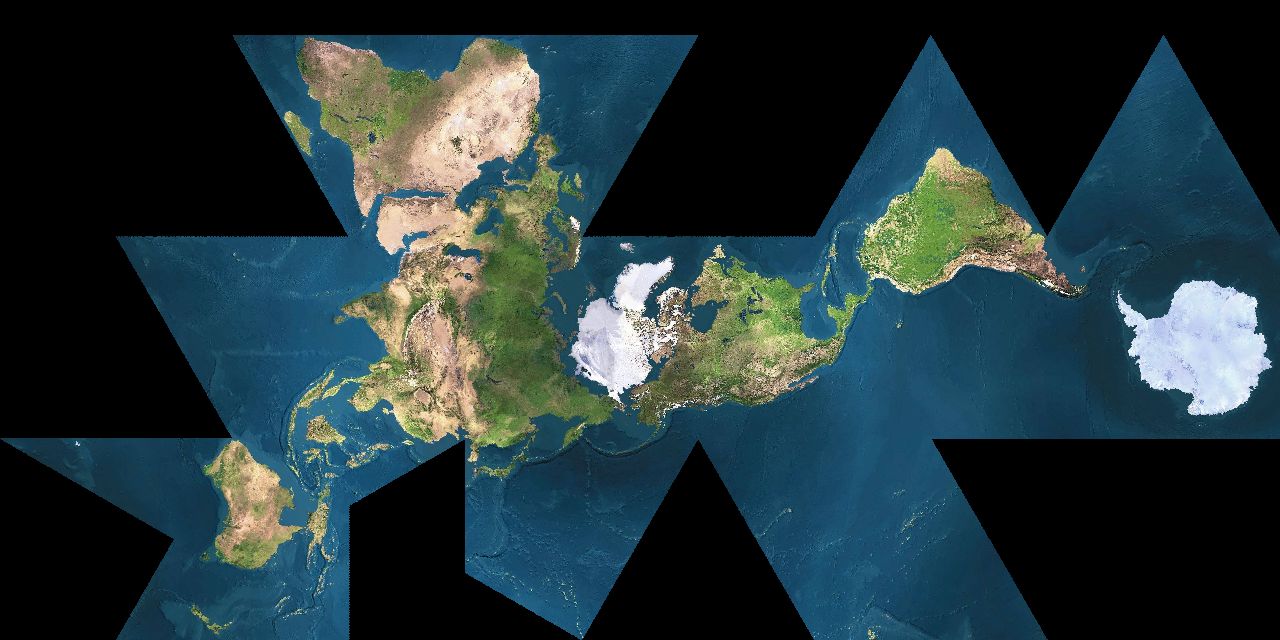
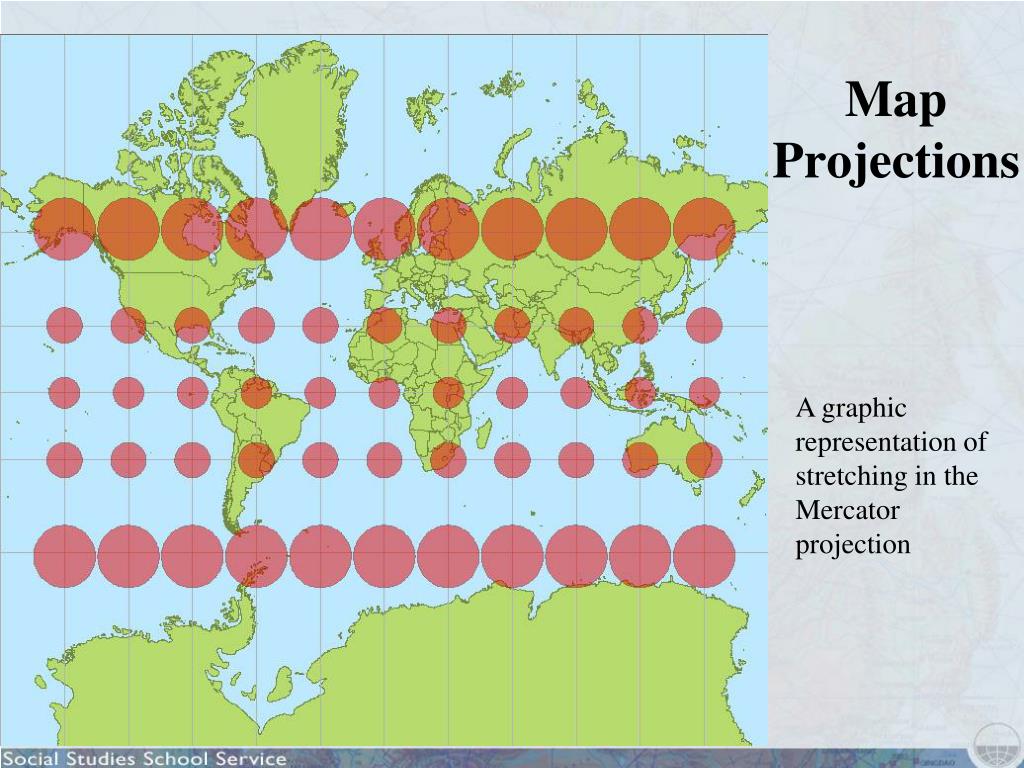
Unlike the Mercator projection
Mercator projection
The Mercator projection is a cylindrical map projection presented by the Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. It became the standard map projection for nautical purposes because of its ability to represent lines of constant course, known as rhumb lines or loxo…
Robinson projection
The Robinson projection is a map projection of a world map which shows the entire world at once. It was specifically created in an attempt to find a good compromise to the problem of readily showing the whole globe as a flat image.
What are the pros and cons of Mercator projection?
What are the pros and cons of Mercator projection? Advantage: The Mercator map projection shows the correct shapes of the continents and directions accurately. Disadvantage: The Mercator map projection does not show true distances or sizes of continents, especially near the north and south poles.
Who would use a Mercator projection?
This projection is widely used for navigation charts, because any straight line on a Mercator projection map is a line of constant true bearing that enables a navigator to plot a straight-line course. It is less practical for world maps, however, because the scale is distorted; areas farther away from the Equator appear disproportionately large.
What are the pros and cons of the Robinson projection?
- It forces the map to create a distortion away from the equator.
- Its usefulness is limited in the polar regions of the planet.
- You cannot compare the area of landmasses with a Mercator projection.
- It makes Europe and North America seem more important.
Why is the Mercator projection so commonly used?
Mercator projection, type of map projection introduced in 1569 by Gerardus Mercator. This projection is widely used for navigation charts, because any straight line on a Mercator projection map is a line of constant true bearing that enables a navigator to plot a straight-line course.

What is the difference between Mercator and Robinson?
Robinson's map is more accurate than a Mercator projection. The shapes and sizes of continents are closer to true. Robinson's map is best within 45° of the equator. Distances along the equator and the lines parallel to it are true.
What is a Robinson map projection best used for?
The Robinson projection is unique. Its primary purpose is to create visually appealing maps of the entire world. It is a compromise projection; it does not eliminate any type of distortion, but it keeps the levels of all types of distortion relatively low over most of the map.
What is the difference between Mercator projection and equal area projection?
The Mercator projection doesn't preserve area correctly, especially as you get closer to the poles. On the other hand, one kind of projection that doesn't distort area is the Cylindrical Equal Area. Notice here how Greenland looks the right size as compared to South America.
What is the main difference between different types of map projections?
The only factor that distinguishes different cylindrical map projections from one another is the scale used when spacing the parallel lines on the map.
What is the advantage of a Robinson projection over a Mercator projection?
Unlike the Mercator projection, the Robinson projection has both the lines of altitude and longitude evenly spaced across the map.
What is the advantage of the Robinson projection?
Advantage: The Robinson map projection shows most distances, sizes and shapes accurately. Disadvantage: The Robinson map does have some distortion around the poles and edges. Who uses it? The Robinson is most commonly used by students, teachers, textbooks and atlases.
What is the Mercator projection used for?
Mercator is a conformal cylindrical map projection that was originally created to display accurate compass bearings for sea travel. An additional feature of this projection is that all local shapes are accurate and correctly defined at infinitesimal scale.
What are the 3 advantages of the Mercator projection?
Advantages of Mercator's projection: - preserves angles and therefore also shapes of small objects - close to the equator, the distortion of lengths and areas is insignificant - a straight line on the map corresponds with a constant compass direction, it is possible to sail and fly using a constant azimuth - simple ...
What do you mean by Mercator projection?
Definition of Mercator projection : a conformal map projection of which the meridians are usually drawn parallel to each other and the parallels of latitude are straight lines whose distance from each other increases with their distance from the equator.
What are the 3 main types of map projections?
These are based on the types of geometric shapes that are used to transfer features from a sphere or spheroid to a plane. Map projections are based on developable surfaces, and the three traditional families consist of cylinders, cones, and planes.
What type of projection is the Robinson?
pseudocylindric projectionRobinson is a pseudocylindric projection. The meridians are regularly distributed curves mimicking elliptical arcs. They are concave toward the central meridian and do not intersect the parallels at right angles. The parallels are unequally distributed straight lines.
Which map projection is the most accurate?
AuthaGraph The AuthaGraphy projectionAuthaGraph. The AuthaGraphy projection was created by Japanese architect Hajime Narukawa in 1999. It is considered the most accurate projection in the mapping world for its way of showing relative areas of landmasses and oceans with very little distortion of shapes.
What type of projection is a Robinson map?
Robinson is a pseudocylindric projection. The meridians are regularly distributed curves mimicking elliptical arcs. They are concave toward the central meridian and do not intersect the parallels at right angles. The parallels are unequally distributed straight lines.
What type of map is a Robinson?
The Robinson projection is a map projection of a world map which shows the entire world at once. It was specifically created in an attempt to find a good compromise to the problem of readily showing the whole globe as a flat image.
Why does National Geographic use the Robinson projection?
Robinson, one of the nation's most respected cartographers. John B. Garver Jr., the society's chief cartographer, said the Robinson projection provides a more realistic view of the world. ''We believe that its balances of size and shape are the most reasonable for a general purpose map,'' he said.
Which map projection is the most accurate?
AuthaGraph The AuthaGraphy projectionAuthaGraph. The AuthaGraphy projection was created by Japanese architect Hajime Narukawa in 1999. It is considered the most accurate projection in the mapping world for its way of showing relative areas of landmasses and oceans with very little distortion of shapes.
Why can't a mercator be modified?
The very reason the Mercator can not be modified here and there is that it would destroy the very lines it set out to create (especially latitude and longitude), making navigation more difficult even though it would be more representative of size.
Why is Mercator good?
This makes Mercator good for navigation, because if you draw a line north-east on the map, it will correspond to north-east on the globe. The price to be paid for this is increasingly large distortion in shapes as you approach the poles, and it’s not possible to represent the poles at all using Mercator.
Why was the Mercator map important?
The original purpose of the Mercator map was to be good for sea faring navigation by allowing ship captains to have a concrete route from one area of the world to another. As we now know, due to the curvature of the earth and various other factors the straightest looking path on this map isn’t the most efficient. However, it did offer effective navigation routes for many sailing expeditions at the time since it didn’t really affect the curvature of the map but instead distorted size.
What is the Gall-Peters projection?
The Gall-Peters Projection (often just called Peters Projection) is the one most common quoted to fix this issue (and the one mentioned in the video clip). It does show size more accurately, but there are other trade-offs, such as not being able to use it for accurate navigation.* It looks like this
Why is it practical to see the difference between Africa and Greenland?
It is also practical because it keeps proportions in area. Now you can see the size difference between Africa and Greenland. But look at Greenland‘s shape: The angles are all wrong…
Is Robinson projection conformal?
Robinson projections are not conformal, but also do not preserve shapes (so the shapes of land masses are still distorted, again with greater distortion towards the poles). But the distortion is less than when using Mercator and the polar regions can be shown. The Robinson projection was a compromise between distorting angles and distorting shapes, while still being able to represent the globe on a flat, rectangular plane. Projections which preserve areas/shapes better generally have to abandon the rectangular shape which is so convenient for printed maps.
What is the mercator used for?
Mercator is used for navigation or maps of equatorial regions. Any straight line between two points is a true line of constant direction, but not usually the shortest distance between the two points. Distances are true only along the equator, but are reasonably correct within 15° either side. Areas and shapes of large areas are distorted.
What is the projection of a sphere on a flat plane?
The projection we have used is commonly known as the Mercator projection (a projection being any method of representing the surface of a sphere on to a flat plane). The Mercator is well-known and familiar: it is the standard map used in most schoolbooks and newspapers; it arguably has the clearest depiction of all countries included in our world ...
What is distortion in polar regions?
Areas and shapes of large areas are distorted. Distortion increases away from the equator and is extreme in polar regions (Greenland appears larger than Africa but is actually 14 times smaller). Parallels and meridians are straight lines which meet at right angles.
What is Peters' argument?
Peters (1973) Peters is an equal-area projection which became the centrepiece of a controversy surrounding the political implications of map design. The argument goes something like this: Mercator inflates the sizes of regions as they gain distance from the equator.
Which point is free of distortion?
The only point free of distortion is the centre point, though distortion of shape is moderate throughout. Central meridian (pole-to-pole) is a straight line half the length of the equator. Other meridians are complex curves, equally spaced along the equator. The equator is straight.