What is the difference between Mobitz type 1 and Type 2 block?
Both Mobitz type 1 block and type 2 block result in blocked atrial impulses (ECG shows P-waves not followed by QRS complexes). The hallmark of Mobitz type 1 block is the gradual prolongation of PR intervals before a block occurs. Mobitz type 2 block has constant PR intervals before blocks occur.
What is the prognosis of Mobitz 2 type of heart block?
Patients having mobitz 2 type heart block are at a higher risk of developing third-degree heart blocks and the chance of them becoming symptomatic is higher than those having mobitz 1 form of the disease.
What are the risks of Mobitz 2?
In mobitz 2 there is a prolonged PR interval whose duration remains constant. An occasional impulse is lost without being transmitted to the ventricles. Complete Heart Block. The risk of getting a complete heart block is low.
Is Wenckebach phenomenon the same as Mobitz type 1 block?
However, Wenckebach phenomenon may also occur in sinoatrial (SA) block which is why the term should not be used. Mobitz type 1 block is characterized by a gradual prolongation of the PR interval over a few heart cycles until an atrial impulse is completely blocked, which manifests on the ECG as a P-wave not followed by a QRS complex.

How can you tell the difference between Type 1 and 2 Mobitz?
The hallmark of Mobitz type 1 block is the gradual prolongation of PR intervals before a block occurs. Mobitz type 2 block has constant PR intervals before blocks occur. Thus, if one can spot the gradual prolongation of PR intervals, Mobitz type 1 block should be diagnosed.
What is the difference between second-degree type 1 and type 2 on ECG?
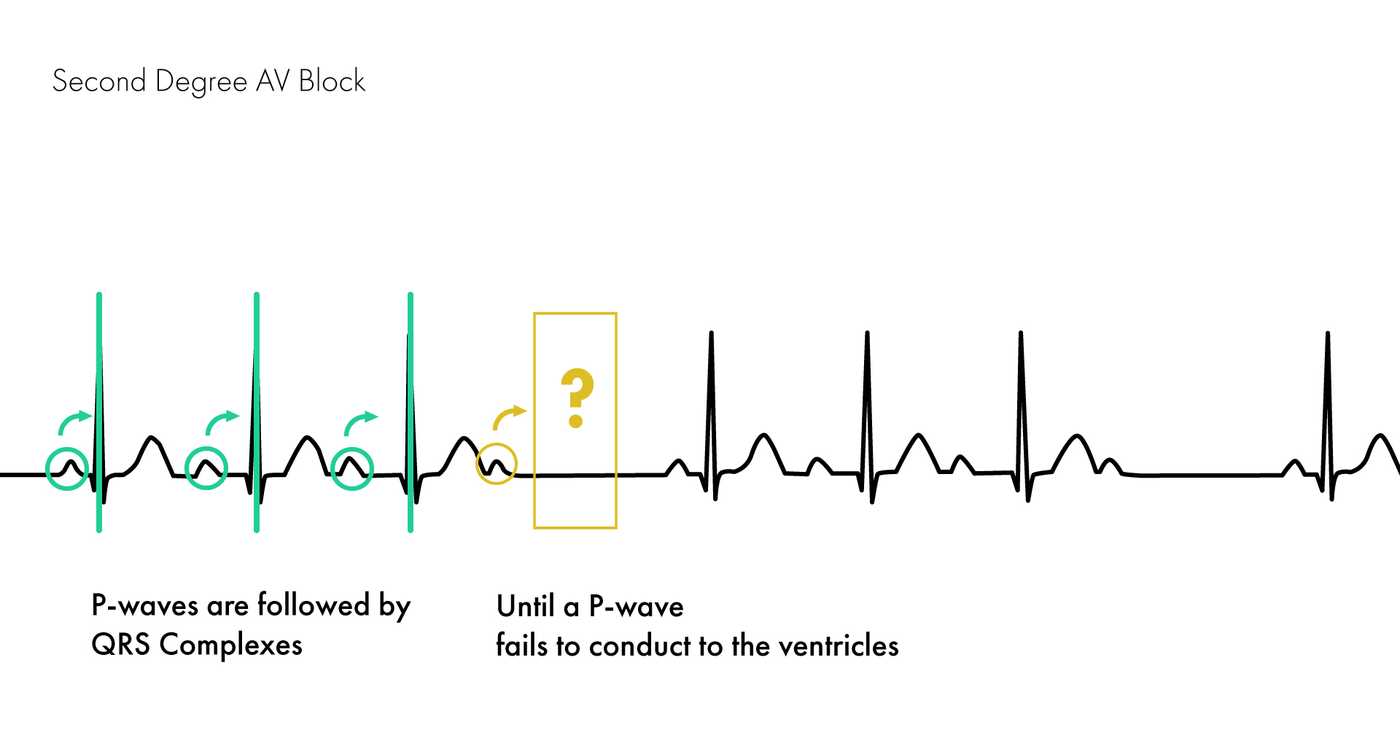
There are two non-distinct types of second-degree AV block, called Type 1 and Type 2. In both types, a P wave is blocked from initiating a QRS complex; but, in Type 1, there are increasing delays in each cycle before the omission, whereas, in Type 2, there is no such pattern.
How can you tell the difference between a second-degree block and a heart block?
A: The main difference is this: Mobitz II: There will be a P-wave with every QRS. There may not always be a QRS complex with every p-wave. The rate will usually be regular.
What is mobitz type II?
Mobitz type II second-degree block is an old term, which refers to periodic atrioventricular block with constant PR intervals in the conducted beats. The distinction between type II and type I block is descriptive; of greater importance to the clinician is the anatomic site of the block and the prognosis.
Does Mobitz Type 1 require treatment?
Mobitz type 1 - this is the least serious type of second degree heart block - it may occasionally cause symptoms of mild dizziness and does not usually require treatment.
What does Mobitz 1 look like?
In Mobitz type I, atrial impulses travelling through the AV node take increasingly longer to fully conduct to the ventricles, until one impulse is completely blocked. On the ECG, this can be seen as a progressive prolongation of the PR interval, until a P wave is not followed by a QRS complex.
How do you know if its second degree type 2?
1:302:202nd Degree Type 2 AV Block ECG - EMTprep.com - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou have a regularly gear regular rhythm with a 2 2 1 3 2 1 or 4 2 1 P wave QRS ratio. There's aMoreYou have a regularly gear regular rhythm with a 2 2 1 3 2 1 or 4 2 1 P wave QRS ratio. There's a very good chance you're looking at a second degree type 2 or a little bits 2 or block you.
Which second-degree heart block is worse?
The level of the block determines the prognosis. AV nodal blocks, which are the vast majority of Mobitz I blocks, carry a favorable prognosis, whereas infranodal blocks, whether Mobitz I or Mobitz II, may progress to complete block with a worse prognosis.
Is Mobitz type 2 reversible?
The slow attenuation of the pharmacological effects of the antipsychotics resulted in symptom improvement and reversible resolution of the Mobitz type II AV block approximately 72 h after transfer to our hospital.
What happens in 2nd degree heart block?
With the second type of second-degree heart block, some electrical signals are not relayed from the upper chambers to the lower chambers. Unlike the first type of second-degree heart block, the electrical signals suddenly fail to conduct.
What causes 2nd degree type 1 Heartblock?
There are multiple causes of second-degree Mobitz type 1 (Wenckebach) AV block, including reversible ischemia, myocarditis, increased vagal tone, status post-cardiac surgery, or even medications that slow AV nodal conduction (e.g., beta-blockers, non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocks, adenosine, digitalis, and ...
How do you treat type 2 Mobitz?
Treatment for a Mobitz type II involves initiating pacing as soon as this rhythm is identified. Type II blocks imply structural damage to the AV conduction system. This rhythm often deteriorates into complete heart block. These patients require transvenous pacing until a permanent pacemaker is placed.
What causes second-degree AV block type 2?
What causes second-degree heart block? Most people with second-degree heart block have an underlying heart condition like coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy or congenital heart disease. It can also be caused by: ageing of the electrical pathways in your heart (so you're more likely to get it if you're older)
What is Mobitz heart block?
In second-degree heart block, the impulses are intermittently blocked. Type I, also called Mobitz Type I or Wenckebach's AV block: This is a less serious form of second-degree heart block. The electrical signal gets slower and slower until your heart actually skips a beat.
Does second-degree AV block type 2 require emergency treatment?
Second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block in the asymptomatic patient does not require any specific therapy in the prehospital setting. If the patient is symptomatic, standard advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) guidelines for bradycardia, including the use of atropine and transcutaneous pacing, are indicated.
What is Mobitz type I?
Mobitz type I is a type of 2nd degree AV block, which refers to an irregular cardiac rhythm (arrhythmia), that reflects a conduction block in the e...
Are Wenckebach and Mobitz type I the same thing?
Yes, Mobitz type I is also known as Wenckebach block or 2nd degree heart block type I. All three names refer to the same ECG rhythm and can be used...
What is the difference between Mobitz I and Mobitz II?
Mobitz I and Mobitz II are both subtypes of a 2nd degree AV block. Mobitz I and Mobitz II can be distinguished on an ECG by the pattern in which P...
What are the causes of Mobitz type I?
Mobitz type I block can occur as a result of a reversible conduction block caused by metabolic abnormalities, such as increased levels of potassium...
What are the signs and symptoms of Mobitz type I?
Most people with Mobitz type I block do not present any symptoms. Some individuals may occasionally feel light-headedness, dizziness, or fatigue wh...
How is Mobitz type I diagnosed?
Mobitz type I block is often diagnosed incidentally during a routine ECG. The key to diagnosing Mobitz type I block is looking closely at the PR in...
How is Mobitz type I treated?
Treatment of Mobitz type I begins by addressing any potentially reversible causes of nodal block, including ceasing medications that can slow nodal...
What are the most important facts to know about Mobitz type I?
Mobitz type I, also known as Wenckebach block, is a type of 2nd degree AV block, which refers to a cardiac arrhythmia that reflects a conduction bl...
What is the difference between Mobitz 1 and 2?
The difference between them is in mobitz 1 there is a gradual increase in the duration of PR interval until an impulse completely wanes off before reaching the ventricles but in mobitz 2 although the PR interval is prolonged it does not change with time.
What is second degree heart block?
delay in the passage of impulses into the ventricles via the AV node increases the duration of the PR interval seen in an ECG. This condition is known as a second-degree heart block. There are main two forms of second-degree heart block as mobitz 1 and 2. In mobitz 1 there is a progressive increase in the duration of PR interval until an impulse is completely blocked before reaching the ventricles whereas in mobitz 2 there is a prolonged PR interval whose duration remains constant and an occasional impulse is lost without reaching its destination. This is the key difference between mobitz 1 and 2.
What is a Mobitz block?
Mobitz type 1 block is characterized by a gradual prolongation of the PR interval over a few heart cycles until an atrial impulse is completely blocked, which manifests on the ECG as a P-wave not followed by a QRS complex. This cycle repeats itself over and over again, such that every cycle ends with a blocked P-wave. Refer to Figure 1.
Which two increases heart rate which induces Wenckebach phenomenon in Mobitz type 1 block?
Atropine or physical activity: these two increases heart rate which induces Wenckebach phenomenon in Mobitz type 1 block.
What is second degree AV block?
Second-degree AV block implies that some atrial impulses are completely blocked, which means that not all P-waves are followed by QRS complexes. Second-degree AV block is subdivided into type 1 and type 2 (also called Mobitz type 1 and Mobitz type 2, respectively).
Is Mobitz type 1 block good?
It is also common among athletes due to their high vagal tone. It is more common in older individuals. The prognosis is good, even in the elderly. Mobitz type 1 block generally does not progress to more advanced blocks. Should it progress to more advanced blocks, which typically is due to a more distal location of the block, an artificial pacemaker is needed.
Does Mobitz block progress to advanced blocks?
The prognosis is good, even in the elderly. Mobitz type 1 block generally does not progress to more advanced blocks. Should it progress to more advanced blocks, which typically is due to a more distal location of the block, an artificial pacemaker is needed.
Is Mobitz type 2 block a sporadically block?
Mobitz type 2 block implies that some atrial impulses are blocked sporadically. The PR interval is constant (although it may be prolonged). Mobitz type 2 is more serious, because it is usually chronic and tends to progress to third-degree AV block. Moreover, cardiac output may be reduced if many impulses are blocked.
What is Mobitz type 1?
Mobitz type I is a type of 2 nd degree AV block, which refers to an irregular cardiac rhythm (arrhythmia), that reflects a conduction block in the electrical conduction system of the heart. The heart is a muscular organ composed of four chambers: two upper chambers—the right and left atria—, and two lower chambers— the right and left ventricles.
How to diagnose Mobitz block?
The key to diagnosing Mobitz type I block is looking closely at the PR interval on the ECG strip. In Mobitz I, the sinus node is healthy and fires right on time, so the P waves come at regular intervals. However, atrial impulses travelling through the AV node take longer and longer to conduct at each subsequent impulse, causing a progressive prolongation of the PR interval, until one impulse is completely blocked. Consequently, QRS complexes are periodically dropped, which can result in a slowed heart rhythm (bradycardia), with more P waves than QRS complexes on the ECG.
What is the difference between a 1st degree and a 2nd degree AV block?
A 1 st degree AV block is not technically a block, but rather a delay in the conduction of atrial impulses to the ventricles , which results in an extended PR interval. Meanwhile, a 2 nd degree AV block occurs when some of the atrial impulses are fully conducted to the ventricles, whereas others are blocked along the way.
What causes Mobitz block?
Other causes of Mobitz type I block include a heart attack, disorders affecting the heart muscle walls (cardiomyopathies), inflammation of the heart muscle ( myocarditis ), infection of the inner layer of the heart ( endocarditis ), inherited heart defects, infiltrative and autoimmune disorders, and cardiac surgical procedures.
Is Mobitz a heart block?
Yes, Mobitz type I is also known as Wenckebach block or 2 nd degree heart block type I. All three names refer to the same ECG rhythm and can be used interchangeably.
Is Mobitz II a good rhythm?
Mobitz I is a benign rhythm that generally reflects a block at the AV node, and typically results in a good prognosis. On the other hand, Mobitz II reflects a block after the AV node, either at the bundle of His or its branches, and often results in a poorer prognosis, as it has a higher risk of progressing to a 3 rd degree AV block.
Can Mobitz block cause syncope?
Most people with Mobitz type I block do not present any symptoms. Some individuals may occasionally feel light-headedness, dizziness, or fatigue when exercising. More rarely, Mobitz type I block may lead to a sudden and temporary loss of consciousness, also known as a syncope, caused by a brief decrease in the oxygen supply to the brain.
Video Teaching Tutorial on Heart Blocks
After you read this article, I highly recommend you watch my teaching tutorial on these heart blocks to further help you understand the material. Then, take the EKG Heart Block Quiz to test your knowledge on what you have learned.
1 st Degree AV Heart Block
The picture above will help illustrate to you what I am talking about. The big thing you need to take away from this rhythm is that it looks normal (like normal sinus rhythm) BUT it has a secret. Note the PR interval on the strip. It is much longer than a normal PR interval.
3 rd Degree Heart Block (Complete Heart Block)
Out of all the heart blocks for a patient, this is the worst one. It requires major interventions. In this rhythm, the atriums and ventricles are NOT beating together and are working independently of each other. Therefore, the important “hallmarks” to take away from this rhythm is the following:
Quiz on Heart Blocks
Now test your knowledge on heart blocks and don’t forget to watch the teaching tutorial above!
What is Mobitz I?
Mobitz I is usually due to reversible conduction block at the level of the AV node
How to tell if Mobitz I is AV?
The first clue to the presence of Mobitz I AV block on this ECG is the way the QRS complexes cluster into groups, separated by short pauses. This phenomenon usually represents 2nd-degree AV block or non-conducted PACs ; occasionally SA exit block.
Is Mobitz I a symptomatic or asymptomatic?
Mobitz I is usually a benign rhythm, causing minimal haemodynamic disturbance and with low risk of progression to third degree heart block. Asymptomatic patients do not require treatment. Symptomatic patients usually respond to atropine. Permanent pacing is rarely required.
