Difference Between DNA Profiling and DNA Sequencing
- Definition. DNA profiling refers to the analysis of unique patterns of DNA sequences in the genome in order to identify individuals, while DNA sequencing refers to the determination of the ...
- Focused Elements. ...
- Purpose of PCR. ...
- Importance. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is the difference between gene sequencing and DNA fingerprinting?
The main difference between gene sequencing and DNA fingerprinting is that the gene sequencing is involved in the identification of the nucleotide sequence of a gene whereas the DNA fingerprinting is involved in the identification of small variations in DNA of a particular individual.
What is the difference between DNA profiling and genetic screening?
The key difference between DNA profiling and genetic screening is that DNA profiling is the process of determining the DNA characteristics of an individual, whereas genetic screening is the process of testing a population for a genetic disease.
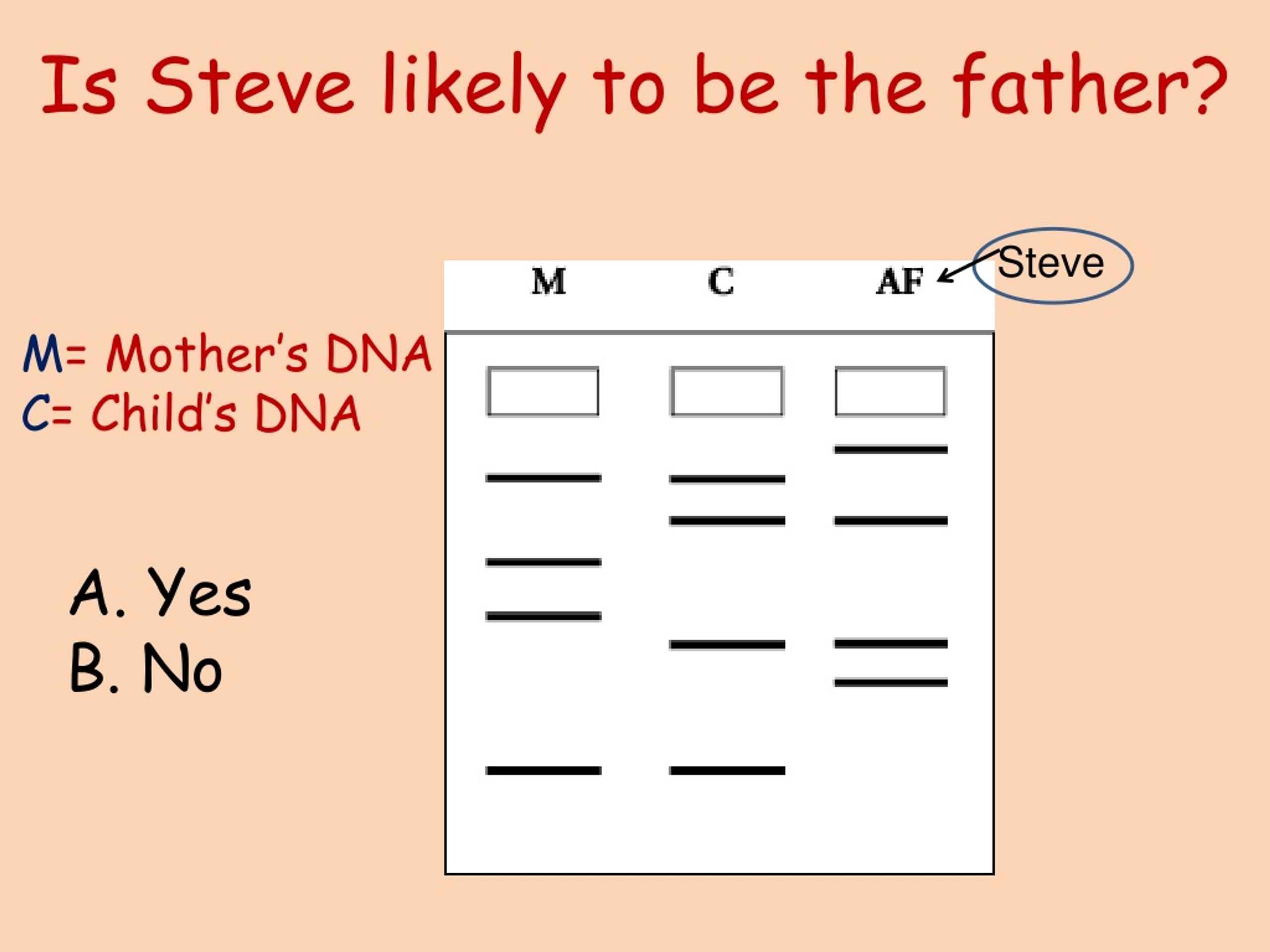
What is DNA profiling and fingerprinting?
DNA profiling is the process of acquiring a specific DNA pattern, known as a profile, from a person or a sample of body tissue. DNA fingerprinting is a type of molecular genetics that uses a person’s unique DNA patterns to identify them.
What is the difference between DNA profiling and PCR?
DNA profiling focuses on STR patterns of a particular locus while DNA sequencing focuses on the nucleotide sequence of a DNA fragment. PCR is responsible for the amplification of STR regions through sequence-specific priming in DNA profiling.
What is the difference between DNA and sequencing?
The key difference between DNA profiling and DNA sequencing is that DNA profiling is a method used to identify an individual from a sample by looking at the unique patterns in the DNA, while DNA sequencing is a method used to determine the sequence of nucleotides in a piece of DNA of an individual.
What is meant by DNA sequencing?
A laboratory process used to learn the exact sequence (order) of the four building blocks, or bases, that make up DNA.
What is the difference between sequencing and genotyping?
Genotyping is like reading a few scattered words on a page. Sequencing reads whole sentences, paragraphs and chapters. To sum it up quickly, genotyping gives you small packets of data to compare while sequencing gives you more data, with more meaning and context, today and down the road.
What is DNA profiling in simple terms?
DNA profiling is a forensic technique used to identify individuals based on differences, or variations, in their DNA sequence. Some regions of the DNA in your cells' chromosomes have a large number of differences among individuals, and even between an individual's two copies.
What does it mean by sequencing?
/ˈsiː.kwən.sɪŋ/ the process of combining things in a particular order, or discovering the order in which they are combined: A common sign of dyslexia is that the sequencing of letters when spelling words may be incorrect.
What is DNA fingerprinting profiling?
… DNA fingerprinting is a laboratory technique used to determine the probable identity of a person based on the nucleotide sequences of certain regions of human DNA that are unique to individuals.
Is genome sequencing the same as DNA sequencing?
Regardless of the approach to the genome as a whole, the actual process of DNA sequencing is the same. Sequencing employs a technique known as electrophoresis to separate pieces of DNA that differ in length by only one base.
How is DNA sequencing used?
In medicine, DNA sequencing is used for a range of purposes, including diagnosis and treatment of diseases. In general, sequencing allows health care practitioners to determine if a gene or the region that regulates a gene contains changes, called variants or mutations, that are linked to a disorder.
What is DNA genotyping?
Genotyping determines differences in genetic complement by comparing a DNA sequence to that of another sample or a reference sequence. It identifies small variations in genetic sequence within populations, such as single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
What is DNA profiling and how does it work?
DNA profiling uses techniques that can reveal small variations in the sequence of nucleobases from one person to another. DNA profiling techniques have become a powerful resource for modern forensic science, and have even allowed old, unsolved cases to be reviewed with fresh evidence.
What are the different methods of DNA profiling?
One of the current techniques for DNA profiling uses polymorphisms called short tandem repeats. Short tandem repeats (or STRs) are regions of non-coding DNA that contain repeats of the same nucleotide sequence. For example, GATAGATAGATAGATAGATAGATA is an STR where the nucleotide sequence GATA is repeated six times.
Is DNA profiling and DNA fingerprinting the same?
Introduction. DNA fingerprinting (also called DNA profiling or forensic genetics) is a technique employed by forensic scientists to assist in the identification of individuals or samples by their respective DNA profiles.
What are the steps of DNA sequencing?
What are the steps in DNA sequencing?Sample preparation (DNA extraction)PCR amplification of target sequence.Amplicons purification.Sequencing pre-prep.DNA Sequencing.Data analysis.
Where is DNA sequencing used?
In medicine, DNA sequencing is used for a range of purposes, including diagnosis and treatment of diseases. In general, sequencing allows health care practitioners to determine if a gene or the region that regulates a gene contains changes, called variants or mutations, that are linked to a disorder.
What are the types of DNA sequencing?
Broadly speaking, there are two types of DNA sequencing: shotgun and high-throughput. Shotgun (Sanger) sequencing is the more traditional approach, which is designed for sequencing entire chromosomes or long DNA strands with more than 1000 base pairs.
What are the 4 sequences of DNA?
Because there are four naturally occurring nitrogenous bases, there are four different types of DNA nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
How many reactions does Sanger sequencing use?
Typically, Sanger sequencing divides DNA sample into four separate sequencing reactions, allowing the addition of four dideoxynucleotides (ddATP, ddCTP, ddGTP, and ddTTP) into each reaction mixture separately. Here, each dideoxynucleotide is fluorescently labeled (ddATP with green dye, ddCTP with blue dye, ddGTP with yellow dye, and ddTTP with red dye). Also, their concentration is approximately 100-fold lower than that of the deoxynucleotide.
What is the difference between DNA sequencing and DNA profiling?
The main difference between DNA profiling and DNA sequencing is that DNA profiling is the forensic technique, which allows the identification of individuals according to their genetic makeup whereas DNA sequencing is the technique in biotechnology, determining the nucleic acid sequence of a particular DNA fragment.
What is the purpose of PCR?
Purpose of PCR. PCR is responsible for the amplification of STR regions through sequence-specific priming in DNA profiling. In contrast, in DNA sequencing, PCR is responsible for the incorporation of labeled dideoxynucleotides to the amplicons.
Why is DNA profiling important?
Importance. DNA profiling is important in the identification of individuals in forensic studies as well as parentage testing while D NA sequencing is important to study genomes and proteomes, identification of new alleles, etc.
What is DNA profiling?
Definition. DNA profiling refers to the analysis of unique patterns of DNA sequences in the genome in order to identify individuals, while DNA sequencing refers to the determination of the nucleotide sequences of a DNA fragment.
How many STRs can be analyzed?
Remarkably, up to 30 STRs can be analyzed in a single capillary electrophoresis injection. For instance, STRs are highly polymorphic regions. However, the number of STR alleles in the human population is very small. Normally, similar STR alleles occur around 5-20% of individuals.
What happens to amplicons after heat denaturation?
Basically, after undergoing polymerase chain reaction, amplicons after heat denaturation are size-fractionated on a denaturing polyacrylamide-urea gel. Ultimately, the nucleotide sequence can be determined through the visualization of the gel.
What is the purpose of DNA fingerprinting?
On the other hand, DNA fingerprinting is a method we use in order to obtain the pattern of STRs at a particular locus of the genome.
What is the difference between DNA fingerprinting and gene sequencing?
The main difference between gene sequencing and DNA fingerprinting is that the gene sequencing is involved in the identification of the nucleotide sequence of a gene whereas the DNA fingerprinting is involved in the identification of small variations in DNA of a particular individual. Furthermore, gene sequencing is a method ...
Why is gene sequencing important?
The information obtained from gene sequencing is important for the identification of mutations within the gene sequence, which in turn reveal the diseased genes. Also, it identifies new forms of genes called the alleles.
What is gene sequencing?
Gene sequencing is a method we use to identify the nucleotide sequence of a gene. Due to the ability of gene sequencing to reveal the information of a gene up to the nucleotide level, it helps to obtain the most detailed information about the gene. Hence, this may help to identify different sequence elements of a gene, ...
Where are short tandem repeats found?
These short DNA sequences are the repeating elements called short tandem repeats (STRs) mainly found in the centromeric regions of a chromosome. Here, the STRs are a type of non-coding DNA categorized under microsatellites. Their repeating unit consists of 2-6 nucleotides.
What is the difference between DNA fingerprinting and DNA profiling?
The main difference between DNA fingerprinting and DNA profiling is that DNA fingerprinting is a molecular genetic method that allows the identification of individuals according to the unique patterns of DNA, whereas DNA profiling is a forensic technique used in both criminal investigations and parentage testing.
Why is DNA fingerprinting important?
Importance. Moreover, DNA fingerprinting is a molecular genetic method that allows the identification of individuals according to the unique patterns of DNA, while DNA profiling is a forensic technique important in both criminal investigations and parentage testing.
What is DNA profiling?
In contrast, DNA profiling is the forensic technique of identification of individuals. However, it is based on the analysis of STR regions of the genome with the use of PCR. Therefore, DNA profiling is ...
How does DNA fingerprinting work?
Furthermore, in classic DNA fingerprinting, restriction enzymes cut DNA from the samples into small pieces. Then, the digested DNA can be separated by Gel electrophoresis and the resulting fragments can be immobilized on to a membrane by Southern blot. After that, these fragments can hybridize with the radio-labeled DNA probes containing minisatellite. Oligonucleotide sequences can also be used as probes, and they may directly hybridize to the DNA fragments on the gel. Moreover, the size of the restriction fragments differs depending on the number of repeats of minisatellites, which is unique to an individual. Therefore, the visualization of the fragments allows the identification of the individual.
How many STRs can be detected in a single capillary electrophoresis?
Then, gel electrophoresis or capillary electrophoresis separates the resulting fragments. Generally, it is possible to analyze up to 30 STRs in a single capillary electrophoresis injection. Although the number of their alleles is very small, STRs are highly polymorphic.
What is PCR used for?
PCR is one of the main techniques used in both methods. Both methods can use biological samples such as blood, hair, semen, etc. for the extraction of DNA.
How much DNA is needed for RFLP?
Thus, RFLP analysis is one of the main techniques used in DNA fingerprinting. RFLP analysis requires a large amount of DNA, generally more than 25 ng , and this DNA must be fairly intact.
What is the difference between DNA fingerprinting and gene sequencing?
The difference between gene sequencing and DNA fingerprinting is that gene sequencing focuses on finding the exact nucleotide order of the gene while DNA fingerprinting focuses on confirmation of the identity of individuals in forensic studies.
What is DNA sequencing?
Sequencing of DNA is an important technique in molecular genetics where the nucleotide sequence of a particular DNA sequence or the whole genome of an organism is determined. This enables the researcher or the diagnostician to determine the mutations of DNA sequences and to distinguish one organism from another based on their genetic composition. Gene sequencing is the sequencing procedure of a gene or a DNA fragment via Sanger sequencing or Next generation sequencing. DNA fingerprinting involves a technique known as Restriction Fragment length polymorphism ( RFLP ), where DNA samples of two or more subjects are fragmented and analyzed to determine the identity of a person. This is the key difference between gene sequencing and DNA fingerprinting.
Why is DNA fingerprinting used in forensic investigations?
DNA fingerprinting is used in forensic investigations to derive conclusions about the identity of a suspect.
What is the purpose of sequencing a gene?
Gene sequencing is done to determine the nucleotide sequence of a particular gene. If the whole genome is sequenced, it is referred to as Whole Genome sequencing. Initially, gene sequencing was done using chemical methods which used harmful chemicals such as Pyridine; this technique was soon discontinued due to the toxic nature of the experiment.
Why is gene sequencing important?
Gene sequencing is mainly used to determine the sequence of a novel gene or to analyze mutations of a gene present in diseased states and to confirm the genetic basis of diseases.
What is DNA fingerprinting?
DNA fingerprinting is a technique mainly used in forensic studies to confirm the identity of a person involved in a forensic investigation. In early days, DNA fingerprinting was done using a hybridization technique using fluorescent or radio labeled markers. At present, DNA fingerprinting is done using the technique RFLP.
What is the difference between microscale and rapid sequencing?
Microscale – reactions are tiny, and many can be done at once on a chip. Rapid – since reactions are done in parallel , results are ready much faster. Shorter length – reads typically range from 505050 -700700700 nucleotides in length. Gene sequencing is mainly used to determine the sequence of a novel gene or to analyze mutations ...