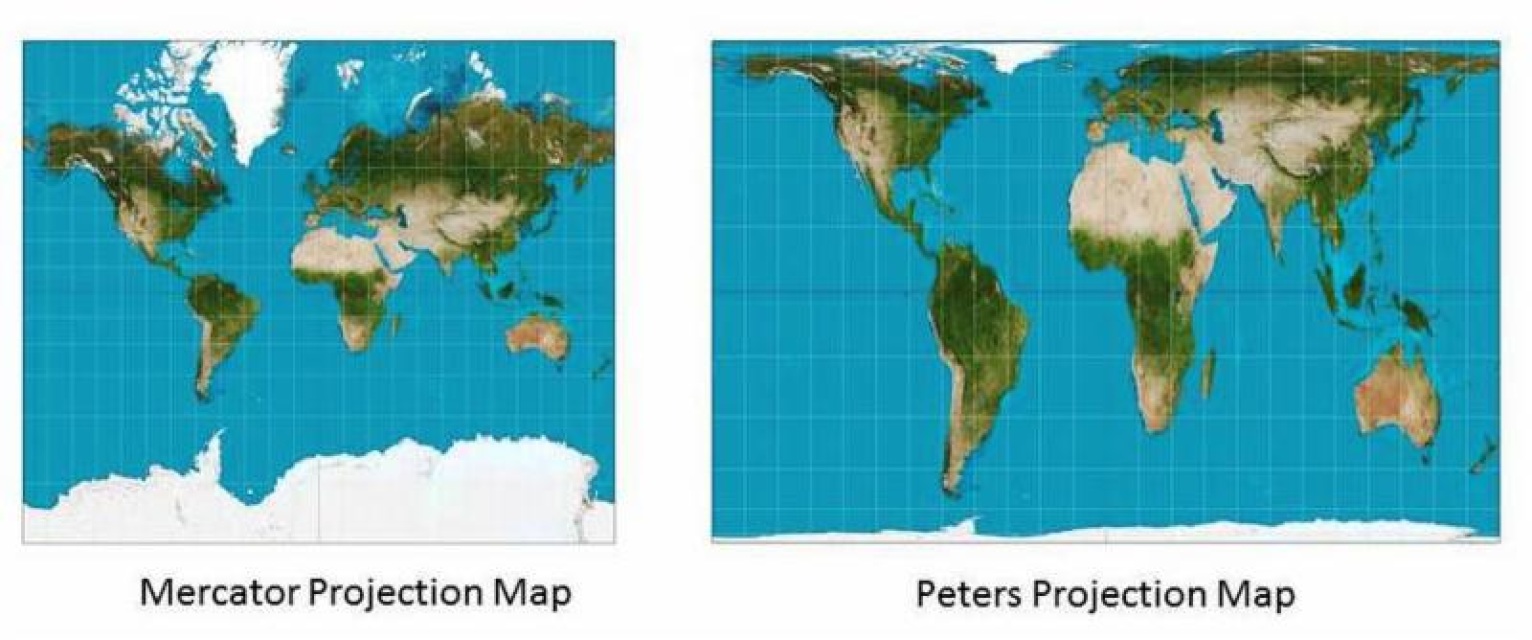
What is the difference between Mercator and Peters Projection? The Mercator projection, by comparison, grossly distorts the sizes of the continents – causing the Greenland-is-larger-than-Africa effect – but stays true to their shapes. The Peters projection, by contrast, shows all the continents according to their true sizes, which is apparently fairer. What is wrong with Peters Projection map?
What are the pros and cons of Mercator projection?
What are the pros and cons of Mercator projection? Advantage: The Mercator map projection shows the correct shapes of the continents and directions accurately. Disadvantage: The Mercator map projection does not show true distances or sizes of continents, especially near the north and south poles.
Who would use a Mercator projection?
This projection is widely used for navigation charts, because any straight line on a Mercator projection map is a line of constant true bearing that enables a navigator to plot a straight-line course. It is less practical for world maps, however, because the scale is distorted; areas farther away from the Equator appear disproportionately large.
Why is the Mercator projection so commonly used?
Mercator projection, type of map projection introduced in 1569 by Gerardus Mercator. This projection is widely used for navigation charts, because any straight line on a Mercator projection map is a line of constant true bearing that enables a navigator to plot a straight-line course.
What is the standard Mercator projection?
the Mercator. One of the most famous map projections is the Mercator, created by a Flemish cartographer and geographer, Geradus Mercator in 1569. It became the standard map projection for nautical purposes because of its ability to represent lines of constant true direction.
Why is the Peters projection better?
The Peters World Map is an Equal Area cylindrical projection with standard parallels at 45 degrees thus resulting in a distortion of shape which is stretched about the equator and squashed towards the poles, but having the great advantage that all countries are correct in size in relation to each other.
What is the major difference between Mercator and Robinson projections?
IntroductionProjectionTypeCommentsMercatorcylindricalCreated in 1569 Best Used in areas around the Equator and for marine navigationRobinsonpseudo-cylindricalCreated in the 1963 Best Used in areas around the EquatorTransverse MercatorcylindricalCreated in 1772 Best Used for areas with a north-south orientation2 more rows
What is the Gall-Peters and Mercator projection show?
Peters pointed out that the Mercator map has a distortion in the northern hemisphere, making North American and Eurasian countries appear much larger than they actually are. For example, Greenland and Africa are shown as roughly the same size, although in reality Africa is about fourteen times larger.
What is the difference between a Mercator and conic projection?
Mercator projection maps are used in navigation due to their ability to label any point on the globe. The gnomonic projection projects points from a globe onto a piece of paper that touches the globe at a single point. It creates circle routes often used in air travel. Our last projection is the conic projection.
What is the most accurate map projection?
AuthaGraph. This is hands-down the most accurate map projection in existence. In fact, AuthaGraph World Map is so proportionally perfect, it magically folds it into a three-dimensional globe. Japanese architect Hajime Narukawa invented this projection in 1999 by equally dividing a spherical surface into 96 triangles.
What is Mercator projection used for?
Description. Mercator is a conformal cylindrical map projection that was originally created to display accurate compass bearings for sea travel. An additional feature of this projection is that all local shapes are accurate and correctly defined at infinitesimal scale.
Is the Peters projection more accurate?
Skilled at marketing, Arno claimed that his map displayed third world countries more subjectively than the popular but highly distorted Mercator projection map. While the Peters projection does (almost) represent land area accurately, all map projections distort the shape of the earth, a sphere.
Why is the Mercator projection so popular?
It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and south as down everywhere while preserving local directions and shapes.
What is the main difference between different types of map projections?
The only factor that distinguishes different cylindrical map projections from one another is the scale used when spacing the parallel lines on the map.
What are the 3 basic projection types?
Each of the main projection types—conic, cylindrical, and planar—are illustrated below.Conic (tangent) A cone is placed over a globe. ... Conic (secant) A cone is placed over a globe but cuts through the surface. ... Cylindrical aspects. A cylinder is placed over a globe. ... Planar aspects. ... Polar aspect (different perspectives)
What are 4 types of map projections?
What Are The 4 Main Types Of Map projectionsAzimuthal projection.Conic projection.Cylindrical projection.Conventional projection or Mathematical projection.
Is Mercator or Robinson projection more accurate?
Robinson makes the world “look right”. Better balance of size and shape of high-latitude lands than in Mercator. Russia, Canada, and Greenland truer to size, but Greenland compressed. Directions true along all parallels and along central meridian.
What is the Robinson projection used for?
The Robinson projection is unique. Its primary purpose is to create visually appealing maps of the entire world. It is a compromise projection; it does not eliminate any type of distortion, but it keeps the levels of all types of distortion relatively low over most of the map.
What does the Robinson projection distort?
Distortion. The Robinson projection is neither conformal nor equal-area. It generally distorts shapes, areas, distances, directions, and angles. The distortion patterns are similar to common compromise pseudocylindrical projections.
What are the pros and cons of the Robinson projection?
Advantage: The Robinson map projection shows most distances, sizes and shapes accurately. Disadvantage: The Robinson map does have some distortion around the poles and edges. Who uses it? The Robinson is most commonly used by students, teachers, textbooks and atlases.
Which projection has the same flaws as the Mercator projection?
The Gall-Peters projection. Despite these benefits, the Gall-Peters projection has its flaws. It doesn't enlarge areas as much as the Mercator projection, but certain places appear stretched, horizontally near the poles and vertically near the Equator.
Who created the Mercator projection?
The most popular version is the Mercator projection, created by Flemish cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. It's been widely used for centuries, including today in various forms by Google Maps and many other online services. This map preserves directional bearing, presenting rhumbs (imaginary lines that cut all meridians at the same angle) ...
What episode of The West Wing is the Gall-Peters?
You may remember this map from season two, episode 16 of "The West Wing," when a group of cartographers visit the White House to ask that the president "aggressively support" requiring every school in America to teach geography using the Gall-Peters instead of the Mercator.
Who invented the mercator?
Wikimedia Commons. One of the best alternatives to the Mercator projection was presented in 1974 at a conference in Germany by Dr. Arno Peters, who claimed he invented it — though well after the discovery of an identical map made by James Gall in the 1800s.
Is Mercator projection misleading?
But to most people, the Mercator projection is highly misleading. Tissot's indicatrix, a geometric equation used to show distortion on maps, explains the problems with Mercator.
Why is the Mercator projection useful?
But however distorted they are, some projections are more useful than others and the Mercator projection has an interest in navigation because it preserves the shape of continents.
Which projection gives a better idea of the continent sizes than the Mercator projection?
I’m perfectly aware that the Gall-Peters projection gives a better idea of the continent sizes than the Mercator projection.
What is the shape distortion of a mercator?
This is the Mercator. The circles vary in size, but they are all true circles. The shape distortion is zero.
What is the angle of a ship called?
If you are on a ship or walking overland and measure the angle to the north between your origin and destination (this is called your rhumb or azimuth) and you follow this azimuth on a compass, you will reach your destination.
Is a kilometer the same size as a road?
A kilometer is the same size in any road .
Is a conformal projection equiareal?
In short, because it is a conformal projection, although it is not equiarea and because it uses an orthogonal grid.
What is the mercator used for?
Mercator is used for navigation or maps of equatorial regions. Any straight line between two points is a true line of constant direction, but not usually the shortest distance between the two points. Distances are true only along the equator, but are reasonably correct within 15° either side. Areas and shapes of large areas are distorted.
What is Peters' argument?
Peters (1973) Peters is an equal-area projection which became the centrepiece of a controversy surrounding the political implications of map design. The argument goes something like this: Mercator inflates the sizes of regions as they gain distance from the equator.
What is the projection of a sphere on a flat plane?
The projection we have used is commonly known as the Mercator projection (a projection being any method of representing the surface of a sphere on to a flat plane). The Mercator is well-known and familiar: it is the standard map used in most schoolbooks and newspapers; it arguably has the clearest depiction of all countries included in our world ...
What is distortion in polar regions?
Areas and shapes of large areas are distorted. Distortion increases away from the equator and is extreme in polar regions (Greenland appears larger than Africa but is actually 14 times smaller). Parallels and meridians are straight lines which meet at right angles.
