
What is the difference between dorsal root and dorsal rami
Mandible
The mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human face. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull.
What is the difference between dorsal and ventral?
• Dorsal is the backside while ventral is the opposite of backside. • When a particular organ (A) is ventral to another (B), the organ-B lies dorsal to the organ-A. • Ventral side bears more external organs than the dorsal side usually does. • Usually, the dorsal side is hardy while the ventral side is tender.
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral roots?
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral roots? Each spinal nerve is formed by the combination of nerve fibers from the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord. The dorsal roots carry afferent sensory axons, while the ventral roots carry efferent motor axons. How many dorsal root ganglion are there?
What are the dorsal and ventral rami of spinal nerves?
The spinal nerves connect to the spine via dorsal and ventral roots. The dorsal root contains sensory input and the ventral root contains motor output. They then combine and further bifurcate into dorsal and ventral rami that include both sensory and motor information before projecting towards the peripheral tissues they innervate.
What does the dorsal rami of the spinal nerves serve?
Spinal Nerve Innervation The dorsal ramus contains nerves that serve the dorsal portions of the trunk; it carries visceral motor, somatic motor, and somatic sensory information to and from the skin and muscles of the back (epaxial muscles). Popular
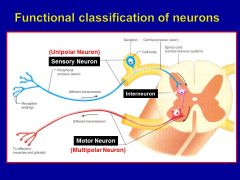
Is dorsal root the same as dorsal rami?
Dorsal primary rami and ventral primary rami are NOT the same as dorsal roots and ventral roots! Think of the spinal nerve as the trunk of a tree - the word ramus means branch in Latin, so the primary rami are the branches of a spinal nerve, whereas the roots unite to form the spinal nerve.
What are dorsal rami?
The dorsal ramus: Contains nerves that serve the dorsal portions of the trunk carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information to and from the skin and muscles of the back.
Are dorsal and posterior rami the same?
The posterior ramus of spinal nerve (or posterior primary division) refers to the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The ramus is also known by a number of other names, “posterior (or dorsal) rami (or branches or divisions) of the spinal nerves”.
What is the dorsal root?
the sensory root of a spinal nerve, which carries sensory information to the spinal cord and enters the posterior side of the cord.
What does dorsal rami innervate?
All dorsal rami (with the exception of those from C1, S4, S5, and Coc1) have medial and lateral branches, which innervate deep back muscles and overlying skin.
What are Rami in nerves?
rami) (Latin for branch) is the anterior division of a spinal nerve. The ventral rami supply the antero-lateral parts of the trunk and the limbs. They are mainly larger than the dorsal rami. Ventral ramus. The formation of the spinal nerve from the dorsal and ventral roots.
What does Rami mean in anatomy?
a branchRamus: In anatomy, a branch, such as a branch of a blood vessel or nerve. For example, the ramus acetabularis arteriae circumflexae femoris medialis is the branch of an artery that goes to the socket of the hip joint. The plural of ramus is rami.
Which function is controlled by dorsal root?
The dorsal nerve root[3]: Controls pain (nociception) and temperature sensations.
What are the dorsal and ventral rami?
Dorsal (posterior), which carries sensory fibers. Ventral (anterior), which carries motor fibers. Rami - originate from mixed spinal nerve, so they carry motor and sensory fibers.
What nerves are found in the dorsal root?
The dorsal root ganglia contain the cell bodies of afferent nerve fibres (those carrying impulses toward the central nervous system); efferent neurons (carrying motor impulses away from the central nervous system) are present in the ventral root ganglia.
Where is the dorsal root located?
The dorsal root ganglia (DRG) are a collection of cell bodies of the afferent sensory fibers, which lie between adjacent vertebrae.
Where is the dorsal nerve root?
the spinal cordThe dorsal root of spinal nerve (or posterior root of spinal nerve or sensory root) is one of two "roots" which emerge from the spinal cord. It emerges directly from the spinal cord, and travels to the dorsal root ganglion.
What are Rami anatomy?
Two vertical portions (rami) form movable hinge joints on either side of the head, articulating with the glenoid cavity of the temporal bone of the skull. The rami also provide attachment for muscles important in chewing.
What are the anterior Rami?
One of the primary branches of a spinal nerve that supplies the lateral and ventral portions of the body wall, limbs, and perineum. See also: ramus.
What are the 4 plexuses of spinal nerves?
Spinal PlexusesCervical Plexus—Serves the Head, Neck and Shoulders. ... Brachial Plexus—Serves the Chest, Shoulders, Arms and Hands. ... Lumbar Plexus—Serves the Back, Abdomen, Groin, Thighs, Knees, and Calves. ... Sacral Plexus—Serves the Pelvis, Buttocks, Genitals, Thighs, Calves, and Feet.More items...•
What is the function of the posterior ramus quizlet?
Spinal nerves trifurcate into a posterior ramus, which collects sensory information from the back; an anterior ramus, which collects sensory information from the body wall and limbs; and the rami communicantes, which collect information from the viscera.
What is the difference between root and Ramus?
What is the difference between Dorsal and Ventral roots and ramus? The roots form a spinal nerve, the ramus are branches of the roots. What do the ventral rami form of a spinal nerve from C1 to T1? What do the ventral rami form of a spinal nerve from T1 to T12?
What are the dorsal roots?
Medical Definition of dorsal root : the one of the two roots of a spinal nerve that passes posteriorly to the spinal cord separating the posterior and lateral funiculi and that consists of sensory fibers. — called also posterior root.
What is a Rami?
Ramus: In anatomy, a branch, such as a branch of a blood vessel or nerve. For example, the ramus acetabularis arteriae circumflexae femoris medialis is the branch of an artery that goes to the socket of the hip joint. The plural of ramus is rami.
What is the difference between anterior rami and posterior Rami?
Generally speaking, the anterior/ventral ramus innervates the skin and muscle on the anterior aspect of the trunk, while the posterior/dorsal ramus innervates the post-vertebral muscles and the skin of the back.
What are the dorsal and ventral roots?
Each spinal nerve is attached to the spinal cord through the dorsal (sensory) root and ventral (motor) root. Both the spinal nerve roots join to form the trunk of spinal nerve which then divide into dorsal and ventral primary rami.
Do dorsal rami form plexuses?
The dorsal ramus: Contains nerves that serve the dorsal portions of the trunk carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information to and from the skin and muscles of the back. … Some ventral rami merge with adjacent ventral rami to form a nerve plexus, a network of interconnecting nerves.
What is spiral cord?
A column of nerve tissue that runs from the base of the skull down the center of the back. It is covered by three thin layers of protective tissue called membranes. The spinal cord and membranes are surrounded by the vertebrae (back bones).
Are Rami the same as roots?
Spinal roots carry sensory (dorsal root) or motor (ventral root) neurons, whereas the spinal nerves and rami contain a mixture of sensory and motor neurons. The dorsal rami seg-mentally innervate deep back muscles (motor) and the skin of the back (sensory).
What is a dorsal ramus?
dorsal ramus: The posterior (or dorsal) branches (or divisions) of the spinal nerves are, as a rule, smaller than the anterior divisions. They are also referred to as the dorsal rami.
What is another name for dorsal root?
The dorsal root of spinal nerve (or posterior root of spinal nerve or sensory root) is one of two "roots" which emerge from the spinal cord.
What is the difference between dorsal and ventral rami?
The dorsal and ventral rami contain nerves that provide visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information, with the dorsal ramus feeding the dorsal trunk (skin and muscles of the back), and the ventral ramus feeding the ventral trunk and limbs through the ventrolateral surface.
What is a short mixed spinal nerve?
Short mixed spinal nerves are formed when a pair of dorsal roots and ventral roots unites beyond the dorsal root ganglion.
What is the ventral root rami?
The ventral root rami are essentially extensions of the anterior horn motor neurons, and innervate the muscles of the cervical, brachial, or lumbosacral plexus.
Where are the dorsal root rami located?
The dorsal root rami are the central processes of the unipolar cells located in the dorsal root ganglion.
Where are nerve roots located?
Nerve roots are attached to each segment of the spinal cord.
What is the name of the spinal cord that floats in the CSF?
Because the cauda equina floats in the CSF, a needle introduced into the subarachnoid space will displace the roots with little possibility of puncture damage.
How many spinal nerves are there?
The 31 pairs of spinal nerves formed by the dorsal and ventral roots are organized as follows: Eight cervical spinal nerves. The first seven cervical spinal nerves, C1-C7, exit the vertebral canal superior to each respective cervical vertebra. The last cervical nerve, C8, exits inferior to the seventh cervical vertebra.
Why do nerve roots follow an oblique course?
As a result of unequal growth between the vertebral canal and the spinal cord ( the vertebral canal is longer than the spinal cord in adults), the nerve roots follow an oblique course from superior to inferior (Figure 1-7A). Only in the cervical region are the segments of the spinal cord at the same level with the corresponding cervical vertebrae.
What is the dorsal root ganglion?
The dorsal root ganglion is a swelling in the dorsal root and houses the cell bodies of all sensory neurons entering the spinal cord for that specific body segment. Ventral roots convey motor (efferent) information away from the spinal cord to the body tissues (i.e., spinal cord to the biceps brachii muscle).
Which section of the vertebral canal shows the spinal roots?
Figure 1-7: A. Coronal section of the vertebral canal from the posterior view. B. Cross-section through the back showing spinal roots, nerves, and rami. Spinal nerves branch into a posterior ramus (mixed), which transports sensory neurons from the skin of the back to the spinal cord and motor neurons from the spinal cord to the erector spinae muscles. C. Caudal end of the vertebral canal revealing spinal roots forming the cauda equina before exiting the vertebral canal through the intervertebral and sacral foramina.
Which spinal nerve exits inferior to the seventh cervical vertebra?
The last cervical nerve, C8, exits inferior to the seventh cervical vertebra. All of the remaining spinal nerves segmentally exit the spinal cord inferior to their respective vertebra, as follows: Twelve thoracic spinal nerves. Exit inferior to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. Five lumbar spinal nerves.
Which region of the spinal cord is the same as the cervical spine?
Only in the cervical region are the segments of the spinal cord at the same level with the corresponding cervical vertebrae. Inferior to the cervical region, each spinal nerve from the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spinal cord segments exits inferior to its similarly numbered vertebra. Dorsal roots convey sensory (afferent) information ...
