
Who's eligible for Section 504?
To be covered under Section 504, a student must be "qualified " (which roughly equates to being between 3 and 22 years of age , depending on the program, as well as state and federal law, and must have a disability) [34 C.F.R. §104.3 (k) (2)].
Who is protected under Section 504?
Section 504 protects qualified individuals with disabilities. Under this law, individuals with disabilities are defined as persons with a physical or mental impairment which substantially limits one or more major life
What qualifies as a disability under Section 504?
disabilities covered under section 504 The ED Section 504 regulation defines an "individual with handicaps" as any person who (i) has a physical or mental impairment which substantially limits one or more major life activities, (ii) has a record of such an impairment, or (iii) is regarded as having such an impairment.
How does Section 504 affect schools?
When the school determines that a child is eligible for services under Section 504, the school must eliminate barriers to his or her access to full participation in school activities, including the general education curriculum. The school can often eliminate barriers by providing accommodations for a student.
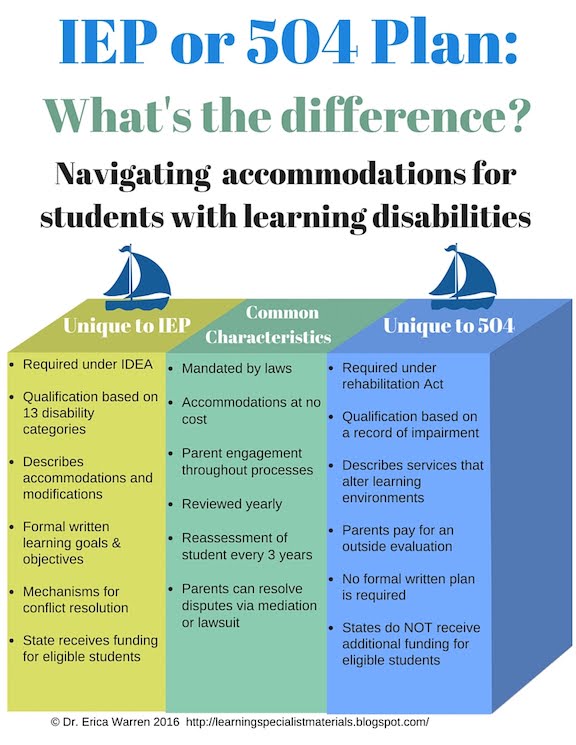
What is the difference between ADA 504 and IDEA?
There are significant differences between Section 504 and IDEA. Perhaps the most significant is that Section 504 is a civil rights law, and IDEA is an educational benefit law. Section 504 is designed to level the playing field for individuals with disabilities.
What is the difference between ADA and IDEA?
Idea Act vs. ADA Act The main difference is that services under IDEA can be obligatory since they are mandated by the federal government in conjunction with the U.S. Department of Education, rather than voluntary under the ADA.
What is the most important difference between IDEA and ADA and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act?
To be eligible for special education under the IDEA, a student must have a categorical disability that results in the student's needing special education. Section 504 and the ADA require that the person have a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more of the person's major life activities.
What do IDEA Section 504 and ADA have in common?
With IDEA, once a student is identified as requiring special education, the school must put together an Individualized Education Program (IEP) to meet that student's specific needs. For the ADA and Section 504, accommodations need to be provided for the student, which may include auxiliary aids such as screen readers.
Why is IDEA and ADA important?
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a law that makes available a free appropriate public education to eligible children with disabilities throughout the nation and ensures special education and related services to those children.
In what way is IDEA and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 alike?
In what way is IDEA and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 alike? They both require placement in the most integrated setting possible.
What are the similarities between an IEP and a 504 plan?
What are the similarities between the two plans? Both plans can provide the student with certain accommodations and modifications to allow a disabled child to be more successful in school.
What is the purpose of Section 504 Rehabilitation Act?
Section 504 forbids organizations and employers from excluding or denying individuals with disabilities an equal opportunity to receive program benefits and services. It defines the rights of individuals with disabilities to participate in, and have access to, program benefits and services.
What is one important difference between of Section 504 and the ADA chapter 6?
Unlike Section 504, the ADA does not have any direct responsibility for providing free and appropriate public education. The ADA does not come up with any specific evaluation or placement procedures. However, Section 504 requires a notice and consent for evaluation process.
Is there a downside to having a 504 plan?
Bad Things About 504 Plans Students have to get labelled with a disability to get at 504 Plan. Some families want to keep disabilities private or disagree their child has a disability. 504 Plans open the door to school disability assessments, which may contain data a parent disagrees with.
Can you get a 504 for anxiety?
Answer: Yes. A student may qualify for a 504 plan if anxiety gets in the way of the student participating at school. The 504 plan aims to remove barriers caused by the anxiety.
What is an example of a 504 plan?
Examples of accommodations in 504 plans include: preferential seating. extended time on tests and assignments. reduced homework or classwork.
How do ADA and IDEA protect the civil rights of individual with disabilities?
The ADA prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability in employment, State and local government, public accommodations, commercial facilities, transportation, and telecommunications. It also applies to the United States Congress.
When was IDEA passed?
It was originally known as the Education of Handicapped Children Act, passed in 1975. In 1990, amendments to the law were passed, effectively changing the name to IDEA. In 1997 and again in 2004, additional amendments were passed to ensure equal access to education.
What is the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 Section 504?
Section 504 forbids organizations and employers from excluding or denying individuals with disabilities an equal opportunity to receive program benefits and services. It defines the rights of individuals with disabilities to participate in, and have access to, program benefits and services.
What is the difference between Idea and Section 504?
The major differences between IDEA and Section 504 are in the flexibility of the procedures. For a child to be identified as eligible for services under Section 504, there are less specific procedural criteria that govern the requirements of the school personnel. Schools may offer a student less assistance and monitoring with Section 504 ...
What is a 504.?
Section 504. Covers individuals who meet the definition of qualified "handicapped" person -- for example, a child who has or has had a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits a major life activity or is regarded as handicapped by others.
How many children with disabilities are in special education?
According to the U.S. Department of Education, approximately 5.5 million children with disabilities receive special education and related services and are protected by IDEA. However, some kids with special needs do not receive services under IDEA, but are served under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Section 504, a civil rights law, prohibits discrimination on the basis of disabling conditions by programs and activities receiving or benefiting from federal financial assistance. This statute does not require the federal government to provide additional funding for students identified with special needs. Schools must provide these children with reasonable accommodations comparable to those provided to their peers under the rulings of Section 504. Although not a financing statute, Section 504 does provide for enforcement of the mandate: A school that is found by the Office of Civil Rights to be out of compliance with Section 504 may lose its federal financing.
What is the idea of the Rehabilitation Act?
IDEA and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 are two federal laws that affect how a child with disabilities is educated. Find out how they differ and which one may apply to your child.
When does a placement need reevaluation?
Requires reevaluation before a significant change in placement.
Do schools have to identify children with disabilities?
In order for children with disabilities to receive services, they must by identified and then determined to be eligible for these services. Under IDEA guidelines, school districts are required to identify and evaluate all children suspected of having a disability whose families reside within the district.
Does the federal government have to provide additional funding for students with special needs?
This statute does not require the federal government to provide additional funding for students identified with special needs. Schools must provide these children with reasonable accommodations comparable to those provided to their peers under the rulings of Section 504.
What is the difference between Idea and 504?
Section 504 guarantees access for a child with a disability whereas IDEA is aimed at guaranteeing the success of a child living with a disability. IDEA often requires substantial modification of learning material relative to Section 504.
What is the idea of 504?
In some cases, IDEA details the exact assessment criteria for inclusion in a category. In other cases, states can specify their own criteria, but this must also be approved by the U.S. Department of Education. Section 504 requires that a person's mental or physical disabilities limit at least one life activity.
How often do you need to do a 504 evaluation?
With IDEA, re-evaluations are required to take place at least every three years. 3 A meeting is required before any change in placement. Section 504 evaluations are designed by the committee working with the child and are limited to the specific questions they need to address.
What are some examples of disabilities that could be potentially disabling according to Section 504.?
It includes a wide group of students with physical or mental disabilities substantially limiting a major life function. HIV, Tourette's syndrome, attention deficit disorder, heart conditions, and tuberculosis are just a few examples of conditions that could be potentially disabling according to Section 504.
What is Section 504?
Cultura RM/yellowdog/Getty Images. Section 504, a civil rights law, was historically intended to prevent discrimination by institutions receiving public funds. Institutions such as public schools, libraries, universities and colleges, and other public services are typically required to comply with Section 504 because they receive such funding in ...
Do school districts require parent input?
Many school districts, however, do require parent input and offer parents the opportunity to consent to or decline services. The IDEA requires much more districts regarding parent notice and consent. Parents are to be notified of and invited to any meetings concerning their children.
What is the difference between ADA and IDEA?
However, for IDEA, it is the school’s responsibility to identify those whose disabilities affect their education.
What is a disability in the ADA?
A disability is defined as “a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities.”.
What are the three major laws relating to digital accessibility?
If you are an educational institution, there are three major laws relating to digital accessibility that you need to know about: Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA) Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
What is an IEP in special education?
With IDEA, once a student is identified as requiring special education, the school must put together an Individualized Education Program (IEP) to meet that student’s specific needs. For the ADA and Section 504, accommodations need to be provided for the student, which may include auxiliary aids such as screen readers.
Does the ADA apply to schools?
The ADA applies to public entities, which is defined as “State or local government and any of its departments, agencies, or other instrumentalities.”. Section 504 also applies to public entities, but only those that receive federal funding. IDEA does not require a school to receive federal funding, but only applies to K-12 schools.
What is the difference between ADA and 504?
Both laws are enforced by the U.S. Department of Justice. The ADA was designed to provide broad protection for people with disabilities . Section 504 provides more limited protection, covering only federal programs and activities.
What is the 504?
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 and the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA) are civil rights laws that prohibit discrimination on the basis of disability in programs and activities that receive federal financial assistance. Both laws are enforced by the U.S. Department of Justice. The ADA was designed to provide broad ...
What is Section 504 notice?
Section 504 demands notice to parents concerning the identification, evaluation, or/and placements. Inscribed notice or report is recommended. The report must be made only before a notable change in placement.
When was Section 504 passed?
Purpose of Section 504 and ADA. The ADA was signed into law on July 26, 1990, by President George Bush and went into effect on July 26, 1992. The ADA is a broad-ranging civil rights law that prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability in employment, public services, and accommodations.
When was the ADA expanded?
In 1992, the ADA was expanded to include Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Section 504 prohibits discrimination based on disability in any program or activity that receives federal financial assistance.
Does the ADA protect people with disabilities?
The ADA is an important civil rights law, but it does not protect everyone with a disability.
Does the ADA have safeguards for special education?
Procedural Safeguards. The ADA doesn’t stipulate procedural safeguards associated with special education. But it does detail the legislative requirements, complaint procedures, and consequences for dissent related to both employment and services.
What is the 504 ADA?
However, most designers and installers are unfamiliar with Section 504 requirements. Section 504 refers to a section of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973.
How are ADA and Section 504 fire alarms similar?
When dealing with residential units, it really depend on who’s occupying the specific units. ADA units are generally set up to be occupied solely by people with disabilities, so they get fire alarm audio/visual devices installed during construction/renovation and are move in ready. On a side note, the strobes have to activate when the local smoke alarm goes off, so making the smoke detector a system device makes that easier to do. Section 504 are units that have to be provided in order to accommodate persons with specific disabilities as needed, so they’re generally set up with A/V pipe, wire & back boxes, as well as demonstrated capacity on the circuit to add any potential A/V devices needed. Technically, all that’s required is the capacity, but if they wait until the devices are needed, they have to install the conduit after the fact. Far better to have it waiting.
What is Section 504?
Section 504 refers to a section of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. As the date suggests, it’s actually the precursor to the ADA. This section was one of the first civil rights laws that protected persons with disabilities from discrimination for reasons related to their disability.
Can ADA units be 504?
ADA units can be Section 504 units and vice versa, but the required quantity of units set aside for this purpose is different, so you can have both to satisfy the percentage needed. Obviously, there’s more to this than a blog can cover, so feel free to contact us for more information.
What is the difference between Idea and Section 504?
In contrast, IDEA includes an elaborate system of procedural safeguards designed to protect the child and parents. These safeguards include written notice before any change of placement and the right to an independent educational evaluation at public expense. Section 504 does not include these protections.
What is Section 504?
Section 504 is a civil rights law.
What is Section 504 protection?
The child who receives Section 504 protections has fewer rights than the child who receives special education services under the IDEA. The child who receives special education services under the IDEA is automatically protected under Section 504. Protection from Discrimination.
What happens if a 504 child is not a disability?
If the Section 504 child misbehaves and the school decides the child's behavior is not a manifestation of the disability, the child can be expelled from school permanently.
What are the requirements for Section 504?
To be eligible for protections under Section 504, the child must have a physical or mental impairment. This impairment must substantially limit at least one major life activity. Major life activities include walking, seeing, hearing, speaking, breathing, learning, reading, writing, performing math calculations, working, caring for oneself, and performing manual tasks. The key is whether the child has an "impairment" that "substantially limits . . . one or more . . . major life activities."
Where is Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act?
NOTE: Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act is in Wrightslaw: Special Education Law, 2nd Edi tion , pages 291 to 298.
Is the ADA 504 a broader basis?
Note: After this article was published, the ADA was amended and provides a broader basis for ADA/504 protections. After you complete this article, be sure to read the more current articles on our website about the Americans with Disabilities Act Amendments Act of 2008 (ADA AA). A portion of this article is taken from a chapter in Wrightslaw: From Emotions to Advocacy - The Special Education Survival Guide by Pete and Pam Wright.