Valine
Valine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must b…
Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it. It is also an excitatory neurotransmitter, in fact the most abundant one, in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the p…
Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it. It is also an excitatory neurotransmitter, in fact the most abundant one, in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the p…
What is the difference between valine and glutamic acid side chains?
Valine's side chain is made up entirely of carbon and hydrogen, while glutamic acid's side chain has oxygen in it as well, and is acidic. The major differences between valine and glutamic acid side chains mean they behave very differently in protein.
What is the replacement for glutamic acid in sickle cell anemia?
In sickle cell anemia, there is a replacement in the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin of glutamic acid by valine. What is the difference between glutamic acid and valine? a. Glutamic acid has a lower pH than valine, so the resulting protein is more acidic.
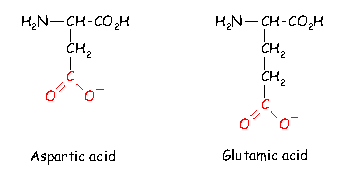
What is the ratio of C to O in glutamic acid?
It contains only C, H, and O atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio. d. It is a monosaccharide a In sickle cell anemia, there is a replacement in the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin of glutamic acid by valine. What is the difference between glutamic acid and valine? a.
What is the difference between glutamic acid and valine quizlet?
Glutamic acid is hydrophilic so it spreads out to increase the amount of surface area exposed to water whereas the valine is hydrophobic so it folds inward to avoid contact with water. Since the polypeptide is a chain of amino acids, when valine folds inward, it brings the other amino acids inward with it.
Why does glutamic acid to valine cause sickle cell?
Sickle cell anemia is caused by homozygous sickle mutation (Hb SS). The sickle mutation causes substitution of a valine for glutamic acid as the seventh amino acid of the beta globin chain. The resulting hemoglobin tetramer (alpha2/betaS2) is poorly soluble when deoxygenated.
What is the important chemical difference between glutamate and valine?
Valine's side chain is made up entirely of carbon and hydrogen, while glutamic acid's side chain has oxygen in it as well, and is acidic. The major differences between valine and glutamic acid side chains mean they behave very differently in protein.
Does glutamic acid have a lower pH than valine?
The R groups between the amino acids are different. D. Glutamic acid has a lower pH than valine, so the resulting protein is more acidic.
What happens when valine replaces glutamic acid?
Sickle cell hemoglobin (HbS) is caused by a mutation that replaces glutamic acid at residue 6 in β-globin with valine (β6 Glu → Val). This amino acid substitution leads to the formation of linear polymers of deoxygenated HbS.
What happens when glutamic acid is replaced by valine?
The sickle cell disease occurs when the sixth amino acid, glutamic acid is replaced by valine to change is structure and function.
Why is glutamic acid so important?
Glutamic acid is an amino acid used to form proteins. In the body it turns into glutamate. This is a chemical that helps nerve cells in the brain send and receive information from other cells. It may be involved in learning and memory.
Is glutamic acid replaced by valine in sickle cell anemia?
In sickle cell anaemia, glutamic acid is replaced by valine.
Why glutamic acid is acidic?
Two amino acids have acidic side chains at neutral pH. These are aspartic acid or aspartate (Asp) and glutamic acid or glutamate (Glu). Their side chains have carboxylic acid groups whose pKa's are low enough to lose protons, becoming negatively charged in the process.
Which is the most acidic amino acid?
In all the given amino acids, only the glutamic acid is one which has two carboxylic groups and one amine group, so it is the acidic amino acid.
Is glutamic acid basic or acidic?
Exercise 18.2. 1Amino AcidClassificationpIhistidinepositively charged (basic)7.6lysinepositively charged (basic)9.8aspartic acidnegatively charged (acidic)3.0glutamic acidnegatively charged (acidic)3.25 more rows•Aug 13, 2022
Is glutamic acid positive or negative?
Among the 20 common amino acids, five have a side chain which can be charged. At pH=7, two are negative charged: aspartic acid (Asp, D) and glutamic acid (Glu, E) (acidic side chains), and three are positive charged: lysine (Lys, K), arginine (Arg, R) and histidine (His, H) (basic side chains).
How does the substitute of valine for glutamic acid affect the shape of hemoglobin?
The substitution is a switch from this glutamate to valine. This alteration causes hemoglobin molecules to clump, as reflected in a change in the shape of the red blood cells, which have a distorted, sickle shape.
What is the mutation that causes sickle-cell anemia?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in both copies of a person's HBB gene. This gene encodes a component of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. The mutation causes hemoglobin molecules to stick together, creating sickle-shaped red blood cells.
Why does acidosis cause sickling?
The root cause of this pathology is the synthesis of an abnormal Hb (HbS) that polymerizes in deoxygenated conditions, leading to the sickling of red blood cells. Acidosis is well recognized as a promoter of HbS polymerization and therefore red blood cell sickling.
What type of point mutation causes sickle-cell anemia?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a monogenetic disorder due to a single base-pair point mutation in the β-globin gene resulting in the substitution of the amino acid valine for glutamic acid in the β-globin chain.
What are the differences between amino acids?
Valine's side chain is made up entirely of carbon and hydrogen, while glutamic acid's side chain has oxygen in it as well, and is acidic. The major differences between valine and glutamic acid side chains mean they behave very differently in protein.
What are the two amino acids that are the building blocks of protein?
View Work. DNA mutations lead to substitutions. Valine and glutamic acid are amino acids with very different structures and properties. They are both building blocks of protein, and sometimes mutations in your DNA can cause substitution of one for the other.
What is the cause of sickle cell anemia?
Sickle Cell Anemia. Sickle cell anemia is caused by the substitution of valine for glutamic acid. Chemist Linus Pauling first determined that it was the result of a mutation in the hemoglobin protein. Hemoglobin carries oxygen from your lungs to your tissues; if there's a mutation in the DNA that codes for the protein, ...
Is valine a substitution for glutamic acid?
Some substitutions in proteins don't make much of a difference in terms of function -- this is most likely to be true when one amino acid is substituted with a very similar one -- but the substitution of valine for glutamic acid is very serious, because of their very different properties. Proteins are held into a three-dimensional shape ...
Does glutamic acid stick to amino acids?
Glutamic acid has a negative charge that allows it to stick to positively charged amino acids, holding the protein's shape. Valine can't stick to positively charged amino acids, so a protein with this substitution won't be shaped correctly. Advertisement.
What are the benefits of valine?
Valine, an essential amino acid, is hydrophobic and, as expected, can be found in the interiors of proteins. Valine differs from threonine in that the hydroxyl group is replaced with a methyl substituent.
Why do different amino acid properties differ?
Proteins act as structural support within the cell and are involved in a variety of chemical reactions. Each protein is made up of a variety of combinations of 20 smaller, simpler amino acids.
What happens when glutamic acid is replaced with valine?
The underlying problem is that in the sixth position of haemoglobin’s -chain, glutamic acid is replaced by valine. As a result, haemoglobin S is formed. When oxygen tension is reduced, the haemoglobin S molecules polymerize and form a crescent-shaped deformity in the red cells.
What are the three amino acid properties that are used to classify them?
The three properties of side chains used to classify amino acids are nonpolar, polar, and electrically charged.
What are the health benefits of glutamic acid?
Glutamic acid has the ability to treat: personality and childhood behavioral issues. Support for epilepsy and muscular dystrophy treatment. Treat cognition disorders.
When the protein hemoglobin A replaces glutamic acid with valine?
The abnormal sickle cell hemoglobin protein (HbS) -globin chain mutation revealed a mutation in which glutamic acid is replaced by a valine (6GluVal) chain in 1949. The pathophysiological mechanism, which was based on the abnormal polymerization of deoxy-HbS, emerged as a result of this discovery.
What are the characteristics of amino acids in general?
Physical and chemical properties of amino acids Amino acids are a colorless, crystalline substance that has both physical and chemical properties. The majority of amino acids are flavorless, but some are sweet.
What's the difference between glutamic acid and valine?
Question: In sickle cell anemia, there is a replacement in the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin of glutamic acid by valine. What is the difference between glutamic acid and valine? ... Glutamic acid has a lower pH than valine, so the resulting protein is more acidic.
What happens when valine replaces glutamic acid?
Sickle cell anemia results from the single amino acid substitution of valine for glutamic acid in the beta-chain owing to a nucleotide defect that causes the production of abnormal beta-chains in hemoglobin S.
Is valine replaced by glutamic acid?
Accordingly, the sixth amino acid (glutamic acid, negatively charged) is replaced by valine, hydrophobic. A hydrophobic site is present on the outside of the HbS β chain. This incurs a hydrophobic bond with the phenylalanine in position 85 and leucine in position 88, in which outsource deoxy haemoglobin.
Is glutamic acid good for you?
Glutamic acid is generally free of side effects for the vast majority of people who take it; however, people with kidney or liver disease should not consume high intakes of amino acids without consulting a healthcare professional.
Which is more acidic, glutamic acid or valine?
Glutamic acid has a lower pH than valine, so the resulting protein is more acidic.
What amino acid is used in sickle cell anemia?
In sickle cell anemia, there is a replacement in the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin of glutamic acid by valine. What is the difference between glutamic acid and valine?