
The difference between distributive and integrative negotiation are explained hereunder:
- Distributive Negotiation connotes a negotiation technique wherein the parties try to gain maximum value for themselves, from definite resources. ...
- Distributive Negotiation is a competitive strategy, whereas integrative negotiation uses a collaborative approach.
- Distributive Negotiation has a win-lose orientation. ...
Is distributive negotiation the same as bargaining?
Distributive bargaining refers to the process of dividing up the resource or array of resources that parties have identified. In many negotiations, that means haggling over issues such as price. By comparison, integrative bargaining involves collaboration or integrating across multiple issues to create new sources of value.
What is integrative negotiations and its characteristics?
Negotiation should focus on realistic issues and not on egos about winning and not losing. Characteristics of Integrative Negotiations. Integrative negotiation is a process in which the negotiating parties jointly work towards goals that are not mutually exclusive so that one party does not necessarily gain at the expense of the other.
What is the basic assumption of distributive negotiation?
Distributive negotiation is based on a win-win assumption, in that the parties want to come up with a creative solution that can benefit both sides. asked Feb 23, 2019 in Business by Yotun. management. Distributive negotiation is a collaborative approach to negotiation that is based on a win-win assumption, whereby the parties want to come up ...
What are distributive negotiations?
What is Distributive Negotiation? Distributive negotiation is the process of dividing up the pie of value in negotiation. Distributive negotiation can be thought of as haggling—the back-and-forth exchange of offers, typically price offers, which the late Harvard professor Howard Raiffa referred to as the “negotiation dance.”
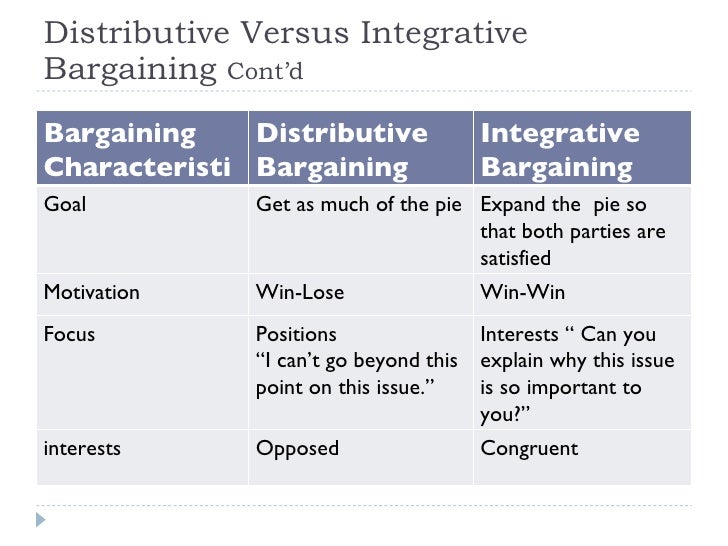
What is the difference between distributive and integrative?
Distributive Negotiation is the negotiation strategy in which fixed amount of resources are divided between the parties. Integrative Negotiation is a type of negotiation in which mutual problem solving technique is used to enlarge the assets, that are to be divided between parties.
What are the differences between distributive and integrative bargaining quizlet?
distributive bargaining: talking down a price to something manageable. Its identifying feature is that it operates under zero-sum conditions—that is, any gain I make is at your expense, and vice versa. integrative bargaining: Negotiation that seeks one or more settlements that can create a win-win solution.
What is integrative negotiation?
Integrative bargaining (also called "interest-based bargaining," "win-win bargaining") is a negotiation strategy in which parties collaborate to find a "win-win" solution to their dispute. This strategy focuses on developing mutually beneficial agreements based on the interests of the disputants.
What is distributive negotiation?
Distributive negotiation is the process of dividing up the pie of value in negotiation. Distributive negotiation can be thought of as haggling—the back-and-forth exchange of offers, typically price offers, which the late Harvard professor Howard Raiffa referred to as the “negotiation dance.”
What is integrative negotiation examples?
In this example, a furniture vendor says the lowest price they will offer a company for five chairs is $3,000, but the customer says the highest they will pay is $2,800. The client convinces the vendor to lower the price to $2,900, and both parties compromise by giving up their original price to make a deal.
What are the differences between integrative and distributive issues what is a compatible issue?
For integrative negotiations to be successful, both parties must be motivated to work collaboratively rather than competitively, and the interests of both parties must be compatible. Distributive negotiations are used when two (or more) parties are trying to claim the maximum amount of profit or benefit for themselves.
What are the characteristics of integrative negotiation?
What personal characteristics of negotiators facilitate a successful integrative negotiation?Common, Shared, & Joint Objectives or Goals. ... Confidence in Problem-solving Ability. ... Openness to Alternative Perspectives. ... Motivation and Commitment to Work Together. ... Trust. ... Clear and Accurate Communications.
What are the two types of negotiations?
The two distinctive negotiation types are distributive negotiations and integrative negotiations.
What are the advantages of integrative negotiation?
In general, integrative negotiation is preferable to distributive because integrative builds long-term relationships and facilitates working together in the future. It allows each negotiator to leave the bargaining table feeling they have achieved a victory.
What is distributive negotiation and give an example?
Usually distributive bargaining approach works well with products which do not have a fixed price. For example, if you go to the supermarket and buy some products, you won't be able to bargain because they have a fixed price. Either you can buy the product or leave it.
Where is distributive negotiation used?
Distributive negotiation is a type of negotiation in which parties bargain for shares of a fixed resource. Also known as distributive bargaining, it can be used in labor negotiations, sales, and in any problem-solving scenario where people are trying to divvy up things of value.
Why is distributive negotiation important?
Through distributive negotiation, even though they cannot distribute the resource in equal share. But they can make sure that one gets that they desire the most. In this way, even if a party gets less share from the distribution process, they will be happy from the distribution as they get what they wanted.
What are the characteristics of distributive bargaining?
In distributive bargaining approach, both the parties try to know each other's walk-away-value to take a decision. After that, they make a deal in that it is closer to their own goal rather than adjusting according to the competitors.
What are some of the features of integrative bargaining?
What personal characteristics of negotiators facilitate a successful integrative negotiation?Common, Shared, & Joint Objectives or Goals. ... Confidence in Problem-solving Ability. ... Openness to Alternative Perspectives. ... Motivation and Commitment to Work Together. ... Trust. ... Clear and Accurate Communications.
What characteristic is associated with distributive bargaining quizlet?
Distributive bargaining generally involves a single issue (compared to multiple issues), little expectation for a continuing relationship, positions vs. interests, limited sharing of information, and claiming value vs. creating/claiming value.
Which of the following is not a key difference in the bargaining environment of the public and private sectors?
Which of the following is not a key difference in the bargaining environment of the private and public sectors? The labor market does not effect the public sector as much as it does the private sector.
What is the difference between integrative and distributive negotiation?
In distributive negotiation every negotiator focuses on meeting his personal interests, regardless of the loss the others may have to face. In contrast, integrative negotiation focuses on mutual interests of all the parties and thus, comes up with constructive solutions that will be beneficial for all.
When to Use Distributive vs. Integrative Negotiation Strategies?
The list of differences between these two negotiation strategies finally brings us to the most important question – which strategy should be used in which situation ?
What is the best way to negotiate a long term deal?
If it’s just a matter of one deal and you think you will never need any sort of help from the other negotiators in the future – distributive negotiation is the way to go. However, when long term dependability among negotiators is noticeable, integrative negotiation strategy is the safest choice.
What is negotiation strategy?
Negotiation strategies have gained a significant amount of attention from management practitioners owing to their conflict resolving attribute. There are two main approaches to negotiations based on the stance adopted by the negotiating parties – distributive and integrative. To choose the most apt strategy for a particular situation it’s important ...
When to use distributive negotiation?
Considering the varying approach of these two strategies, distributive negotiation is best used when you have some strong advantage points and you’re in a good position to bargain. Contrary to this, integrative negotiation will be most beneficial in situations where your position is not strong but you still want to win something in the bargain.
Is integrative negotiation safe?
However, when long term dependability among negotiators is noticeable, integrative negotiation strategy is the safest choice. The end result of a negotiation is dependent completely on the stance the negotiators adopt, thus you must understand the difference between distributive and integrative negotiation strategies to make the right move on ...
Distributive Negotiation
Imagine you are going out to buy a piece of furniture. You will try to negotiate the price in your favor and the seller tries to negotiate the price in their favor. Here, you both are trying to protect your interests and maximize your outcome. The above transaction is an example of distributive negotiation.
Integrative Negotiation
In an integrative negotiation scenario, both the parties put forward their interests to try and agree to a solution that creates a mutual gain for both.
Difference between Distributive and Integrative Negotiation
To highlight the differences between distributive negotiation and integrative negotiation for you:
What is distributive and integrative negotiation?
Distributive and integrative, sometimes called communicative, forms of negotiation are not so much strategies as they are states. These are two sets of “rules” for the negotiating game. They are very different and assume different sets of values, purposes and ends.
What is strategy in negotiations?
As a “strategy,” it stresses competition in the race to gain as much of a limited good as possible.
What is integrative bargaining?
Integrative bargaining is about procedures . The assumption is that an unfair procedure leads to unfair results. If a class of people is left out of the lawmaking in a society, chances are this group's interest will be overlooked. Distributive ideas are about the results of the integrative approach. It is possible that an unfair integrative approach can lead to fair results, or that a just and moral integrative idea will lead to distorted distributive results. For example, a society decides that it will give each adult one vote in electing lawmakers. However, the results turn out to be unfair because the bulk of these people live in cities. Only a small minority are farmers in rural areas, and, therefore, while the integrative approach seems fair, the results will reflect the cities and their biases. Therefore, the integrative strategy must change, and the countryside must be weighted to make it equal with the more populous cities.
What is distributive justice?
Aristotle defined “distributive justice” as the proper apportionment or allotment of certain goods such as money, position or honor.
Can integrative approach lead to fair results?
It is possible that an unfair integrative approach can lead to fair results, or that a just and moral integrative idea will lead to distorted distributive results. For example, a society decides that it will give each adult one vote in electing lawmakers.
What are Integrative Negotiations?
Any value claimed by one party is not at the expense of the other party; rather, the parties negotiate to create or generate value in the situation and both parties may achieve mutual gains beyond what they could achieve independently. This is a potentially (win-win) scenario.
What is the purpose of tradeoffs in a negotiation?
These tradeoffs allow each party to gain in an interest that is important to her in exchange for the other party gaining in an interest that is important to him. The net result is both parties being better off because of the negotiation.
How does interdependence affect the nature of the interests?
The interdependence of parties is often affected by the nature of the differing interests or objectives. The parties may find themselves in situations where the interest or objective of both parties is the same and is finite.
Is a win-lose negotiation a competitive situation?
The interests or objectives of the parties are the same and are mutually exclusive. As such, it is a competitive (win-lose) situation. Any value claimed by one party in the negotiation is at the expense of the other party. This scenario generally is very competitive and does not foster cooperative behavior.
Can a negotiation have multiple interests?
Note (IMPORTANT): A single negotiation may have multiple interests at stake - each of which is either distributive, integrative, or compatible.
Is the interest of objectives mutually exclusive?
The interests of objectives of the parties are the same and NOT mutually exclusive. In fact, the parties desire the exact same outcome. There is no need for tradeoff. The parties want the exact same outcome with regard to the interest or objective at stake in the negotiation.
What is distributive negotiation?
What exactly is distributive negotiation, and what are its characteristics? In distributive bargaining, both parties attempt to maximize their gains at the expense of the other. Thus, negotiators term distributive negotiations as zero-sum or win/lose.
Why is it important to have an integrative negotiation?
Integrative negotiations also create a less intense environment in which to negotiate. And a spill-over-benefit from that is, it can enhance long-term relationships. That can make future negotiations between these partners more manageable.
What is the meaning of caution in negotiation?
If you are negotiating with a negotiator with the mindset that the only way for him to win is for you to lose , caution would be the word for you. Integrative negotiations strive for win-win outcomes. Thus, if engaging in this negotiation form does not deliver the perception of that outcome, it becomes a disincentive to use this approach. Suffice it to say; if the opposing negotiator is reluctant about striving for a win-win outcome, you must be prepared to use a distributive negotiation style.
What does a good negotiator do?
People don’t realize they’re always negotiating. A good negotiator must contemplate his counterpart’s most minor negotiation position. And, he must do so while considering that person’s generalities related to his wants from the negotiation. He must do so by reflecting on the past and looking forward at the same time.
What is a stern demeanor in negotiation?
Negotiators that have a stern demeanor find this style of negotiating appealing. They are the ones that want to steamroll their opponent. And based on that person’s negotiation counterpart, that approach may serve the steamroller well.
Why are hagging sessions so deceptive?
Because some negotiators feel they must use any tactic to secure the outcome they seek, depending on the stakes. And they may do whatever it takes to achieve their goals.
Why do negotiators take a longer view of relationships?
They do so because they know they may be negotiating with that entity in the future or someone in that person’s stead. The one thing that negotiators must be aware of when using this approach is its limits.
What is integrative negotiation?
During the integrative negotiation, negotiators must be firm about their wants and needs but flexible as to how they are met to reach a solution to fit both sides. This cooperative type of negotiation was used at times during NBA free agent negotiations involving Howard.
What is integrative and distributive bargaining?
Integrative and Distributive Bargaining Whether a negotiation involves working together toward a goal or working against one another to win, each party must use a strategy to reach a solution. The differences of distributive bargaining and integrative bargaining are parallel. The ways in which one method is competitive and the other is cooperative is described and related to a well-known case involving basketball player Juwan Howard. Distributive Bargaining
How does integrative bargaining help Howard?
Integrative bargaining involves understanding the other party’s needs, creating an open exchange of information, and reach options for both parties to benefit.
How to enter a distributive bargaining situation?
To enter a distributive bargaining situation, each party should have established their starting, target, and resistance points. The starting point is each party’s opening statement. The target point is learned throughout the negotiation as the party makes concessions between their starting point and target point.
What happens when there are many alternatives to a deal?
If there are many alternatives to the deal, the negotiators will not have to make as many concessions. When dealing with less alternatives, the party will have less bargaining power in the negotiation. Each party should have alternatives when going into the negotiation so each has a good idea how firm to be.
Why is Batna important in a negotiation?
BATNA is the term for “best alternative to a negotiated agreement” to be used to ensure the party has accepted the alternative that best fits their needs (Lewicki, Saunders, & Barry, 2006). Having the BATNA will help the party achieve their goals in the negotiation. Juwan Howard knew he had alternative deals when he was considering offers from teams besides the Bullets.
When there is something to be divided up, this is not the best method to use for negotiation?
Another con to this method is that if one side fails to understand the other side, there will be conflict without reaching an agreement. The four steps to the integrative negotiation process are to indentify and define the problem, understand the problem and bring interests and needs to the surface, generate alternative solutions to the problem, and evaluate those alternatives and select among them. The process is designed to first create value, then to claim the value associated.
