What happens during intramembranous ossification?
Intramembranous ossification is one of the two main processes of bone formation, known as osteogenesis. During intramembranous ossification, the mesenchymal tissue transforms directly into a bone. This process occurs primarily in the bone of the skull.
What is the difference between dermal and endochondral ossification?
The key difference between dermal and endochondral ossification is that dermal ossification is the development of bone from fibrous membranes, while endochondral ossification is the development of bone from hyaline cartilage. Ossification or osteogenesis is the formation of bones from osteoblast cells.
What are the two types of bone ossification?
A normal bone ossification process can be of two different types: endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification. During endochondral ossification, cartilage is utilized as a precursor for bone formation.
What are the steps involved in endochondral ossification of long bones?
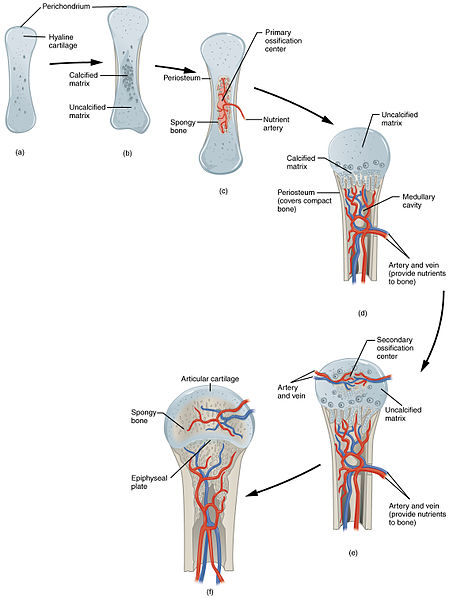
Endochondral Ossification of Long Bones – Steps 1 Around 6-8 weeks after conception, mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondrocytes, which form the cartilaginous bone precursor. ... 2 The matrix of the cartilage calcifies. ... 3 The osteogenic cells also migrate into the spaces and become osteoblasts. More items...

What is the difference between intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification quizlet?
INTRAMEMBRANOUS OSSIFICATION: forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. bone is formed in sheet-like layers that reseamble a membrane. ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION: forms most bones in the body, mostly long bones, and replace cartilage with bone.
What is the key difference between intramembranous and endochondral bone development quizlet?
4) The primary difference is that in endochondral ossification, bone develops from mesenchymal cells, whereas in intramembranous ossification, bone develops from a cartilage model.
What is the main difference between intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification in terms of initial development?
Before this time, the embryonic skeleton consists entirely of fibrous membranes and hyaline cartilage. The development of bone from fibrous membranes is called intramembranous ossification; development from hyaline cartilage is called endochondral ossification. Bone growth continues until approximately age 25.
What is the difference between intramembranous and ossification?
0:412:02Ossification: Intramembranous and Endochondral - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if you see his clavicle actually is also magenta the clavicle also undergoes membraneMoreSo if you see his clavicle actually is also magenta the clavicle also undergoes membrane detoxification. And there's an exception in the skull. Itself. If you'll see the base of the skull is actually
What are the major events of intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification and how are they different quizlet?
There are two processes: Intramembranous ossification (conversion event) is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme); perichondral membrane converted to osteoblasts. Endochondral ossification (replacement event) involves cartilage as a precursor; cartilage is replaced with bone.
What do intramembranous and endochondral ossification have in common?
Similarities Between Endochondral Ossification and Intramembranous Ossification. Endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification are the two methods of ossification/osteogenesis. Osteoblasts help in the synthesis of bones in both processes. Both processes are essential in the healing of bone fractures.
What are the main differences between dermal and endochondral ossification?
The key difference between dermal and endochondral ossification is that dermal ossification is the development of bone from fibrous membranes, while endochondral ossification is the development of bone from hyaline cartilage.
What is the endochondral ossification process?
Endochondral Ossification This process involves the replacement of hyaline cartilage with bone. It begins when mesoderm-derived mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondrocytes. Chondrocytes proliferate rapidly and secrete an extracellular matrix to form the cartilage model for bone.
What is the process of intramembranous ossification?
Intramembranous ossification is the characteristic way in which the flat bones of the skull and the turtle shell are formed. During intramembranous ossification in the skull, neural crest-derived mesenchymal cells proliferate and condense into compact nodules.
What is the difference between intramembranous and endochondral?
In intramembranous ossification, bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal connective tissue. In endochondral ossification, bone develops by replacing hyaline cartilage.
How are intramembranous and endochondral ossification similar and different?
In intramembranous ossification, bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal connective tissue. In endochondral ossification, bone develops by replacing hyaline cartilage. Activity in the epiphyseal plate enables bones to grow in length (this is interstitial growth).
What are the key differences between endochondral and intramembranous ossification in terms of starting point and processes involved?
Based on its embryological origin, there are two types of ossification, called intramembranous ossification that occurs in mesenchymal cells that differentiate into osteoblast in the ossification center directly without prior cartilage formation and endochondral ossification in which bone tissue mineralization is ...
Which bones develop by intramembranous ossification quizlet?
Intramembranous ossification is the process of bone development from fibrous membranes. It is involved in the formation of the flat bones of the skull, the mandible, and the clavicles.
What is intramembranous ossification quizlet?
Intramembranous ossification: Intramembranous ossification: begins within fibrous connective tissue membranes formed by mesenchymal cells.
Which of the following bones is formed by intramembranous ossification quizlet?
The flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and a good deal of the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification, while bones at the base of the skull and the long bones form via endochondral ossification.
Which bones are produced by intramembranous ossification quizlet?
INTRAMEMBRANOUS OSSIFICATION: also known as DERMAL OSSIFICATION, produces: flat bones of the skull, some of the facial bones, mandible, central part of the clavicle.
What is the Difference Between Endochondral Ossification and Intramembranous Ossification?
Intramembranous ossification is a process which leads to the formation of jaw bones, collar bones or clavicles without the involvement of a cartilage precursor.
What is Intramembranous Ossification?
Intramembranous ossification is a type of bone ossification process that doesn’t involve a cartilage precursor, but the bone tissue is directly formed over the mesenchymal tissue. Intramembranous ossification is a process which leads to the formation of jaw bones, collar bones or clavicles. It is also involved in the primary formation of skull bones and occurs during the healing of bone fractures. The bone formation during intramembranous ossification is initiated by the mesenchymal cells that are present within the medullary cavity of a bone fracture.
What is the epiphyseal plate?
The epiphyseal plate is an important element during the formation of new cartilage which is replaced by bone. This process leads to the increment of the length of the bone. Once completed, the primary and secondary ossification centres will unite at a point referred to as an epiphyseal line. The growth of the bone is completed once ...
What is the process of endochondral ossification?
Endochondral ossification is a process which is essential for the formation of long bones (femur) and flat and irregular bones such as ribs and vertebrae. Endochondral ossification is a process that involves two main functions; it is involved in the natural growth of bones and its lengthening and is also involved in the healing of bone fractures naturally. During this type of ossification process, which leads to the formation of long bones and other types of bones, the involvement of a cartilage precursor takes place. The whole ossification process takes place in two centres of ossification, primary and secondary.
What is the process of ossification?
Ossification Process. A small group of adjacent mesenchymal stem cells begin to replicate and form a small cluster of cells called a nidus. This replication process is stopped once a nidus is formed, and development of morphological changes in the mesenchymal stem cells start to occur.
Which process leads to the formation of the mid-region of the long bone?
Ossification Process. In the primary centre of ossification first site of ossification which leads to the formation of the mid-region of the long bone is diaphysis. Diaphysis is the region where the bone tissue first appears in long bones. In the primary ossification centre, osteoblasts and osteoclasts absorb cartilage which is produced by ...
Where is the secondary ossification centre located?
The secondary ossification centre is found around the regions of epiphysis. Secondary ossification centre has similar functions to that of primary ossification centre. The unossified cartilage between the primary and secondary ossification centres is referred to as the cartilage plate or epiphyseal plate.
What is endochondral ossification?
Endochondral ossification is an Intramembranous ossification is a process essential process for the formation of which leads to the formation of jaw bones, long bones (femur) and flat and collar bones or clavicles without the irregular bones such as ribs and involvement of a cartilage precursor. vertebrae.
What is the process of laying new bone tissue?
Osteogenesis, more commonly referred to as ossification, is a process by which new layers of bone tissues are laid by osteoblasts. Bone ossification is not the same as bone calcification process. It is a process which involves the laying of calcium-based salts within the cells and tissues. A normal bone ossification process can be of two different types: endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification. During endochondral ossification, cartilage is utilized as a precursor for bone formation. In intramembranous ossification, the bone tissue is directly laid on a primitive connective tissue referred to as mesenchyma without the involvement of an intermediate cartilage. This is the key difference between endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification. In the context of fractures, the healing process by plaster of Paris occurs through endochondral ossification whilst the fractures which are treated by open reduction and internal fixation get healed by intramembranous ossification.
Is cartilage used in endochondral ossification?
During endochondral ossification, No cartilage is used as a precursor during the cartilage is utilized as a precursor for formation of bone, but the bone tissue is bone formation. directly formed over the mesenchymal tissue in intramembranous ossification.
What is the Difference Between Dermal and Endochondral Ossification?
Dermal ossification is a type of intramembranous ossification that produces dermal bone, while endochondral ossification is the essential process of rudimentary formation of long bones. So, this is the key difference between dermal and endochondral ossification. Moreover, in dermal ossification, the bone is developed from fibrous tissue. In contrast, in endochondral ossification, the bone is developed from hyaline cartilage.
What is the role of chondrocytes in endochondral ossification?
In endochondral ossification, the bone is developed from hyaline cartilage. In long bones, chondrocytes produce a template of the hyaline cartilage diaphysis. Due to developmental signals, the matrix begins to calcify.
What is Dermal Ossification?
Dermal ossification is a type of intramembranous ossification that produces dermal bone that forms components of the vertebrate skeleton, including the skull, jaws, gill covers, shoulder girdle, fin spines rays, and the shell. Intramembranous ossification is an essential process during the natural healing process of bone fractures and the rudimentary formation of bones of the skull. The mammalian skull is an ossified structure where flat dermal bones of the calvaria craniofacial region and the mandible are formed from dermal ossification.
Where is hyaline cartilage found in bone?
Osteoblasts and blood vessels enter these areas and convert hyaline cartilage into spongy bone. Until adolescence, hyaline cartilage is present at the epiphyseal plate. The epiphyseal plate is the region between diaphysis and epiphysis that is responsible for the lengthwise growth.

Key Difference – Endochondral Ossification vs Intramembranous Ossification
What Is Endochondral Ossification?
- Endochondral ossification is a process which is essential for the formation of long bones (femur) and flat and irregular bones such as ribs and vertebrae. Endochondral ossification is a process that involves two main functions; it is involved in the natural growth of bones and its lengthening and is also involved in the healing of bone fractures naturally. During this type of ossification pro…
What Is Intramembranous Ossification?
- Intramembranous ossification is a type of bone ossification process that doesn’t involve a cartilage precursor, but the bone tissue is directly formed over the mesenchymal tissue. Intramembranous ossification is a process which leads to the formation of jaw bones, collar bones or clavicles. It is also involved in the primary formation of skull bones and occurs during t…
Summary – Endochondral Ossification vs Intramembranous Ossification
- Osteogenesis is a process by which new layers of bone tissues are laid by osteoblasts. A normal bone ossification process can be of two different types; endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification. During endochondral ossification, cartilage is utilized as a precursor for bone formation. In intramembranous ossification, the bone tissue is directly laid o…