The key distinction between interstitial and appositional growth is that it is the bone’s longitudinal growth that increases its length, whereas appositional growth is the bone’s diameter. Bones can grow in size. Soft cartilage develops into hard bones over time.
How is interstitial growth different from Appositional growth?
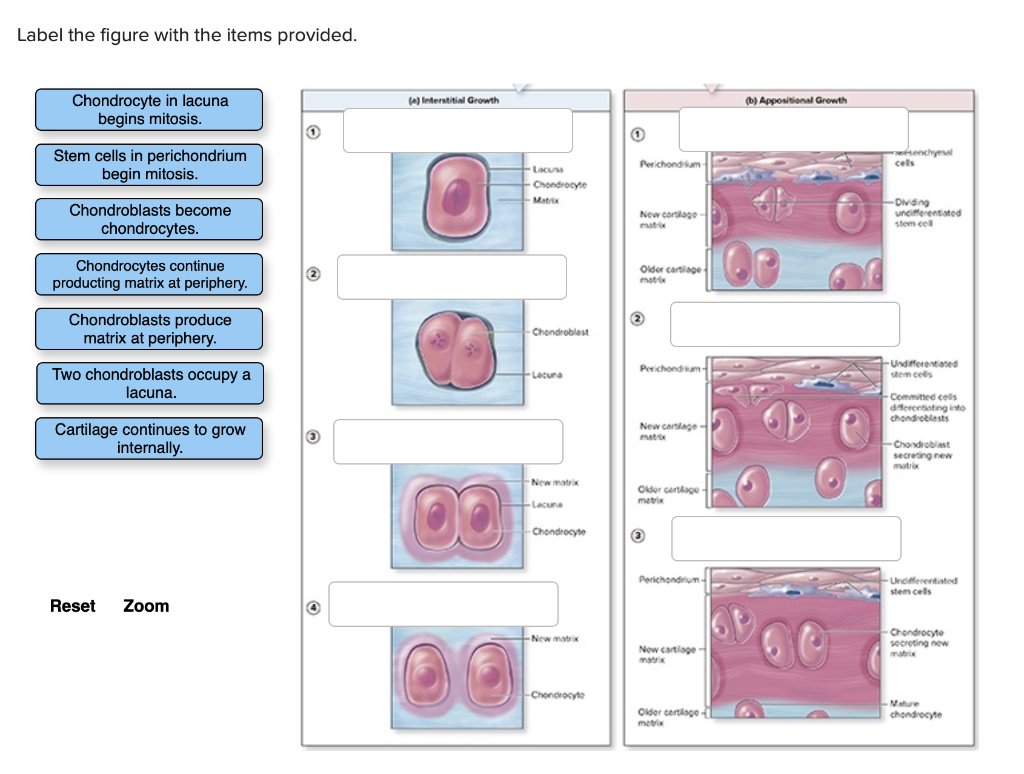
Interstitial growth is the increase in the length of bones by the cartilage lengthening and is replacing by bone tissue while appositional growth is the increase in the diameter of bones by the addition of bony tissue at the surface of the pre-existing bone.
What grows by interstitial and appositional growth?
Activity in the epiphyseal plate enables bones to grow in length (this is interstitial growth). Appositional growth allows bones to grow in diameter. Remodeling occurs as bone is resorbed and replaced by new bone.
What does interstitial growth mean?
Interstitial growth is the process that adds or removes solid mass at locations inside a solid material. For this process to occur, there must be interstitial space within this material to allow atoms or molecules to bind to the underlying substrate.
What does Appositional growth mean?
Growth by the addition of new layers on those previously formed, characteristic of tissues formed of rigid materials.
What does Appositional growth produce?
During appositional growth, osteoclasts resorb old bone that lines the medullary cavity, while osteoblasts, via intramembranous ossification, produce new bone tissue beneath the periosteum. Mesenchymal stem cell migration and differentiation are two important physiological processes in bone formation.
What is Appositional growth and where does it occur?
Appositional growth is the increase in the diameter of bones by the addition of bone tissue at the surface of bones. Bone remodeling involves the processes of bone deposition by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts. Bone repair occurs in four stages and can take several months.
What is interstitial growth quizlet?
interstitial growth (bone) growth from within the middle. cartilage increases with length, dies off, and replaced by bone.
What is Appositional growth quizlet?
appositional growth. increase in the diameter of the bone. osteoblasts. secrete matrix near the periosteum.
Which of the following statements best describes interstitial growth?
Answer and Explanation: The answer is c. Unspecialized cells from mesenchyme develop into chondrocytes, which divide and form cartilage. Interstitial growth is a process that forms new cartilage within an existing cartilage mass.
What means apposition?
Definition of apposition 1a : a grammatical construction in which two or more usually adjacent words, phrases, or clauses (especially nouns or noun equivalents) that have the same referent stand in the same syntactical relation to the rest of a sentence (such as the poet and Burns in "a biography of the poet Burns")
What are the steps of interstitial growth?
Interstitial growth which includes: Cell division of the chondrocytes....Appositional growth which includes:Differentiation of the chondroblasts or perichondrial cells.Synthesis of the extracellular matrix.Expansion of the girth of the cartilage.
What is apposition in biology?
apposition - (biology) growth in the thickness of a cell wall by the deposit of successive layers of material.
What are the two types of cartilage growth?
Growth of cartilage is attributable to two processes:Interstitial growth which includes: Cell division of the chondrocytes. Synthesis of the extracellular matrix. ... Appositional growth which includes: Differentiation of the chondroblasts or perichondrial cells. Synthesis of the extracellular matrix.
What is Appositional growth quizlet?
appositional growth. increase in the diameter of the bone. osteoblasts. secrete matrix near the periosteum.
Is interstitial growth in the epiphyseal plate?
Answer and Explanation: The growth of the epiphyseal plate which adds to the length of bone is called interstitial growth. The epiphyseal plate is a plate of cartilage tissue that will grow in length, and will eventually be replaced by bone tissue. This is the main site for lengthening of long bones.
Which part of a bone allows it to grow?
Bone Growth Bones grow in length at the epiphyseal plate by a process that is similar to endochondral ossification. The cartilage in the region of the epiphyseal plate next to the epiphysis continues to grow by mitosis. The chondrocytes, in the region next to the diaphysis, age and degenerate.
What is the difference between interstitial and appositional growth?
Interstitial growth produces longer bones as the cartilage lengthens and is replaced by bone tissue, while appositional growth occurs when new bone tissue is deposited on the surface of the bone, resulting in bone thickening.
How does interstitial growth occur?
Interstitial growth is the lengthening of the bone resulting from the growth of cartilage and its replacement with bone tissue. A person grows taller because of interstitial growth. This growth occurs at the epiphyseal plate and continues until the person reaches the teenage years. Most bones stop growing at this point, but some, such as those in the nose and lower jaw, continue to lengthen throughout a person's life.
What type of growth occurs when osteoblasts deposit new bone matrix layers onto already-formed layers of the outer surface of?
This type of growth, called appositional growth, happens when osteoblasts in the periosteum deposit new bone matrix layers onto already-formed layers of the outer surface of bone. At the same time, osteoclasts on the endosteum break bone tissue down.
Why do bones grow?
In order to accommodate for increases in length, bones also need to increase in thickness. This type of growth, called appositional growth, happens when osteoblasts in the periosteum deposit new bone matrix layers onto already-formed layers of the outer surface of bone. At the same time, osteoclasts on the endosteum break bone tissue down. This results in a greater concentration of bone being built than being destroyed, which produces thicker and stronger bones.
Why do people grow taller after birth?
A person grows taller because of interstitial growth.
Where does cartilage calcify?
Blood vessels enter the spaces. Calcified cartilage forms at the juncture of the diaphysis and the epiphyses.
What happens to cartilage in hypertrophic zone?
This results in the formation of large spaces. At the calcification zone, cartilage is calcified, and the matrix breaks down. Blood vessels enter the spaces.
What is interstitial growth?
In terms of cartilage interstitial growth means “Growth from Within the tissue” that Results in Increase in Length Of Cartilage (Note- cartilage Grows unidirectionally). This type of Growth in Cartilage Occurs when it is Young ( During Childhood& Adolescence).
Why do chondrocytes start dividing?
These chondrocytes start dividing and also producing extracellular Matrix Due to which Interstitial Growth occurs that Results in Increased Cartilage Length.