normally favours the average phenotype within a population. Stabilizing selection is the quantitative equivalent of balancing selection for a single gene trait.
Why is stabilizing selection important?
Stabilizing selection makes the population more uniform since natural selection works against the two extremes. Therefore, it reduces the genetic variation of the population.
What are some examples of natural selection?
Another example is the body size of a species of a lizard belo nging to genus Aristelliger. Small lizards and large lizards are eliminated, and the average size lizards are favoured by the natural selection.
Does stabilizing selection increase or decrease genetic variance?
In contrast, stabilizing selection favours middle phenotypes against both extremes. Therefore, stabilizing selection decreases the genetic variance of the population.
/2000px-Disruptive_selection_after.svg-58ee97e35f9b582c4d07e67a.png)
Directional Selection
Stabilizing Selection
- Stabilizing selection can be thought of as “middle-of-the-road” selection, meaning a non-extreme trait is favored instead of one of the two extreme traits. An example of this is plant height. In a population of plants, those that are short may not get enough sunlight, but those that are tall may be subjected to wind damage. This results in an increase in the number of medium-height plant…
Disruptive Selection
- This type of natural selection is bimodal and favors both extreme traits in a population. For example, in a population of plants, there are some pollinators that visit the tallest plants, a different species of pollinator visits medium-height plants and a third species of pollinator that prefers the shortest plants. If the pollinator that prefers medium-height plants is removed, natur…
Comparison Chart
- The image above shows the three patterns of natural selection using an allele that determines fur color.