As nouns the difference between induction and inductance is that induction is an act of inducting while inductance is the property of an electric circuit by which a voltage is induced in it by a changing magnetic field.
What is induction?
Induction is the magnetic field which is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic field. This definition of induction holds for a conductor. Induction is also known as inductance. L is used to represent the inductance and Henry is the SI unit of inductance. 1 Henry is defined as the amount of inductance required to produce an emf ...
What is the difference between inductor and inductance?
The inductor is the physical object a coil of wire usually. The inductance is the value in Henry of the inductor. All electronic components have some inductance, not only inductors. Inductor is a device which stored energy in form of magnetic field and inductance is a property of inductor
What is the difference between self induction and mutual induction?
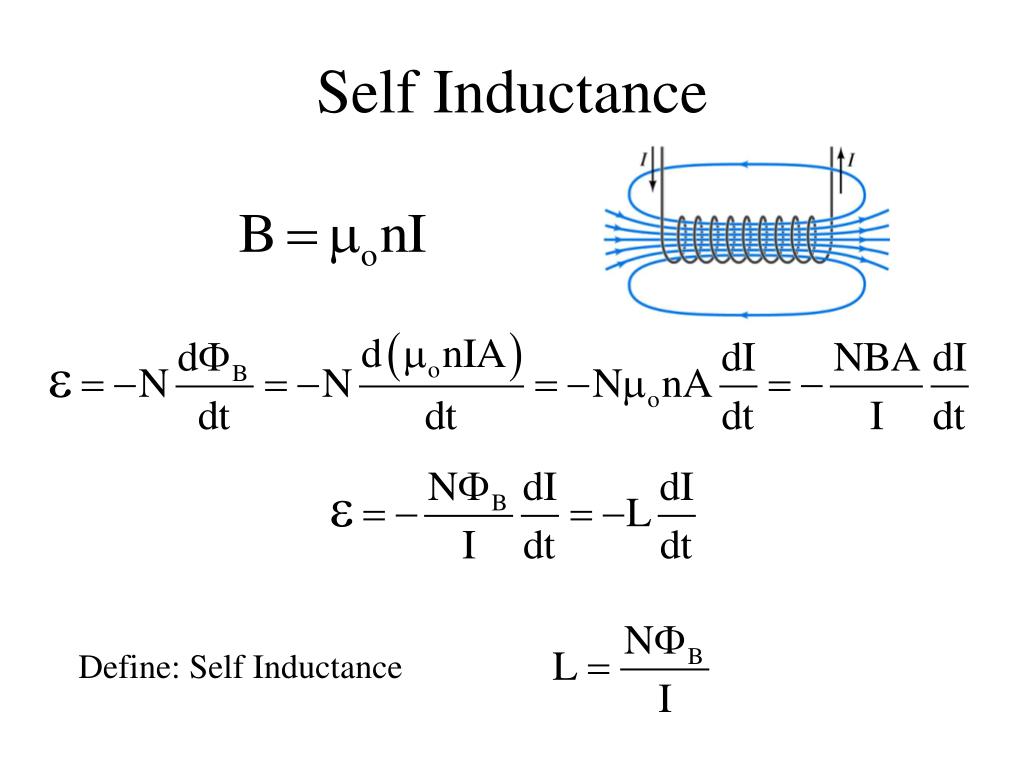
Self induction: Mutual induction: Self inductance is the characteristic of the coil itself. Mutual inductance is the characteristic of a pair of coils. The induced current opposes the decay of current in the coil when the main current in the coil decreases.
What is the difference between inductance and capacitance?
The key difference between inductance and capacitance is that inductance is a property of a current carrying conductor which generates a magnetic field around the conductor whereas capacitance is a property of a device to hold and store electric charges.
What is called induction?
1 : the act or process of placing someone in a new job or position induction into the Hall of Fame. 2 : the production of an electrical or magnetic effect through the influence of a nearby magnet, electrical current, or electrically charged body. induction. noun.
What's the difference between inductance and Inductive reactance?
Inductance is the property of a circuit to oppose any change in current and is measured in henries. Inductive reactance is a measure of how much the countering emf in the circuit will oppose current variations.
What are the induced and inductor?
An Inductor, also called a choke, is another passive type electrical component consisting of a coil of wire designed to take advantage of this relationship by inducing a magnetic field in itself or within its core as a result of the current flowing through the wire coil.
What is inductance in simple words?
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The flow of electric current creates a magnetic field around the conductor. The field strength depends on the magnitude of the current, and follows any changes in current.
What is difference between inductance and resistance?
The main difference between ideal resistors and ideal inductors is therefore that resistors dissipate electrical power as heat, while inductors turn electrical power into a magnetic field. Ideal resistors have zero reactance and as a result zero inductance.
What is inductive inductance?
When induction occurs in an electrical circuit and affects the flow of electricity it is called inductance (L). Self-inductance, or simply inductance, is the property of a circuit whereby a change in current causes a change in voltage in the same circuit.
What is SI unit of inductance?
The SI unit of inductance is Henry abbreviated as 'H'. It is defined as the measure of electric current changes at one ampere per second resulting in an electromotive force of one volt across the inductor.
Why inductor is called as inductor?
An inductor is described by its distinctive nature of inductance, which is defined as the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. Inductance is a result of the induced magnetic field on the coil. It is also determined by several factors such as; The shape of the coil.
What is unit of inductance?
henry, unit of either self-inductance or mutual inductance, abbreviated H, and named for the American physicist Joseph Henry. One henry is the value of self-inductance in a closed circuit or coil in which one volt is produced by a variation of the inducing current of one ampere per second.
What is the example of inductance?
Since self-inductance is associated with the magnetic field produced by a current, any configuration of conductors possesses self-inductance. For example, besides the wire loop, a long, straight wire has self-inductance, as does a coaxial cable.
What is the symbol of inductance?
It is very customary to use the symbol L for the inductance, in honour of the great physicist Heinrich Lenz. However, in the SI system, henry (H) is the unit of the inductance. It is the amount of inductance that causes a voltage of a single volt.
Do wires have inductance?
Inductance of wires and coils Straight wires and coils have an inductance. Normally coils are used for inductors because the linking of the magnetic field between the different turns of the coil increases the inductance and enables the wire to be contained within a smaller volume.
What is inductive reactance?
Definition: Inductive reactance is the opposition offered by the inductor in an AC circuit to the flow of ac current. It is represented by (XL) and measured in ohms (Ω). Inductive reactance is mostly low for lower frequencies and high for higher frequencies.
Is inductive reactance proportional to inductance?
The inductive reactance of an inductor increases as the frequency across it increases therefore inductive reactance is proportional to frequency ( XL α ƒ ) as the back emf generated in the inductor is equal to its inductance multiplied by the rate of change of current in the inductor.
What is the difference between inductive reactance and capacitive reactance?
If the reactance releases energy in the form of a magnetic field, it is called inductive reactance whereas if the reactance releases energy in the form of an electric field, it is called capacitive reactance.
Is inductive reactance the same as resistance?
Mathematically, resistance is simply voltage divided by current. Reactance is a property that opposes a change in current and is found in both inductors and capacitors. Because it only affects changing current, reactance is specific to AC power and depends on the frequency of the current.
What is Inductance?
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. It is denoted by L.
Define one henry.
One henry is defined as the amount of inductance required to produce an emf of 1 volt in a conductor when the current change in the conductor is at...
What are the factors that affect inductance?
The following factors affect the inductance in a circuit: Number of Wire Turns in the Coil Coil Area Core Material Coil Length
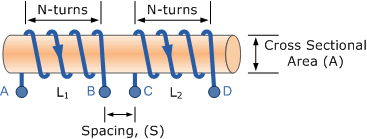
How is the mutual inductance of a pair affected when the separation between the coils is increased?
When the separation between the coils is increased, the magnetic flux linked with the secondary coil will decrease. Therefore, the mutual inductanc...
What is the application of mutual inductance?
Mutual inductance can be used in transformers, generators and electric motors.
As nouns the difference between induction and inductance
is that induction is an act of inducting while inductance is the property of an electric circuit by which a voltage is induced in it by a changing magnetic field.
English
The property of an electric circuit by which a voltage is induced in it by a changing magnetic field.
What is induction in physics?
What is Induction? Induction is the magnetic field which is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic field. This definition of induction holds for a conductor. Induction is also known as inductance. L is used to represent the inductance and Henry is the SI unit of inductance. 1 Henry is defined as the amount of inductance required ...
What is the definition of induction?
Inductance can be defined as the electromotive force generated to oppose the change in current at a particular time duration.
What factors affect the inductance of a wire?
Following are the factors that affect the inductance: The number of turns of the wire used in the inductor. The material used in the core. The shape of the core. Electromagnetic Induction law was given by Faraday which states that by varying the magnetic flux electromotive force is induced in the circuit.
What is the difference between self and mutual inductance?
Difference between Self and Mutual Inductance. Self inductance is the characteristic of the co il itself. Mutual inductance is the characteristic of a pair of coils. The induced current opposes the decay of current in the coil when the main current in the coil decreases.
When a coil changes magnetic flux?
When there is a change in the current or magnetic flux of the coil, an opposed induced electromotive force is produced. This phenomenon is termed as Self Induction. When the current starts flowing through the coil at any instant, it is found that, that the magnetic flux becomes directly proportional to the current passing through the circuit.
What are the two coils in a battery?
The two coils are P - coil (Primary coil) and S- coil (Secondary coil). To the P-coil, a battery, and a key is connected wherein the S-coil a galvanometer is connected across it. When there is a change in the current or magnetic flux linked with two coils an opposing electromotive force is produced across each coil, ...
What is the law of induction?
Figure 01: Oersted’s Law. According to Faraday’s law of induction, a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in nearby conductors. This change of the magnetic field is relative to the conductor, that is, either the field can vary, or the conductor can move through a steady field.
What is the difference between capacitance and inductance?
The key difference between inductance and capacitance is that inductance is a property of a current carrying conductor which generates a magnetic field around the conductor whereas capacitance is a property of a device to hold and store electric charges. 1.
What is the property of an electrical conductor by which a change in current through it induces an electromotive
Inductance is the “the property of an electrical conductor by which a change in current through it induces an electromotive force in the conductor itself”. When a copper wire is wrapped around an iron core and the two edges of the coil are placed on battery terminals, the coil assembly becomes a magnet.
What is the electrical component associated with inductance?
The electrical component associated with inductance is known as inductors, which usually coils with a core or without a core. Capacitance is associated with capacitors. There are several types of capacitors used in circuits. Behavior on a Change of Voltage. Inductors response to slow changing voltages.
Is capacitance a property of a current carrying conductor?
While the inductance is a property of a current carrying conductor to build a magnetic field, capacitance is a measure of the ability of a device to hold electrical charges. Both these properties are used in various applications as the basis. Nevertheless, these become a disadvantage as well in terms of power losses.
What is induction in electrical?
When induction. Induction - The process of generating current in a conductor by placing the conductor in a changing magnetic field. occurs in an electrical circuit. Circuit - A closed path followed or capable of being followed by an electric current. and affects the flow of electricity.
What is the process of generating current in a conductor?
or just induction. Induction - The process of generating current in a conductor by placing the conductor in a changing magnetic field. . It is called induction. Induction - The process of generating current in a conductor by placing the conductor in a changing magnetic field. because the current.
What is the process of generating electrical current?
in an electrical conductor. This process of generating electrical current. Electrical Current - The movement of electrons or holes (missing electrons) in an electrical conductor. in a conductor by placing the conductor in a changing magnetic field. Magnetic Field - The space in which a magnetic force is exerted.
