What are Howell-Jolly bodies and Heinz bodies?
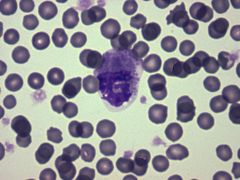
Heinz bodies. Howell jolly bodies. Inclusions within red blood cells composed of denatured hemoglobin. They are formed as a result of oxidative damage or mutations (i.e G6PD) Macrophages in the spleen remove the denatured hemoglobin giving rise to the classic “bite cells” (see below) Nuclear (basophilic) inclusions within RBCs.
What is a Howell Jolly body?
Jan 09, 2022 · Howell jolly bodies: Heinz bodies: Nuclear (basophilic) inclusions within red blood cells; Normally: During maturation, after leaving the bone marrow, the erythroblast nuclei are expelled into the spleen. Although, in patients, without a spleen (asplenia) secondary to (i.e. surgery, radiation, or sickle cell anaemia) they will retain these remnants
How are Jolly bodies formed?
Oct 02, 2014 · Howell-Jolly bodies are little fragments of the red cell nucleus. You see them most commonly in patients with splenectomies (normally, the spleen just bites them out). You can see them without a special stain – they look like dark, round dots. Heinz bodies are seen in G6PD deficiency. They represent denatured globin chains.
What does a Heinz body look like?
Jan 25, 2022 · What Is The Difference Between Howell Jolly Bodies And Heinz Bodies? Despite the fact that both physiques are available on red bloodstream cells, Heinz physiques won’t be the same as Howell-Jolly physiques.When red bloodstream cells are finished maturing within the bone marrow, they are able to go into the circulation to start supplying oxygen towards the body.

How can you tell the difference between Howell-Jolly bodies and pappenheimer bodies?
Howell-Jolly bodies are fragments of DNA and typically seen in the peripheral smears of individuals with sickle cell disease following auto-splenectomy. A nucleated RBC is also present in this view. Pappenheimer bodies are abnormal granules of iron found inside red blood cells on a routine blood stain.Mar 17, 2014
What is a Heinz body?
Heinz bodies are indicative of oxidative injury to the erythrocyte. They are clumps of irreversibly denatured hemoglobin attached to the erythrocyte cell membrane.Jul 26, 2021
What do Howell-Jolly bodies indicate?
Howell-Jolly bodies are pathognomonic for splenic dysfunction. The nuclear remnants do not have a specific function or role. However, they only act as a clue to an underlying pathological process. Howell-Jolly bodies are one of many types of inclusions found in circulating erythrocytes.Apr 27, 2021
What are Heinz bodies in G6PD?
Heinz bodies are denatured hemoglobin, which occurs in G6PD deficiencies and in unstable hemoglobin disorders. Abdominal ultrasound may be useful in assessing for splenomegaly and gallstones. These complications are typically limited to patients with severe chronic hemolysis.Jul 19, 2021
What does a Heinz body look like?
Heinz bodies appear as small round inclusions within the red cell body, though they are not visible when stained with Romanowsky dyes. They are visualized more clearly with supravital staining (e.g., with new methylene blue, crystal violet or bromocresol green).
What stain is used for Heinz body?
New methylene blue (NMB) stains Heinz bodies dark blue, making them easier to identify on a blood smear.
When do you see Howell-Jolly bodies?
Howell-Jolly bodies are remnants of RBC nuclei that are normally removed by the spleen. Thus, they are seen in patients who have undergone splenectomy (as in this case) or who have functional asplenia (eg, from sickle cell disease). Target cells (arrows) are another consequence of splenectomy.
What causes Howell-Jolly bodies in dogs?
Presence of Howell-Jolly bodies in dogs and cattle, or excessive numbers in cats and horses, can be associated with: regenerative anemia, impaired splenic function (ie. splenectomy, corticosteroids), and erythroid dysplasias. Howell-Jolly bodies. Canine.Jan 8, 2018
Why are Howell-Jolly bodies seen in megaloblastic anemia?
The formation of numerous Howell-Jolly bodies occurs as a dyserythropoietic feature observed in megaloblastic anemia. In the absence of a spleen, these red cell inclusions are not removed and they become very prominent in the blood film.Apr 25, 2014
What is the difference between Howell-Jolly bodies and pappenheimer bodies?
Howell-Jolly bodies are fragments of DNA and typically seen in the peripheral smears of individuals with sickle cell disease following auto-splenectomy. Pappenheimer bodies are abnormal granules of iron found inside red blood cells on a routine blood stain.
What is a Heinz body?
Heinz bodies are indicative of oxidative injury to the erythrocyte. They are clumps of irreversibly denatured hemoglobin attached to the erythrocyte cell membrane.
What do Howell-Jolly bodies indicate?
A Howell–Jolly body is a cytopathological finding of basophilic nuclear remnants (clusters of DNA) in circulating erythrocytes. During maturation in the bone marrow, late erythroblasts normally expel their nuclei; but, in some cases, a small portion of DNA remains.
How do I identify my Howell-Jolly body?
Howell-Jolly bodies occur where there is no spleen or an non-functioning spleen, referred to as asplenia. They are usually one of these at most in a red cell, round, dark purple to red in color and often located peripherally on the red blood cell.
When do you see Heinz bodies?
The presence of Heinz bodies on a blood smear test indicates oxidative damage to the hemoglobin in red blood cells. Conditions associated with Heinz bodies include certain blood conditions, such as thalassemia or hemolytic anemia.
What are pappenheimer bodies indicative of?
Pappenheimer bodies are seen in certain types of anemia that are characterized by an increase in the storage of iron, such as sideroblastic anemia and thalassemia. These inclusions are also seen in the peripheral blood following a splenectomy.
What does a Heinz body look like?
Heinz bodies appear as small round inclusions within the red cell body, though they are not visible when stained with Romanowsky dyes. They are visualized more clearly with supravital staining (e.g., with new methylene blue, crystal violet or bromocresol green).
What do Howell-Jolly bodies indicate?
A Howell–Jolly body is a cytopathological finding of basophilic nuclear remnants (clusters of DNA) in circulating erythrocytes. During maturation in the bone marrow, late erythroblasts normally expel their nuclei; but, in some cases, a small portion of DNA remains.
What diseases cause Howell-Jolly bodies?
Howell-Jolly bodies persist in those with functional hyposplenia or asplenia:
What are Howell-Jolly bodies composed of?
Howell-Jolly bodies are thought to be nuclear remnants or aggregates of chromosomes that have separated from the mitotic spindle and remain behind after the remainder of the RBC nucleus is expelled.
What do pappenheimer bodies indicate?
Pappenheimer bodies are seen in certain types of anemia that are characterized by an increase in the storage of iron, such as sideroblastic anemia and thalassemia. These inclusions are also seen in the peripheral blood following a splenectomy.
What causes Stomatocytosis?
Most cases of stomatocytosis are due to alteration in permeability, leading to an increase in red cell volume. Stomatocytes form at a low blood acidic pH, as seen in exposure to cationic detergents and in patients receiving phenolthiazine or chlorpromazine. Stomatocytosis can be an inherited or acquired condition.
Why are Howell-Jolly bodies seen in megaloblastic anemia?
The formation of numerous Howell-Jolly bodies occurs as a dyserythropoietic feature observed in megaloblastic anemia. In the absence of a spleen, these red cell inclusions are not removed and they become very prominent in the blood film.
What is the difference between Howell-Jolly bodies and Heinz bodies?
Even though both bodies can be found on red blood cells, Heinz bodies are not the same as Howell-Jolly bodies. When red blood cells are finished maturing in the bone marrow, they can enter the circulation to begin providing oxygen to the body. As they enter the circulation, they discard their nucleus.
What is a Heinz-Erlich body?
Symptoms. Treatment. Vs. Howell-Jolly bodies. Takeaway. Heinz bodies, first discovered by Dr. Robert Heinz in 1890 and otherwise known as Heinz-Erlich bodies, are clumps of damaged hemoglobin located on red blood cells. When hemoglobin becomes damaged, it can cause your red blood cells to stop working properly.
What disorders are associated with Heinz bodies?
While Heinz bodies have been studied in both humans and animals, in humans they’re associated with a handful of red blood cell disorders, including: thalassemia. hemolytic anemia. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency.
What does it mean when you see Heinz bodies on a blood smear?
The presence of Heinz bodies on a blood smear test indicates oxidative damage to the hemoglobin in red blood cells. Conditions associated with Heinz bodies include certain blood conditions, such as thalassemia or hemolytic anemia. Heinz bodies may also be associated with the ingestion of or exposure to toxic substances.
Why do Heinz bodies have anemia?
Heinz bodies can also be caused by exposure to certain toxic elements. In an early case study. Trusted Source. from 1984, a patient experienced Heinz-body hemolytic anemia after ingesting a petroleum-based oil containing cresol.
Can Heinz bodies be produced in humans?
Although exposure to toxic wild plants is a cause of Heinz bodies primarily in animals, certain medications can also cause the production of Heinz bodies in humans. Medications that may cause Heinz bodies are used to treat a variety of conditions, such as psychosis and methemoglobinemia.
Can Heinz bodies show up on lab results?
Other conditions mentioned above can cause Heinz bodies to show up on lab test results, even without hemolytic anemia .
Is Heinz the same as Howell-Jolly?
Even though both bodies can be found on red blood cells, Heinz bodies are not the same as Howell-Jolly bodies. When red blood cells are finished maturing in the bone marrow, they can enter the circulation to begin providing oxygen to the body. As they enter the circulation, they discard their nucleus.