
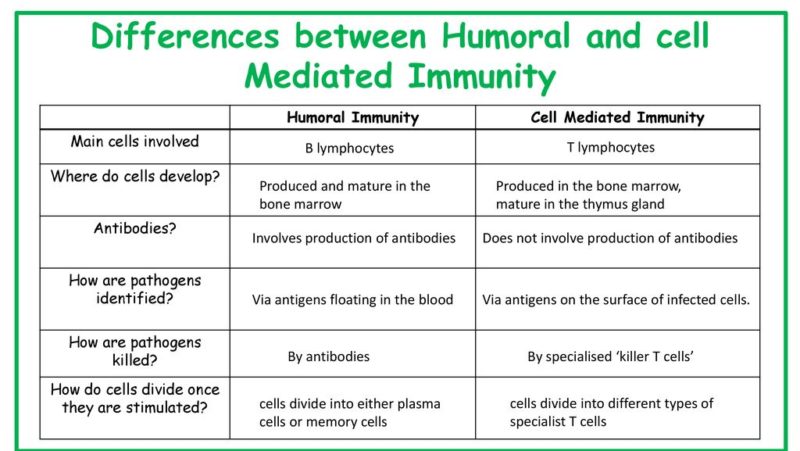
- The cell-mediated immune response is mediated by T-cells. The humoral immune response is mediated by antibodies (produced by B-cells).
- Antibodies are not formed in cell-mediated immune response. Antibodies are formed in humoral immune response.
- Receptors are used in cell-mediated immunity to detect antigens. ...
Full Answer
What do cells carry out the humoral immune response?
Humoral Immunity is the arm of the Adaptive Immune Response which results in the release of antigen-specific Antibodies that target an invading microbe. This response is largely carried out by B-cells but requires the help of CD4+ T-cells and thus in part depends on successful Cell-mediated Immunity.Here we outline the steps of Humoral Immunity and organize this section according to the "Basic ...
What is cell mediated responses attacks?
The cell-mediated immune system is the host’s primary response against invasive bacteria and viruses that cause intracellular infections. It is also essential for fighting against and destroying cancer cells. Furthermore, the cell-mediated immune system plays a role in the rejection of organ transplants or graft tissue.
What is the mechanism of cell mediated immunity?
The mechanism of cell mediated immunity includes: (1) Activation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes that is able to induce apoptosis in body cells displaying epitopes of foreign antigen on their surface such as cells with intracellular bacteria, virus-infected cells and cancer cells displaying tumor antigens.
What do plasma cells become in humoral response?
The humoral immune response is mediated by antibody molecules that are secreted by plasma cells. Antigen that binds to the B-cell antigen receptor signals B cells and is, at the same time, internalized and processed into peptides that activate armed

1. What is Active Immunity?
The immunity is defined as the production of antibodies by the immune system in response to the presence of an antigen. Active immunity in the huma...
2. What is the Primary Function of Humoral Immunity and Cell-Mediated Immunity?
The main function of humoral, or antibody-mediated, immunity is to control freely circulating pathogens. Pathogens that travel through the body via...
3. How can the PDF of the difference between Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity help?
The free pdf of Difference between Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity from Vedantu can help students to know the biology subject and topic thorough...
4. What is Humoral Immunity?
The adaptive immunity process is described as humoral immunity. It is manifested by the production of antibodies by B lymphocytes. Humoral immunity...
5. Is the Difference between Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity an important part of NEET?
Yes, the Difference between Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity is an important chapter and topic to study for the main medical entrance examination...
Humoral immunity
When foreign material - antigens - is recognized in the body, the body responds with an antibody-mediated reaction. Extracellular intruders, such as bacteria, are commonly found in this foreign material. B cell lymphocytes, a type of immune cell that makes antibodies after detecting a specific antigen, are principally responsible for this method.
Cell-mediated immunity
Cell-mediated immunity, unlike humoral immunity, does not rely on antibodies to perform adaptive immunological activities. Mature T cells, macrophages, and the production of cytokines in response to an antigen are the main drivers of cell-mediated immunity.
Humoral vs cell-mediated
B cells activate humoral immunity, whereas T cells activate cell-mediated immunity. The major difference between humoral and cell-mediated immunity is that humoral immunity produces antigen-specific antibodies, whereas cell-mediated immunity does not. T lymphocytes, on the other hand, kill infected cells by triggering apoptosis.
Significance of humoral and cell-mediated immune response
T-cell responses, which are part of cell-mediated immunity, play a vital role in controlling viral infections. T-cells do this through developing effector activities such as the generation of chemokines and cytokines, which can have direct and indirect antiviral effects, as well as assisting in the overall immune response regulation.
References
Dornell, J. (2021). Humoral vs Cell-mediated Immunity. [online] Technology Networks (Immunology and Microbiology). Available at: https://www.technologynetworks.com/immunology/articles/humoral-vs-cell-mediated-immunity-344829
Further Reading
What is the difference Between a Phagocyte, Macrophage, Neutrophil and Eosinophil?
What is the difference between a humoral and a cell-mediated immunity?
Humoral immunity secretes antibodies to fight against antigens, whereas cell-mediated immunity secretes cytokines and no antibodies to attack the pathogens. The Humoral immunity is rapid or quick in their action against antigens, while the Cell-mediated immunity show delay though permanent action against any pathogens.
What is humoral immunity?
Humoral immunity is known for working against extracellular pathogens. 1. Cell-mediated immunity is related to T-lymphocytes, which work by identifying viruses and microorganisms,thus destroying them by the cell lysis or phagocytosis or pinocytosis. 2. It is known for working against intracellular pathogens.
What is the role of B cells in the immune system?
Humoral immune response or antibody-mediated response is associated with the B cells, where the role of these cells (B cells) is to identify the antigens or any foreign particle that are present in the circulation in blood or lymph.
How do T cells produce antigens?
This following points can explain the eventual process: 1 Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) will display the antigens present on its surface and binds to T cells. 2 Interleukins (secreted by helper T cells) facilitates the activation of T cells. 3 Along with the MHC-I and the endogenous antigens, the T cells proliferate and produce the cytotoxic T cells. 4 The T cells destroy the infected cells exhibiting antigens. 5 In case of exogenous antigens and MHC-II displayed on the plasma membrane together, the T cells trigger to proliferate helper T cells which release interleukins and cytokines and also arouse the B cells to produce antibodies against them. This process is also supported by the natural killer cells (NK) and macrophages, which destroys the antigens.
What is the immune system?
The immune system has complex networks of the molecules, cells and their interactions are designed to eradicate the infectious organisms from the body. Immunity or immune system is divided into two types – innate (non-specific) and acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity.
Which cells are immune to humoral?
Humoral immunity is intimately associated with B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and macrophages, on the contrary, the cell-mediated immunity is associated with T-lymphocytes, helper T cells, natural killer cells, and macrophages. Humoral immunity plays a major role in recognizing antigen or any foreign particle and in producing antibodies against it. ...
Which type of immunity is associated with the B lymphocytes?
The humoral immunity is associated with the B-lymphocytes and is responsible for destroying the pathogens by producing antibodies against it, whereas the cell-mediated immunity is associated with the T-lymphocytes and is responsible for the destroying the pathogens or microorganism which have invaded the cells without producing antibodies.
What is the difference between humoral and cell mediated immunity?
During adaptive immunity, the antigen is first recognized through receptors of the lymphocytes, and immune cell clones are produced to attack that particular antigen. Humoral immunity is triggered by B cells while cell mediated immunity is triggered by T cells. The main difference between humoral and cell mediated immunity is that antigen-specific antibodies are produced in humoral immunity whereas antibodies are not produced in cell mediated immunity. Instead, T cells destroy the infected cells by inducing apoptosis.
Which receptors are involved in humoral immunity?
Humoral Immunity: The BCR receptors are involved in the humoral immunity.
What are the two types of adaptive immunity?
Humoral immunity and cell mediated immunity are two types of adaptive immunity.
What are the two types of antibodies produced by T helper cells?
The IgG and IgM are the main two types of antibodies produced by T helper cells in response to plasma B cells. The memory T cells are differentiated T cells, but their action requires the activation by the specific antigen. The major characteristic feature of the cell mediated immunity is that it destroys intracellular pathogens. The cell mediated immunity is shown in figure 2 .
Which cells secrete antibodies in the humoral immune system?
Humoral Immunity: The plasma B cells secrete antibodies in the humoral immunity.
Which cells are responsible for humoral immunity?
Humoral Immunity: The humoral immunity is mediated by B cells.
Which receptors are the accessory receptors of cell mediated immunity?
Cell Mediated Immunity: The CD2, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD28, and integrins are the accessory receptors of the cell mediated immunity.
What are the similarities between humoral and cell-mediated immunity?
The similarities between humoral and cell-mediated immunity are: 1 Both types of immunity systems are active immunities and have a lag period 2 Both humoral and cell-mediated are active against several types of pathogens. 3 Both immunity systems are not effective in immune-deficient individuals.
What is the function of humoral immunity?
Ans: The primary function of the humoral, or antibody-mediated, immunity is to control freely circulating pathogens. Pathogens which travel across the body through the blood and lymph are destroyed by humoral immunity. The major cells involved in this type of immunity are B-cells, CD4+ T cells and macrophages.
What is the immune system that produces antibodies?
The humoral immune system starts with the production of proactive antibodies against infection or reinfection by common microorganisms such as staphylococci and streptococci. B- Lymphocytes, which have specific antigen receptors react when they come to contact with the specific antigen by producing plasma cells. These plasma cells produce antigen-specific antibodies and memory cells which enable the body to rapidly produce antibodies if the same antigen appears later. The differentiation of B-cells is stimulated by interleukin-2 (IL-2) which is secreted by CD4+ T cells and foreign antigens processed by macrophages.
What is humoral immune activity?
Humoral immune activity is one of the mechanisms of the active immune system and is associated with circulating antibodies in contrast to cellular immunity. The wide range antibody activities is a response to rapid production of antigen-specific B cells during infections which increases antibody titres with enhanced affinity for the inciting agent and more directed and effective response.
What is cell mediated immunity?
Cell-mediated immunity is a type of adaptive immune response that does not involve antibodies but it does involve the activation of NK cell and macrophages and the production of antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and the release of several cytokines in response to a foreign antigen.
What are the major cells involved in the immune system?
The major cells involved in this type of immunity are B-cells, CD4+ T cells and macrophages. As for antibody-mediated immunity, it protects the body which invades cells. The cells involved in this type of immunity are T cells, cytotoxic T-cells, NK cells and macrophages. Share this with your friends. Share.
What is the function of cytokines in the immune system?
The response stimulates the cells to produce a wide range of cytokines that regulates the function of other cells involved in adaptive immune responses and innate immune responses. Cell-mediated immunity is directed primarily towards microbes which survive phagocytes and microbes that infect non-phagocytic cells.
What is the difference between humoral and cell mediated immunity?
The key difference between humoral and cell mediated immunity is that the humoral immunity (antibody-mediated immunity) involves antibodies while the cell mediated immunity does not involve antibodies. Immunity is the ability of an organism to defend against pathogens and toxins and to avoid infections and diseases.
What are the three main mechanisms of humoral immunity?
Thus, B cell activation, B cell proliferation and antigen-antibody interaction are three main mechanisms of humoral immunity.
How does humor immunity work?
Humoral immunity works against specific pathogens outside the cells (extracellular pathogens). B-cells are bone marrow-derived, and each cell makes only one kind of antibody which specifically reacts on a particular pathogen. DNA rearrangement makes sure the antibody diversity. Figure 01: Humoral Immunity.
What is adaptive immunity?
Adaptive immunity is a synonym for specific immunity, which provides pathogen-specific immunity in vertebrates. Moreover, this adaptive immune system basically composes of T-lymphocyte and B-lymphocyte cells. And it is is very special as it is present only in vertebrates, and is able to recognize different foreign antigens in a very precise way. ...
Which cells are responsible for cell mediated immunity?
Cell mediated immunity is mainly facilitated by the T helper cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Each T-cell makes only one kind of T-cell antigen receptor. Thus, the t-cell receptor has four proteins, namely, two large (α) and two small (β) chains. Each chain has constant and variable regions.
Why is the cell-mediated immune system important?
Thus, the cell-mediated immune system is important as it eliminates tumour cells before they can grow and spread very much.
When do both immunity types activate?
Both immunity types activate upon the exposure to foreign antigens.
Which cells are involved in the humoral immune response?
Both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are involved in cell mediated immune response. Only TH cells are involved in humoral immune response.
What is humoral immunity?
Humoral Immunity (antibody-mediated immunity): The Humoral immunity is mediated through antibodies. Antibodies are produced by the B cells. These antibodies bound to specific microbial antigens. Binding of antibodies to antigens neutralize the microbes and target them for elimination by various effector mechanisms.
What are the two main mechanisms of active immunity?
The active immunity is mediated through two distinct mechanisms, and they are named as (1) Cell-mediated immunity and (2) Humoral immunity . These two immune pathways show considerable differences in their components, their targets, and the method of killing of pathogens.
What is the function of T-cell receptors in the immune system?
Antibodies are used in humoral immunity to detect antigens. T-cell receptors binds to the T-cells and then the T-cell themselves binds to the antigen.
Which cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity?
The cell-mediated immunity is facilitated by the activated TH cells (T-Helper cells) and Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs). Cytokines secreted by the TH cells activate the phagocytic cells. These activated phagocytic cells then phagocytosis and kill the microbes. The cell-mediated immunity is particularly important against the bacterial and protozoan pathogens.
Does humoral immunity eliminate tumor cells?
It can eliminate tumor cells and thus can provide immunity against cancer. It cannot eliminate tumor cells. 10. Cell-mediated immune response also participates in the rejection of organ transplants. Humoral immunity may be involved in the early graft rejection due to pre-formed antibodies. 11.
Humoral Immunity
Cell-Mediated Immunity
- Cell-mediated immunity, unlike humoral immunity, does not rely on antibodies to perform adaptive immunological activities. Mature T cells, macrophages, and the production of cytokines in response to an antigen are the main drivers of cell-mediated immunity. To recognize intracellular target antigens, T cells that participate in cell-mediated immunity rely on antigen-presenting cell…
Humoral vs Cell-Mediated
- B cells activate humoral immunity, whereas T cells activate cell-mediated immunity. The major difference between humoral and cell-mediated immunity is that humoral immunity produces antigen-specific antibodies, whereas cell-mediated immunity does not. T lymphocytes, on the other hand, kill infected cells by triggering apoptosis. Humoral immunity de...
Significance of Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immune Response
- T-cell responses, which are part of cell-mediated immunity, play a vital role in controlling viral infections. T-cells do this through developing effector activities such as the generation of chemokines and cytokines, which can have direct and indirect antiviral effects, as well as assisting in the overall immune response regulation. Certain effector T-cells can kill virus-infecte…
References
- Dornell, J. (2021). Humoral vs Cell-mediated Immunity. [online] Technology Networks (Immunology and Microbiology). Available at: https://www.technologynetworks.com/immunology/articles/humoral-vs-ce...
- Pampuria, P., and Lang, L., M. (2018). Regulation of Humoral Immunity by CD1d-Restricted Natural Killer T Cells (Chapter-5). Immunology (Academic Press), pp 55-73. https://doi.org/10…
- Dornell, J. (2021). Humoral vs Cell-mediated Immunity. [online] Technology Networks (Immunology and Microbiology). Available at: https://www.technologynetworks.com/immunology/articles/humoral-vs-ce...
- Pampuria, P., and Lang, L., M. (2018). Regulation of Humoral Immunity by CD1d-Restricted Natural Killer T Cells (Chapter-5). Immunology (Academic Press), pp 55-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12...
- Panawala, L. (2017). Difference Between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity.
- Zajac, A., J. and Harrington, L., E. (2014). Immune Response to Viruses: Cell-Mediated Immunity. Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences, Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.02604-0.
Further Reading